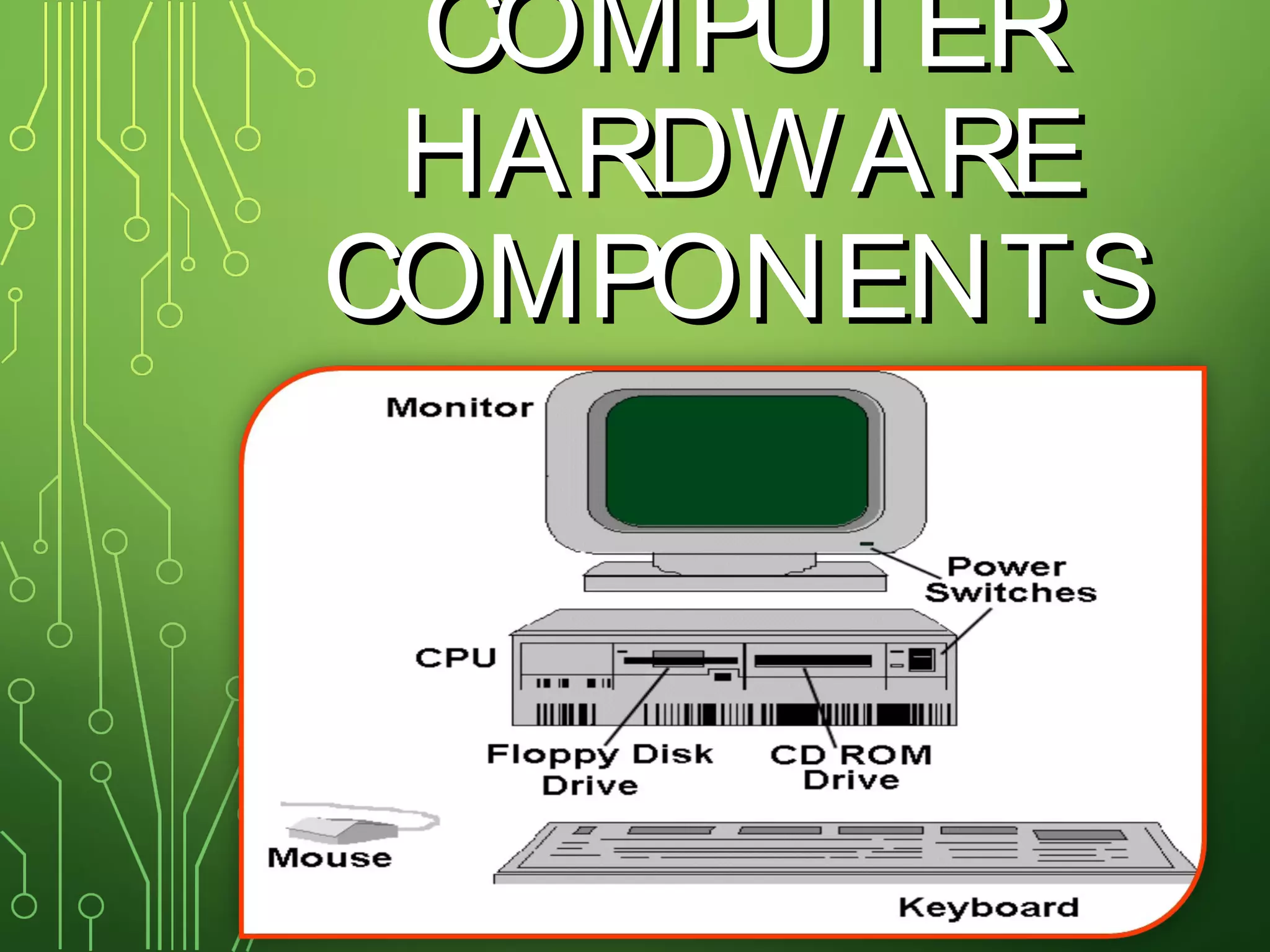
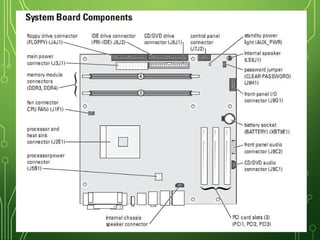
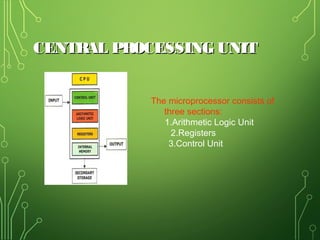
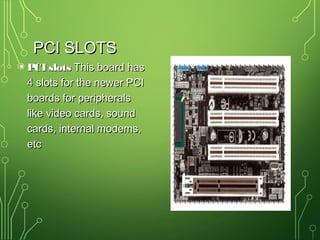
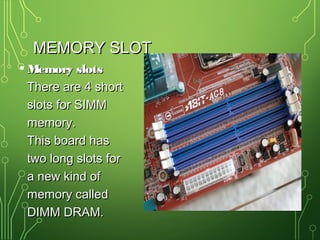
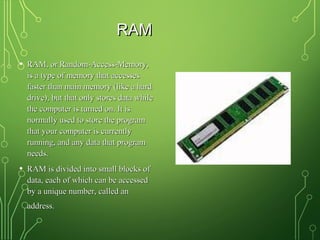
The document lists and describes the main hardware components of a computer system. It includes the central processing unit (CPU), motherboard, memory (RAM), storage devices (hard disk drive, floppy disk drive, CD-ROM drive, DVD drive), ports, and input/output devices (keyboard, mouse, monitor). The motherboard contains slots and connectors for attaching these components. Memory is used for temporary storage of running programs and data, while storage devices provide permanent storage even when the computer is turned off.