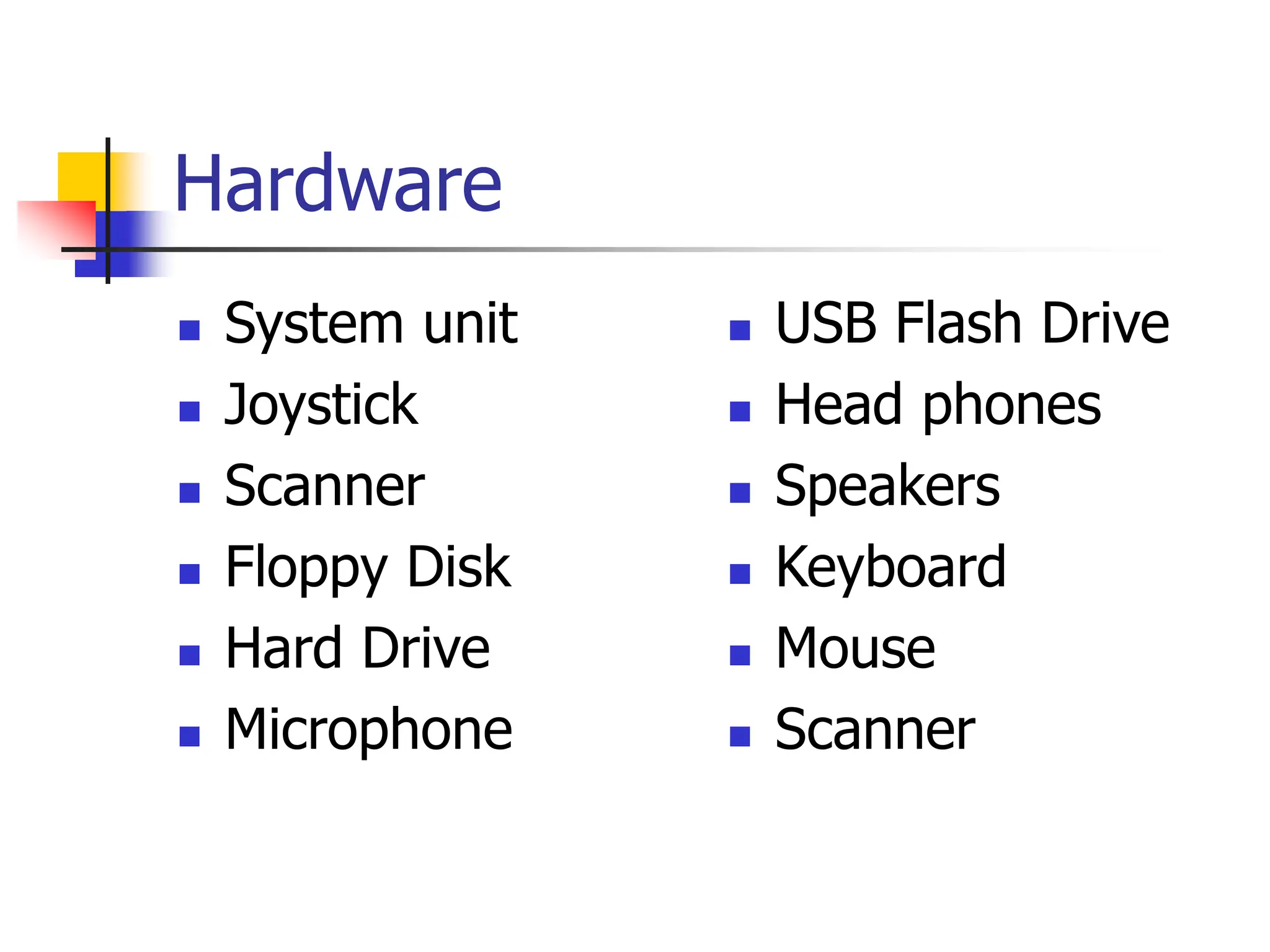
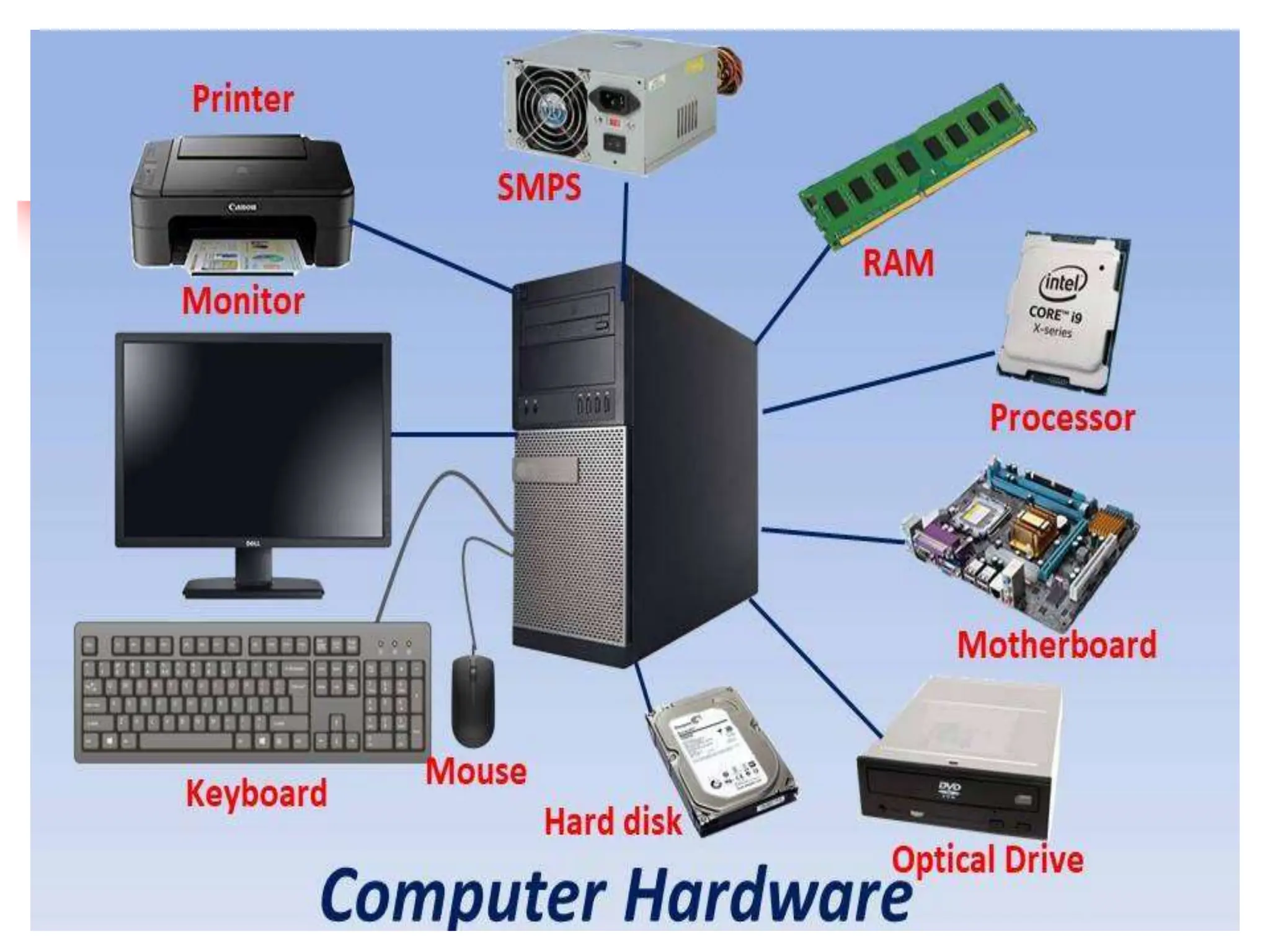
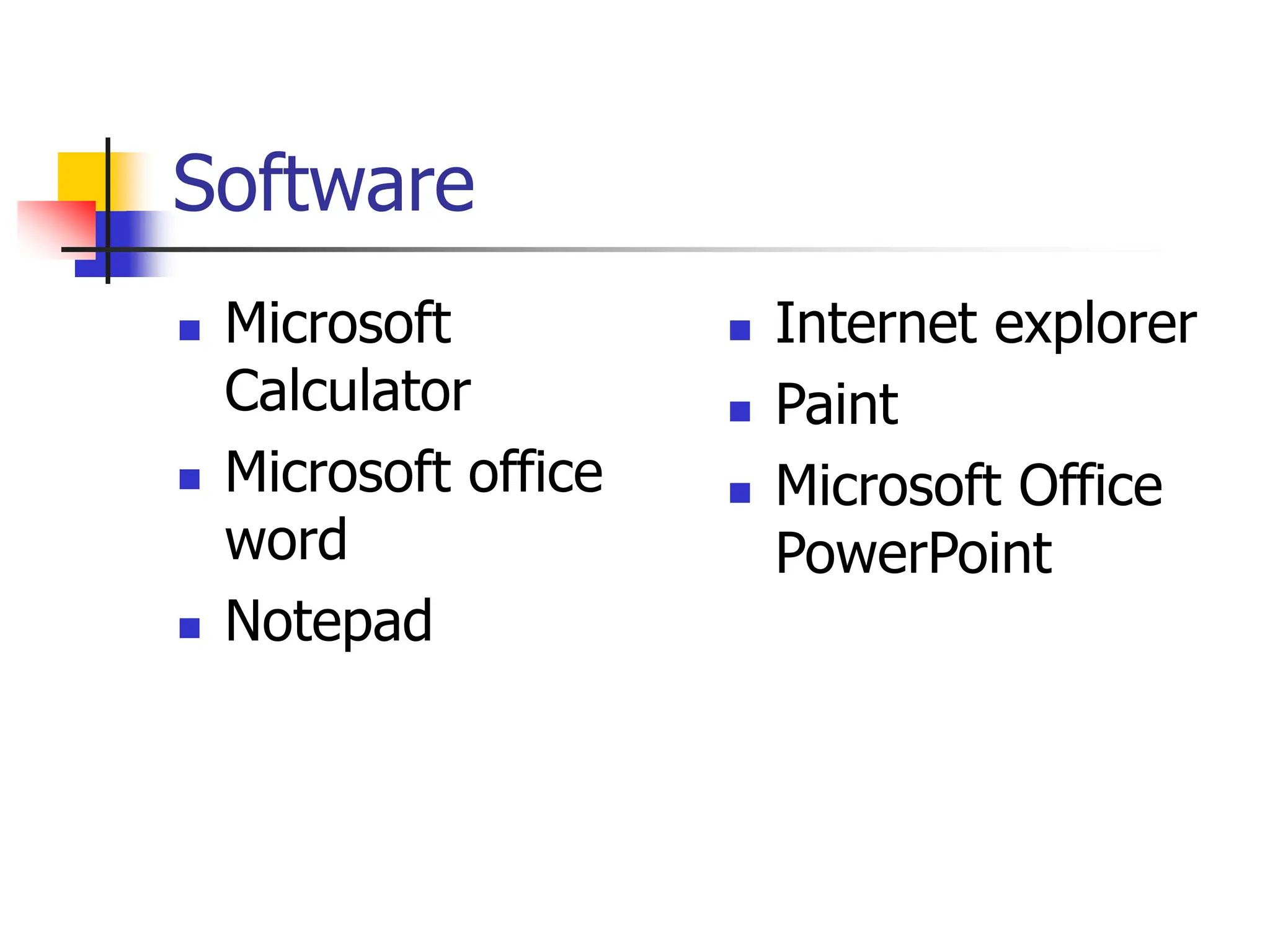
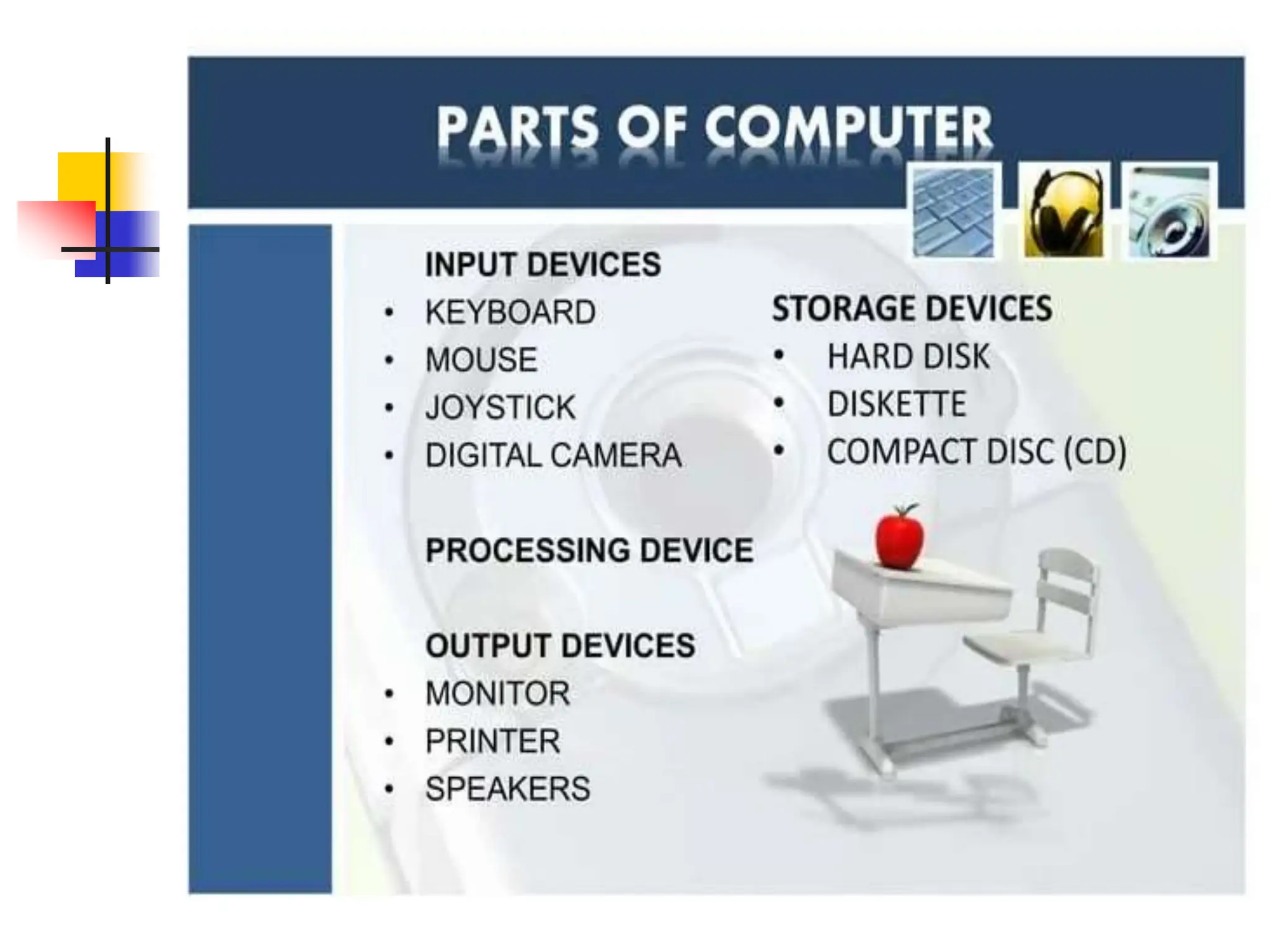
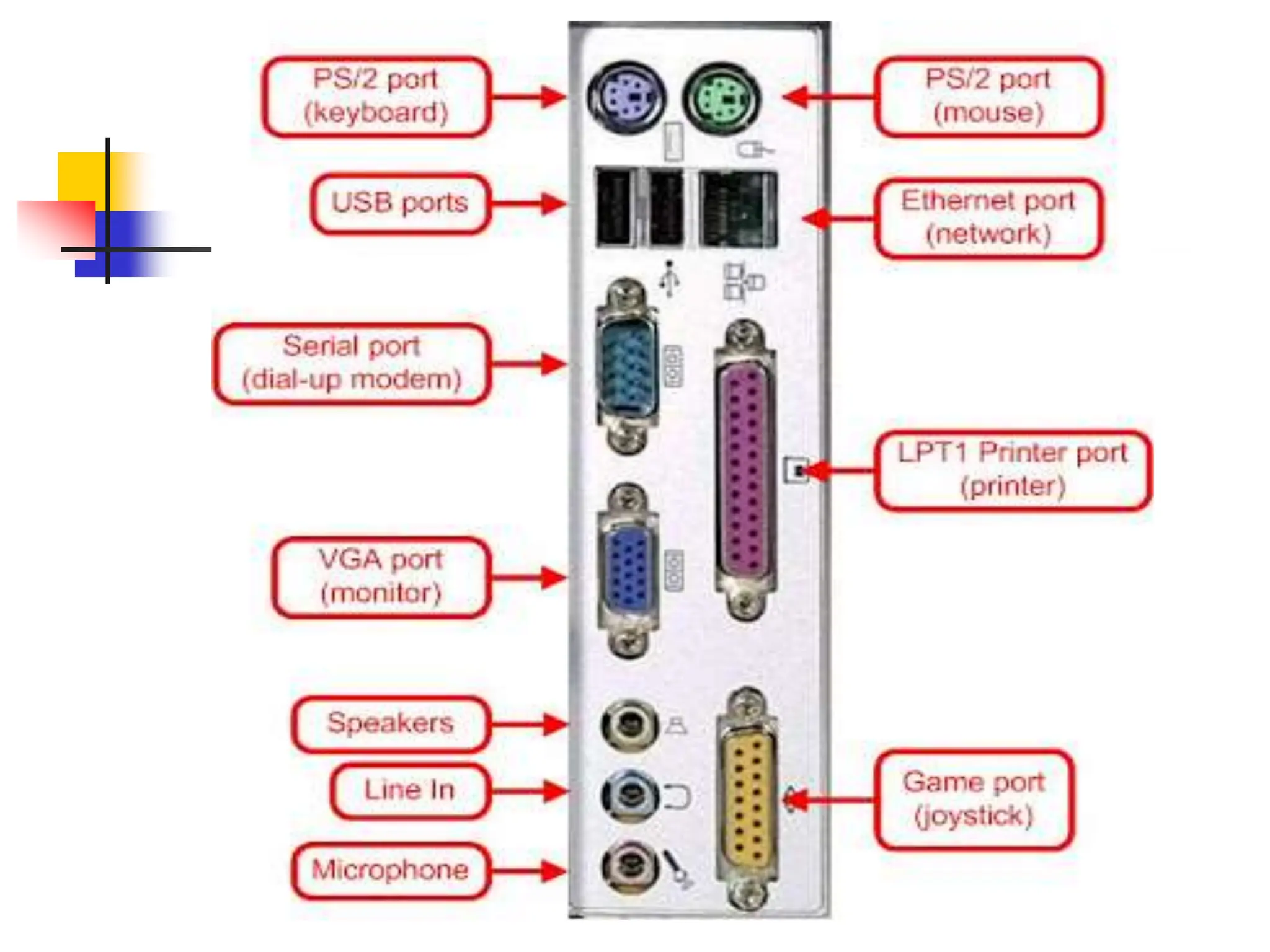
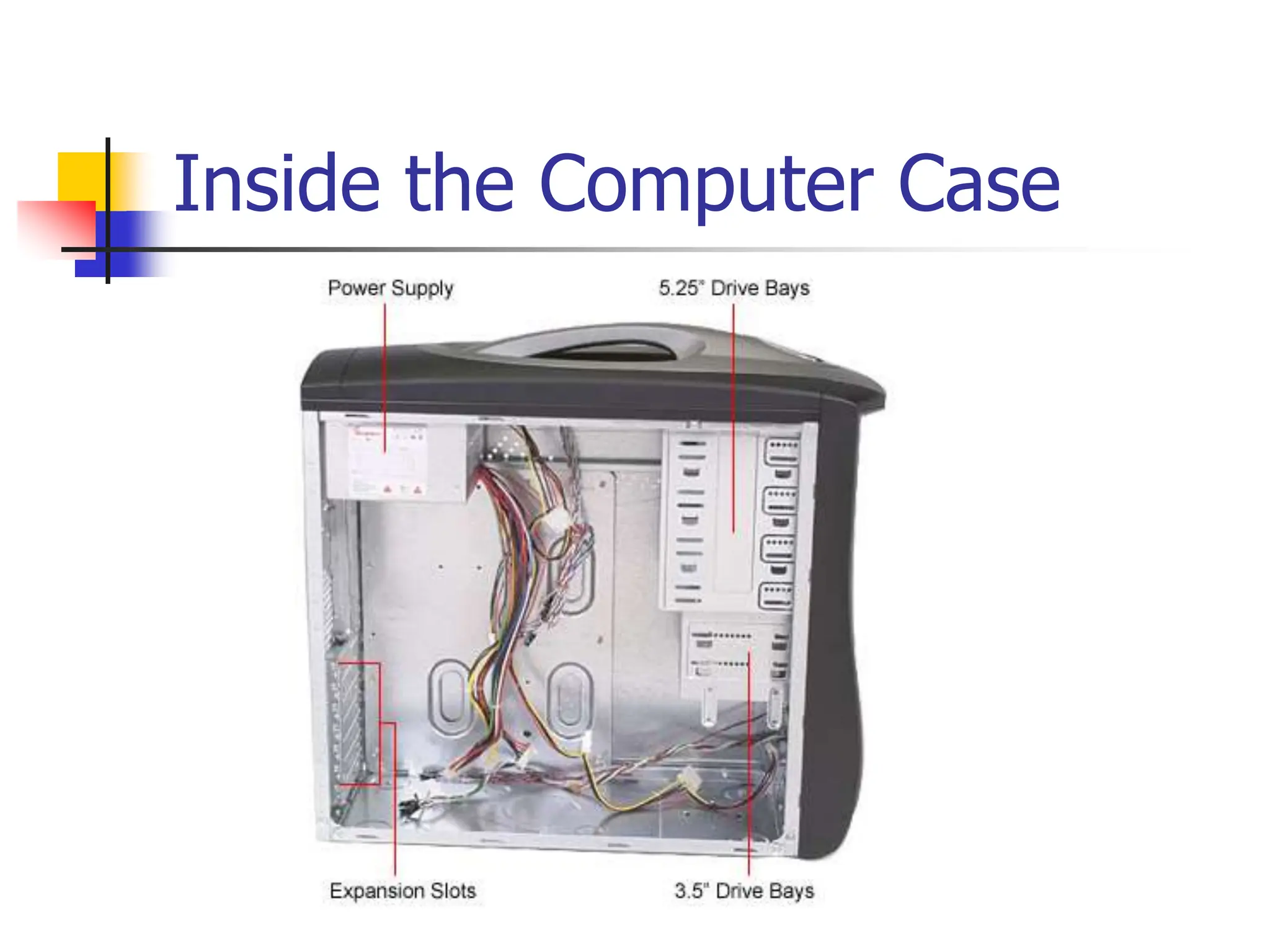
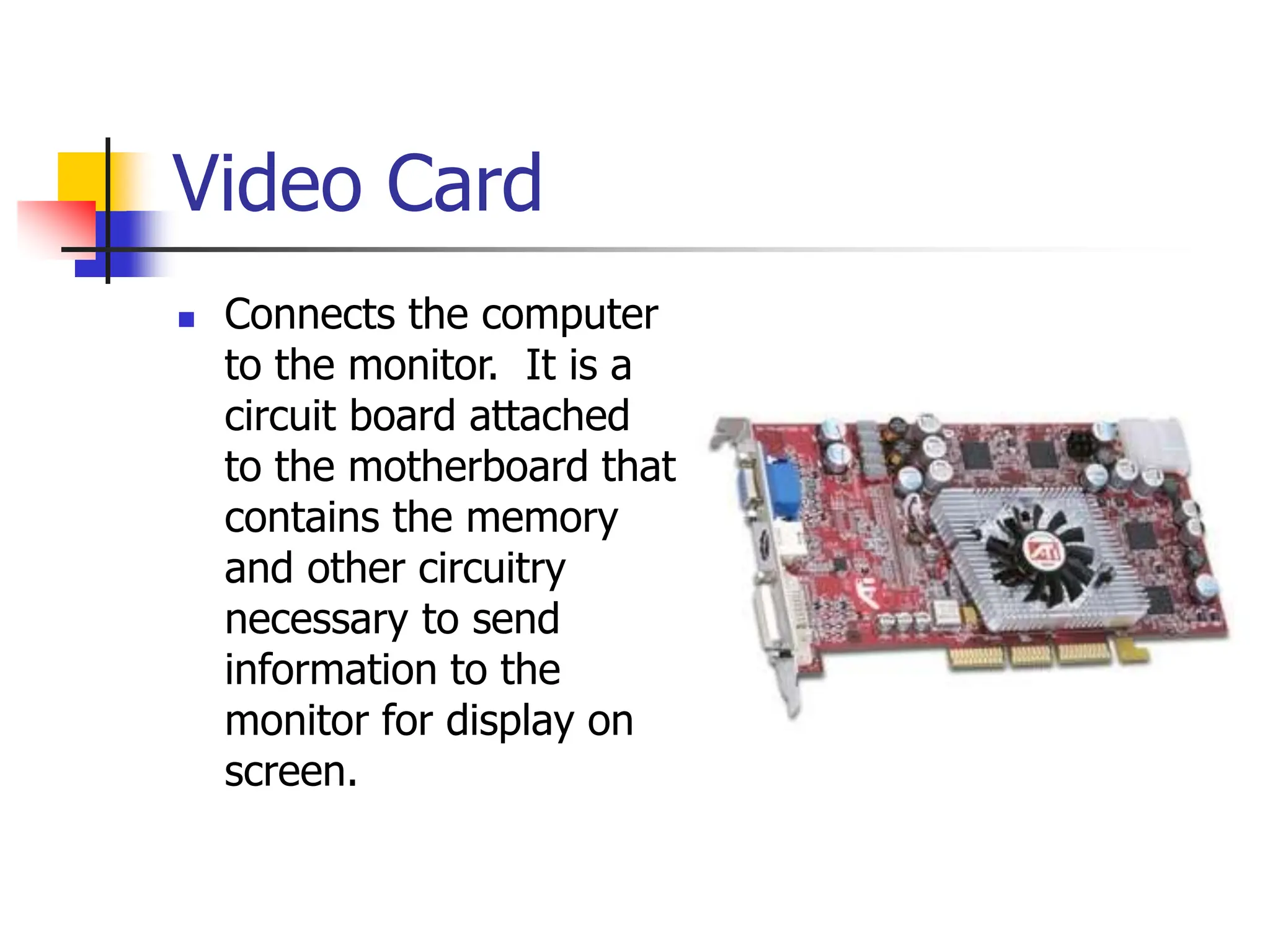
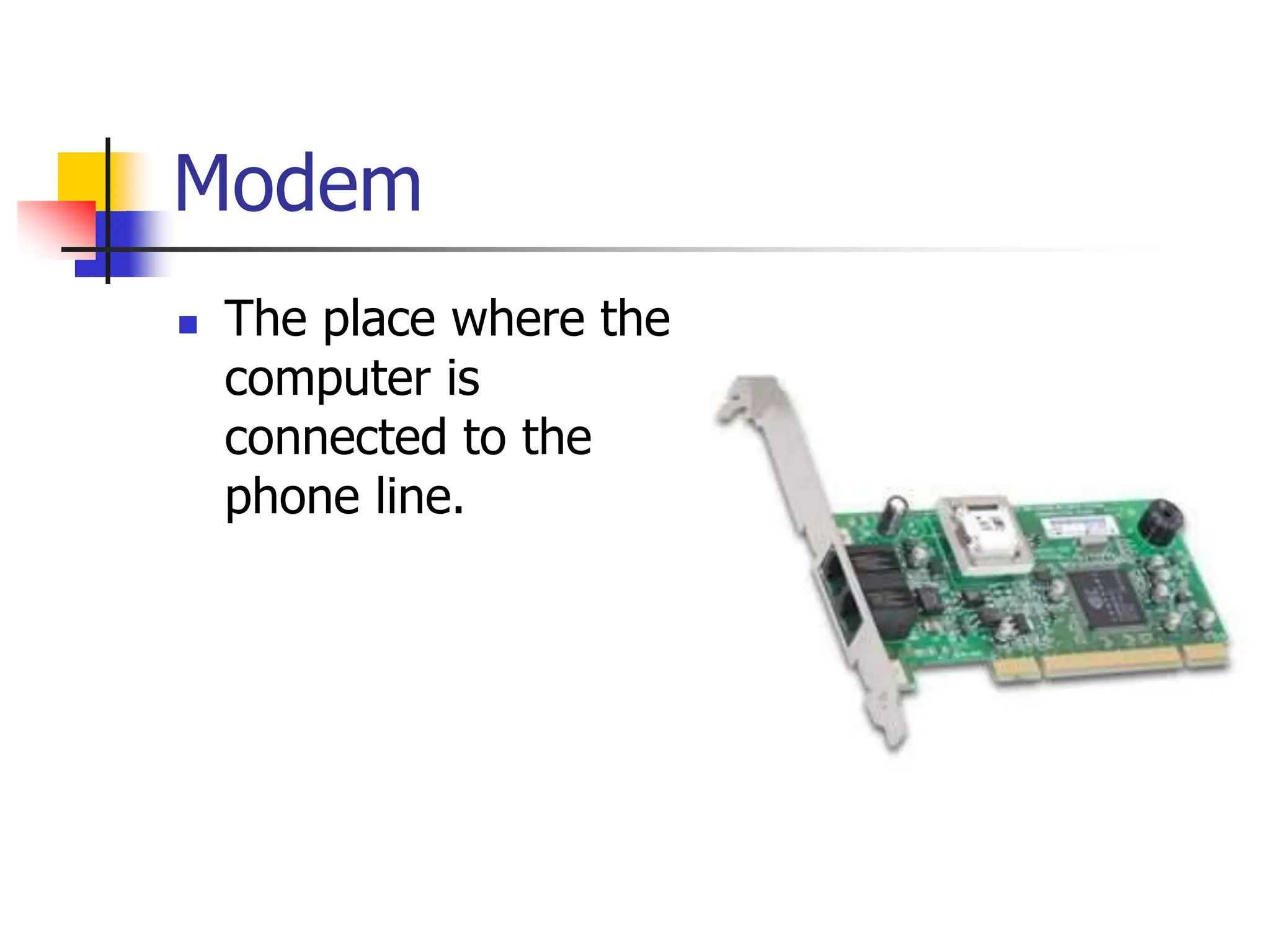
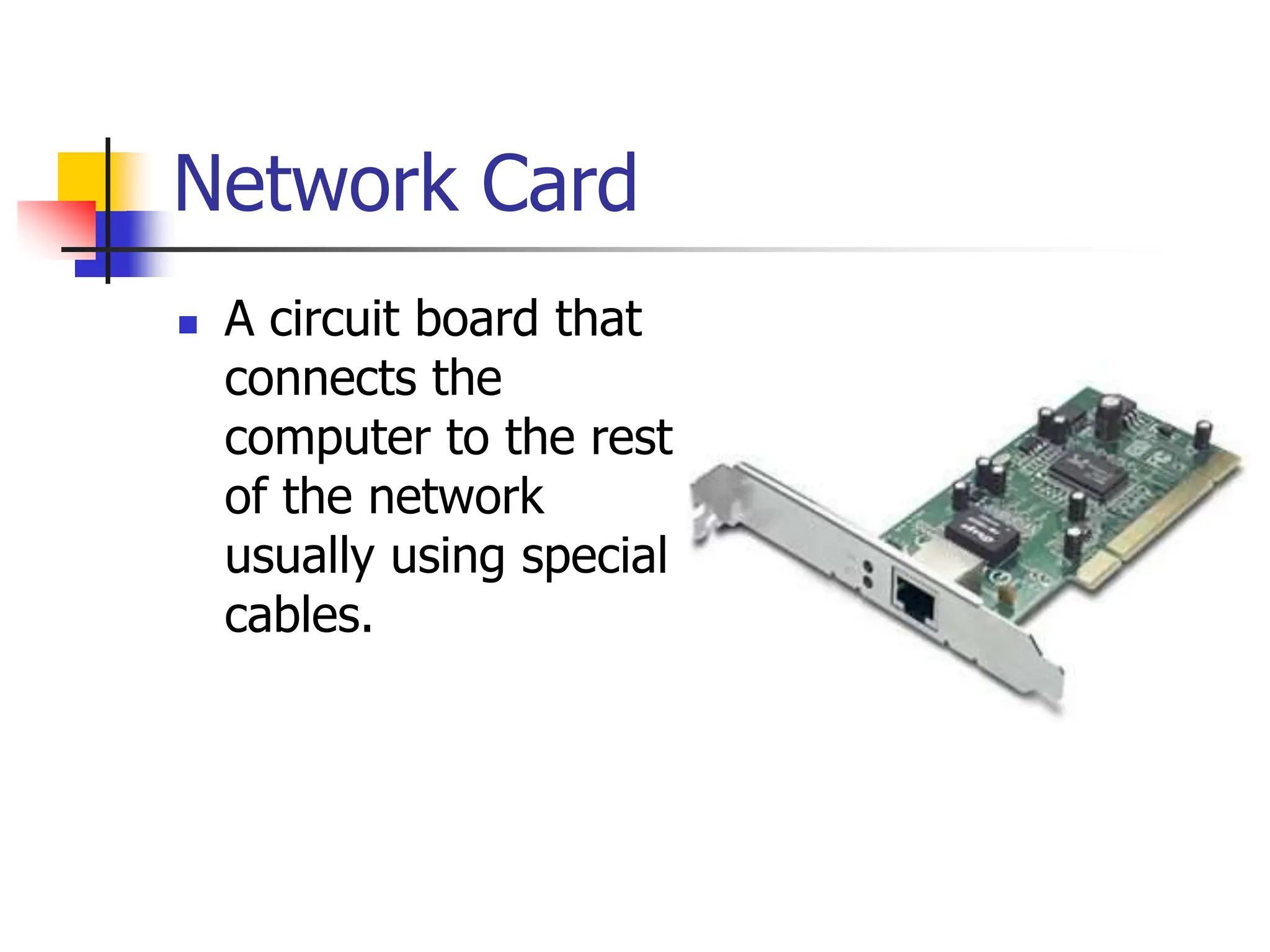
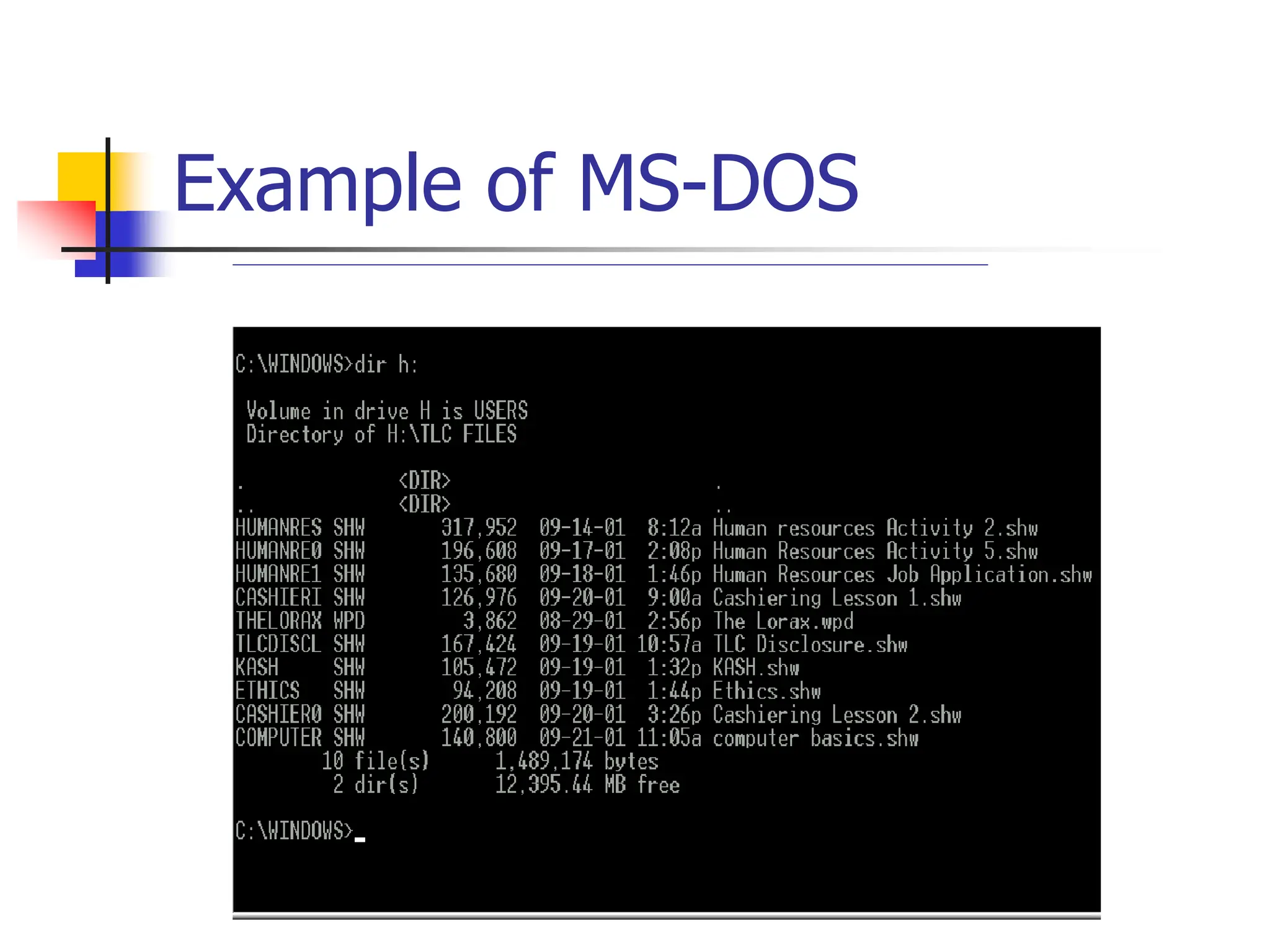
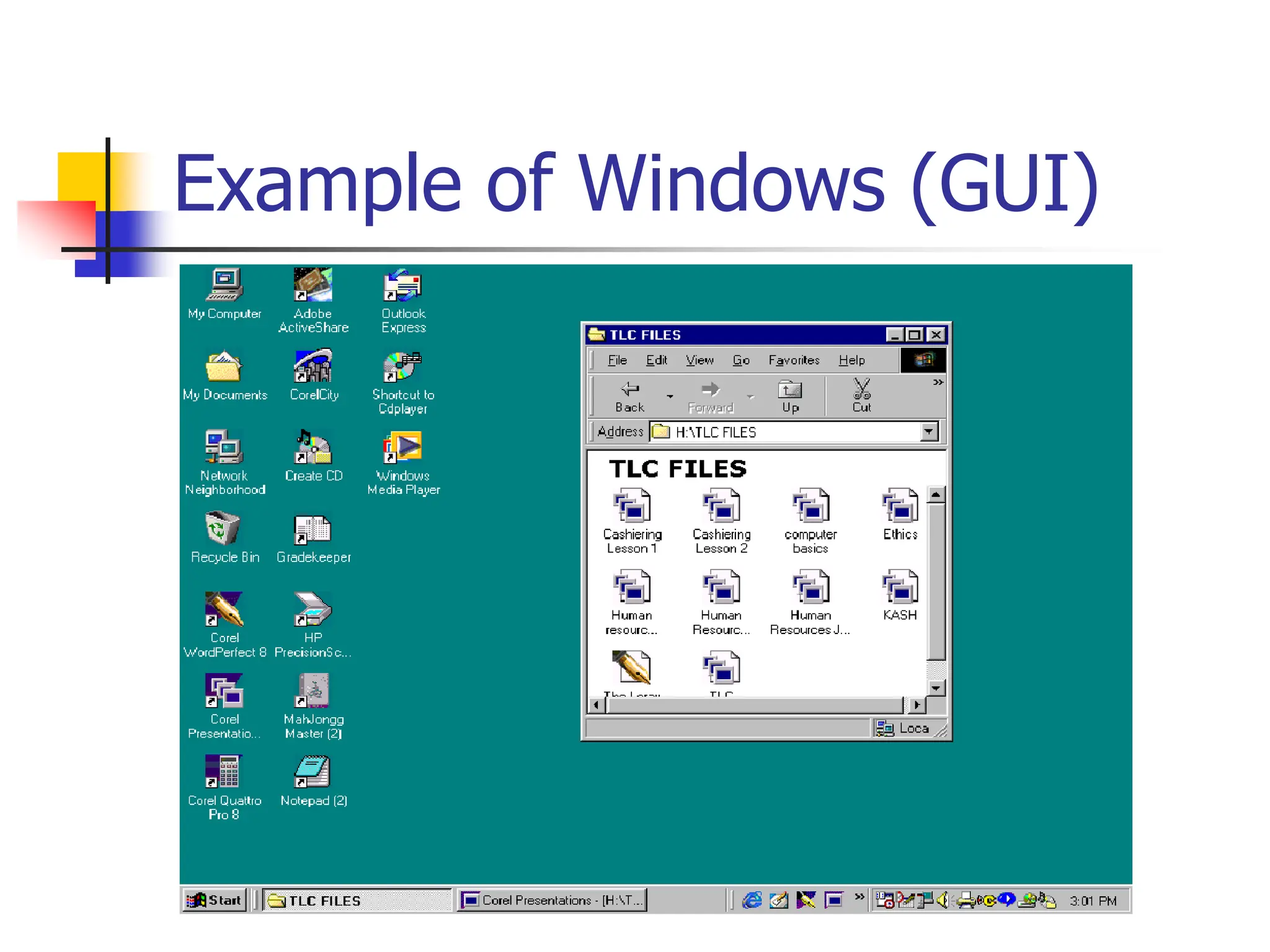
The document discusses the key elements of a computer system, including hardware, software, peopleware, and data. It provides details on common computer parts like the system unit, motherboard, CPU, memory, ports, storage devices, input devices, output devices, and communication devices. It also defines software, operating systems, and gives examples of MS-DOS and Windows. The overall topic is the components that make up a basic computer system.