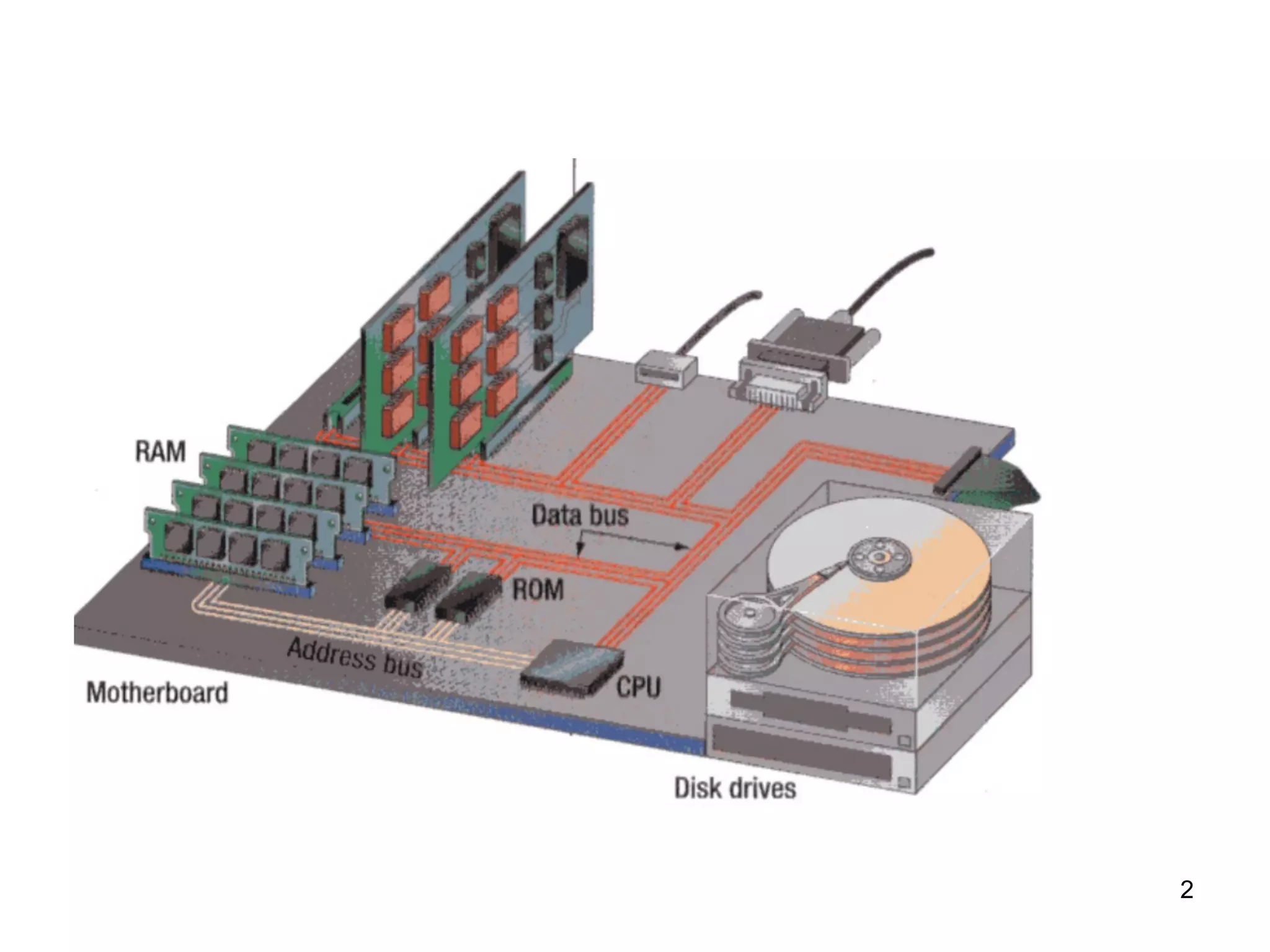
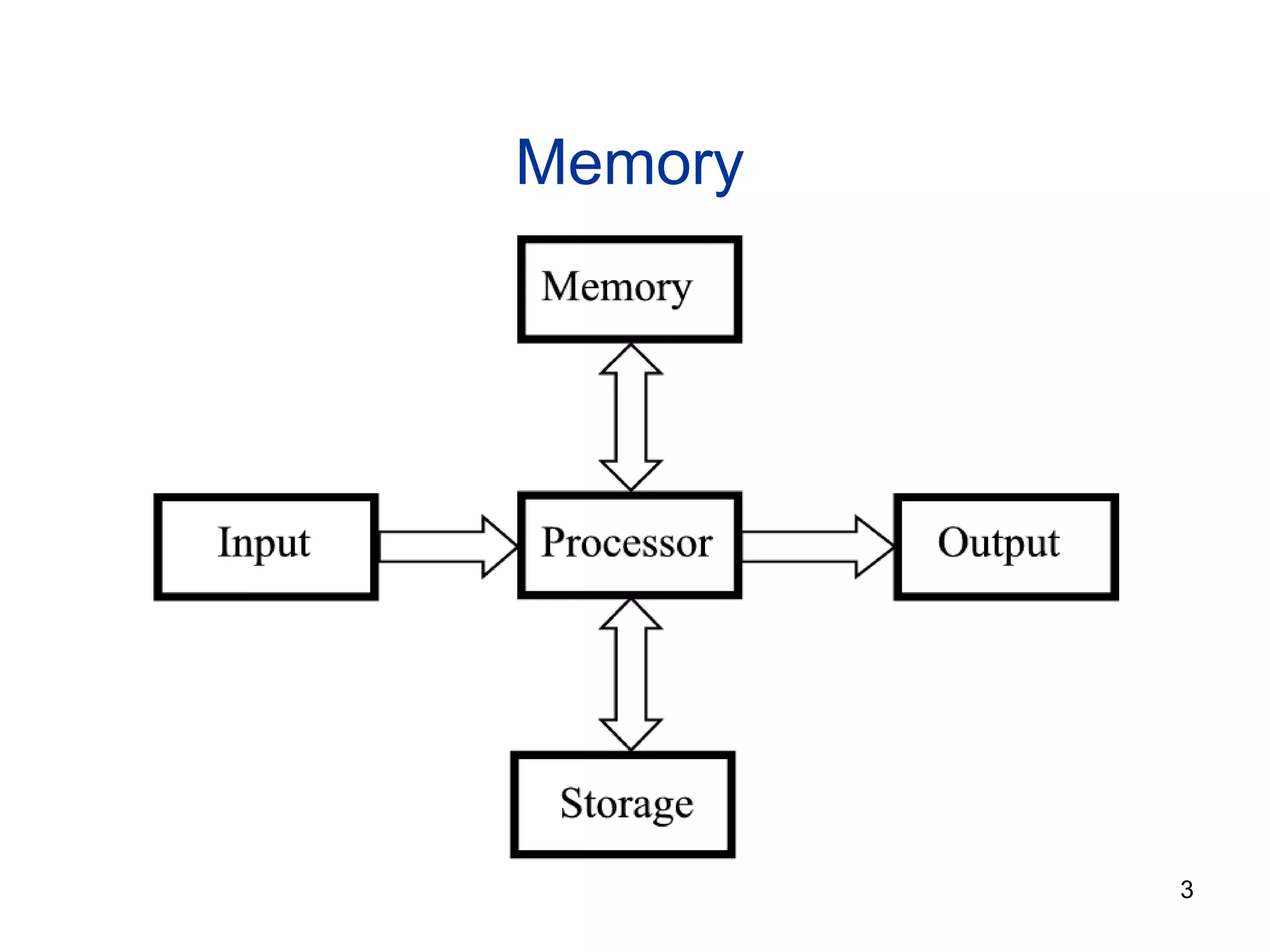
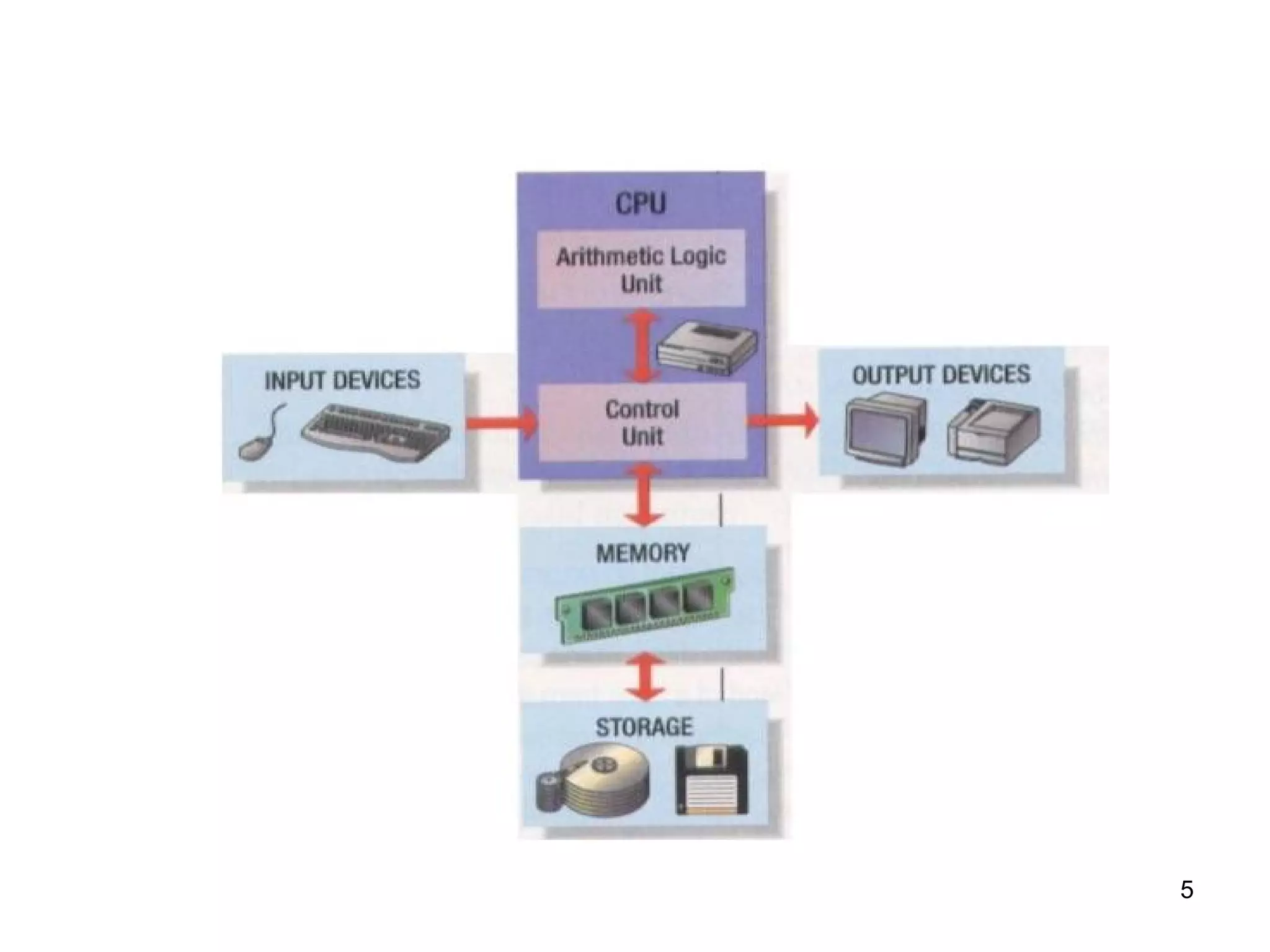
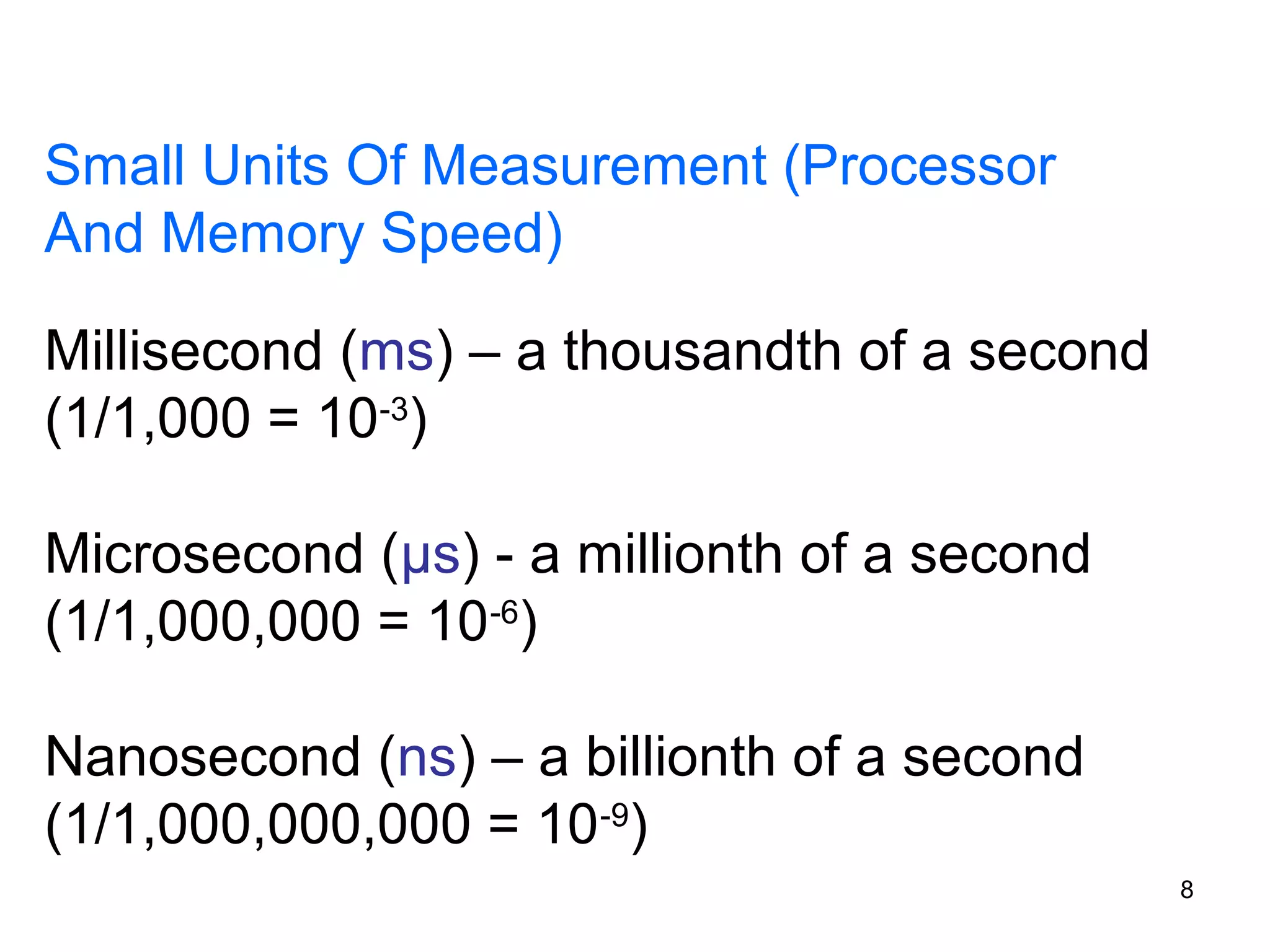
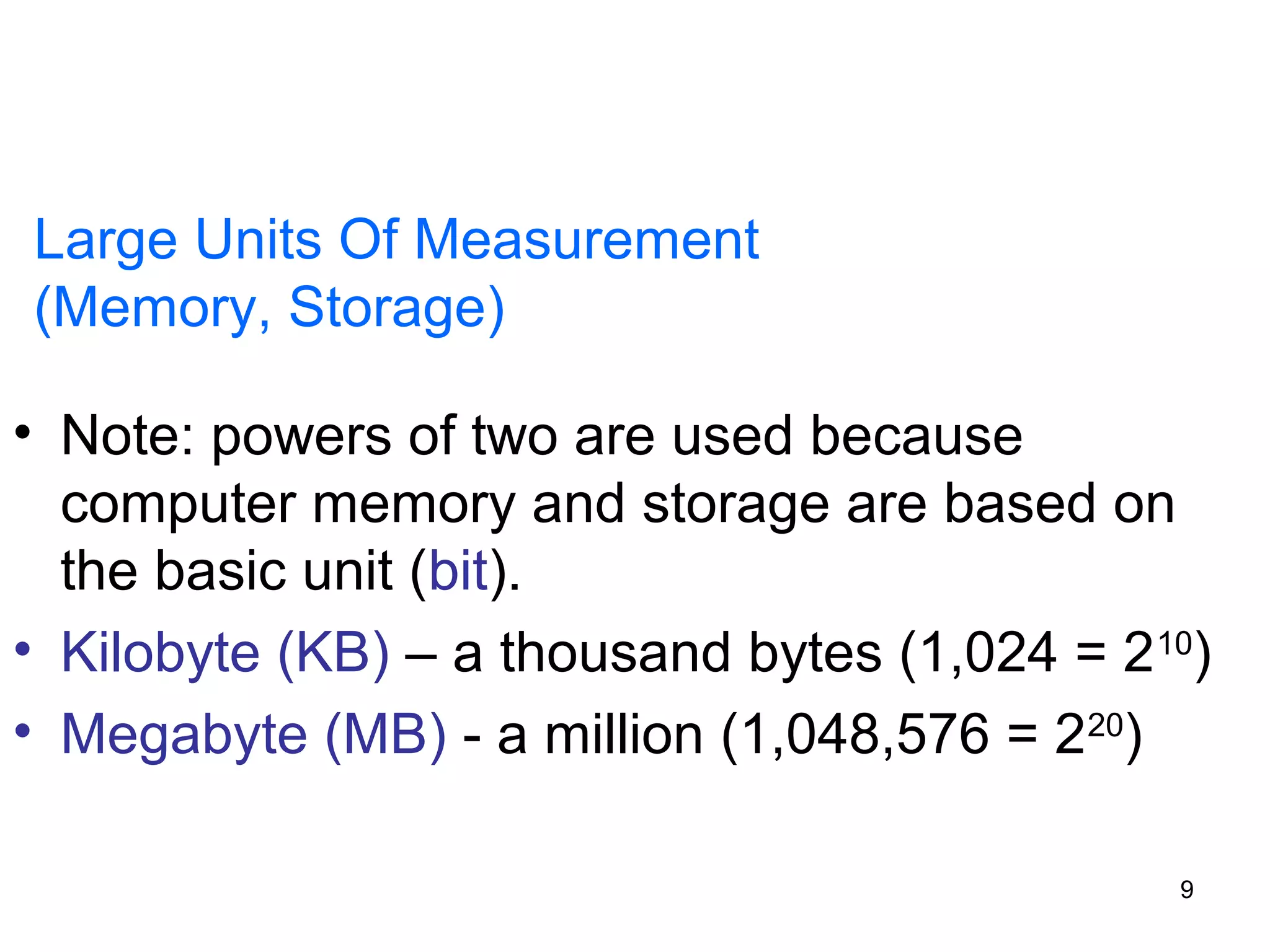
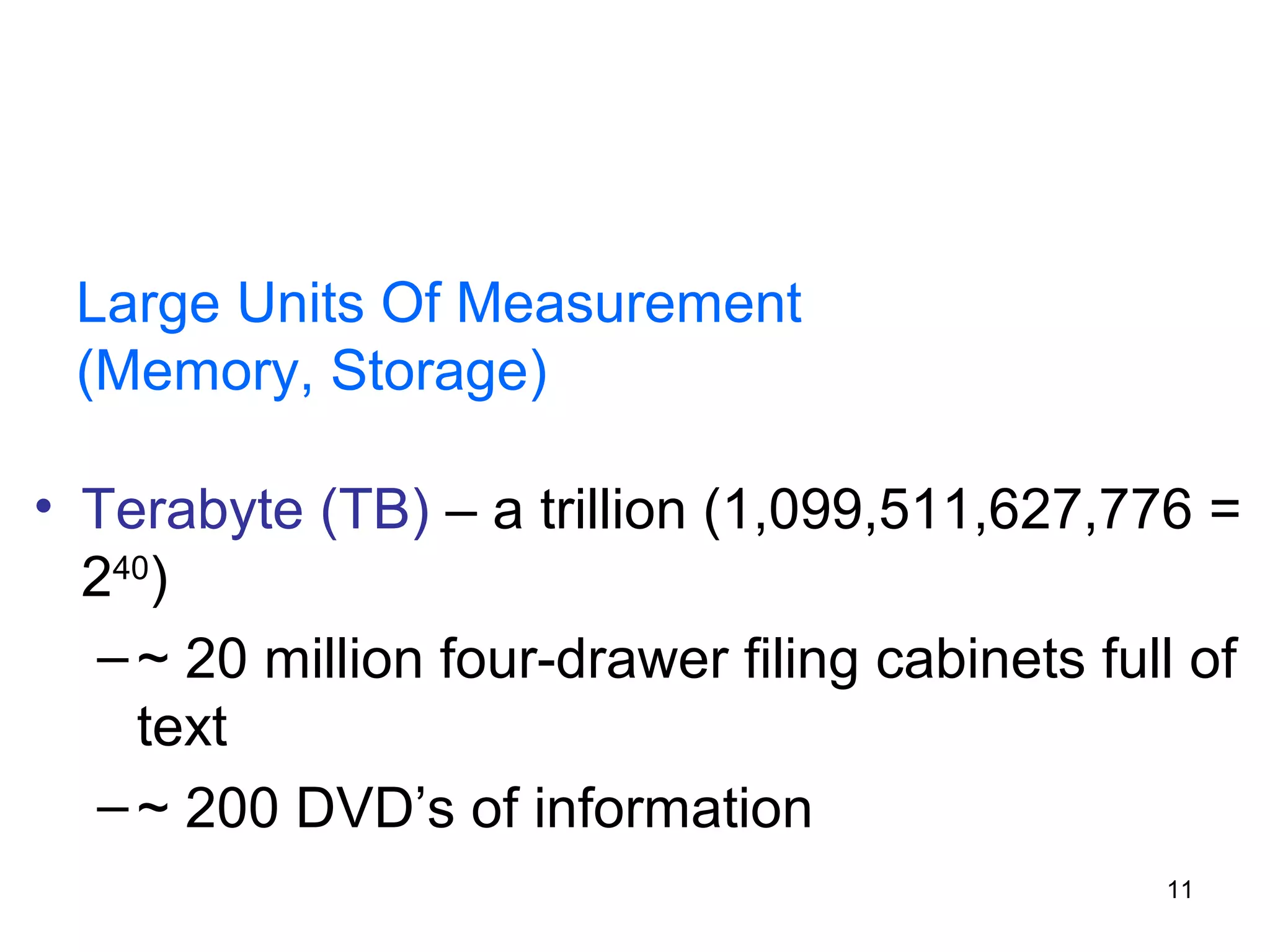
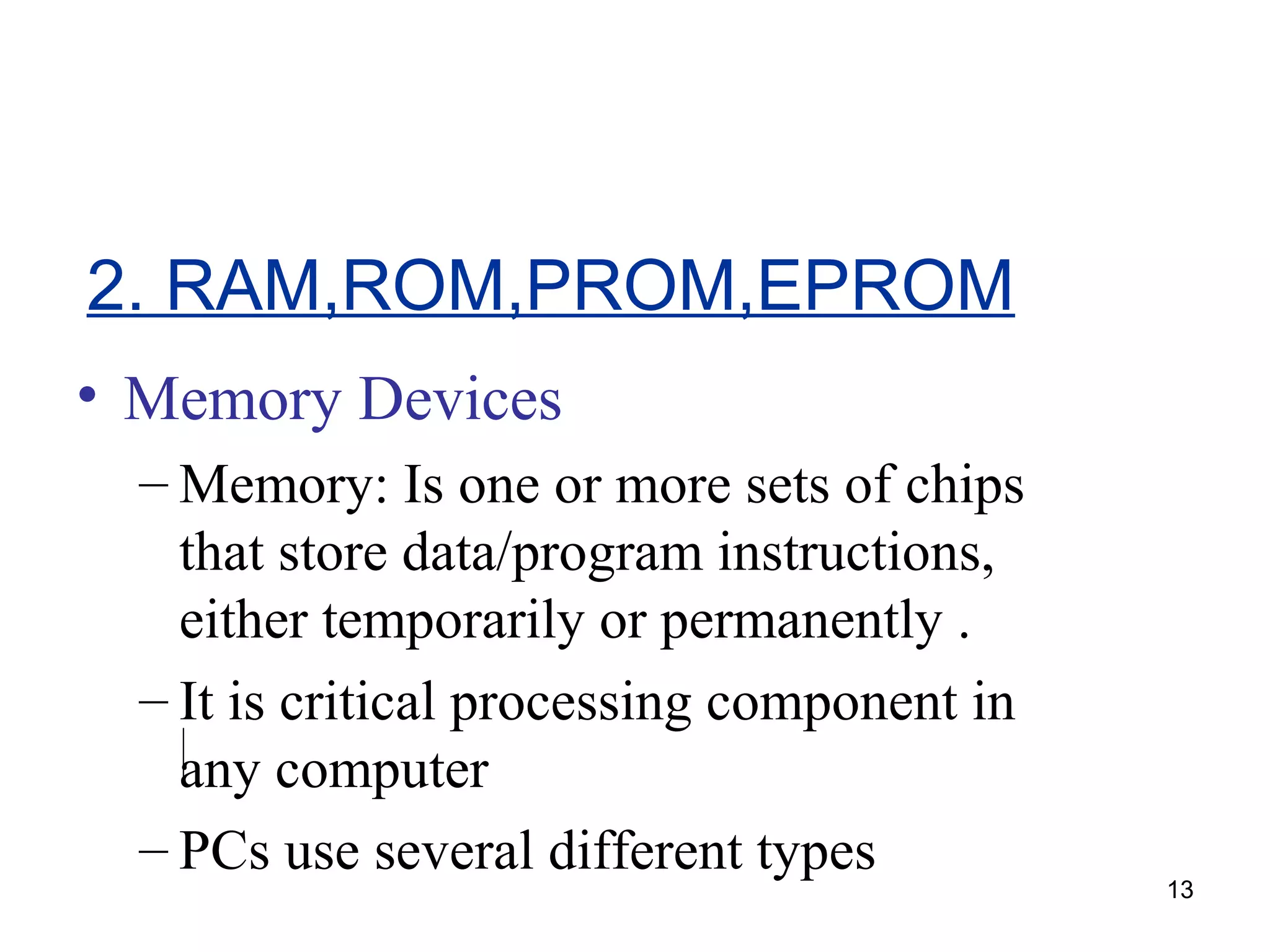
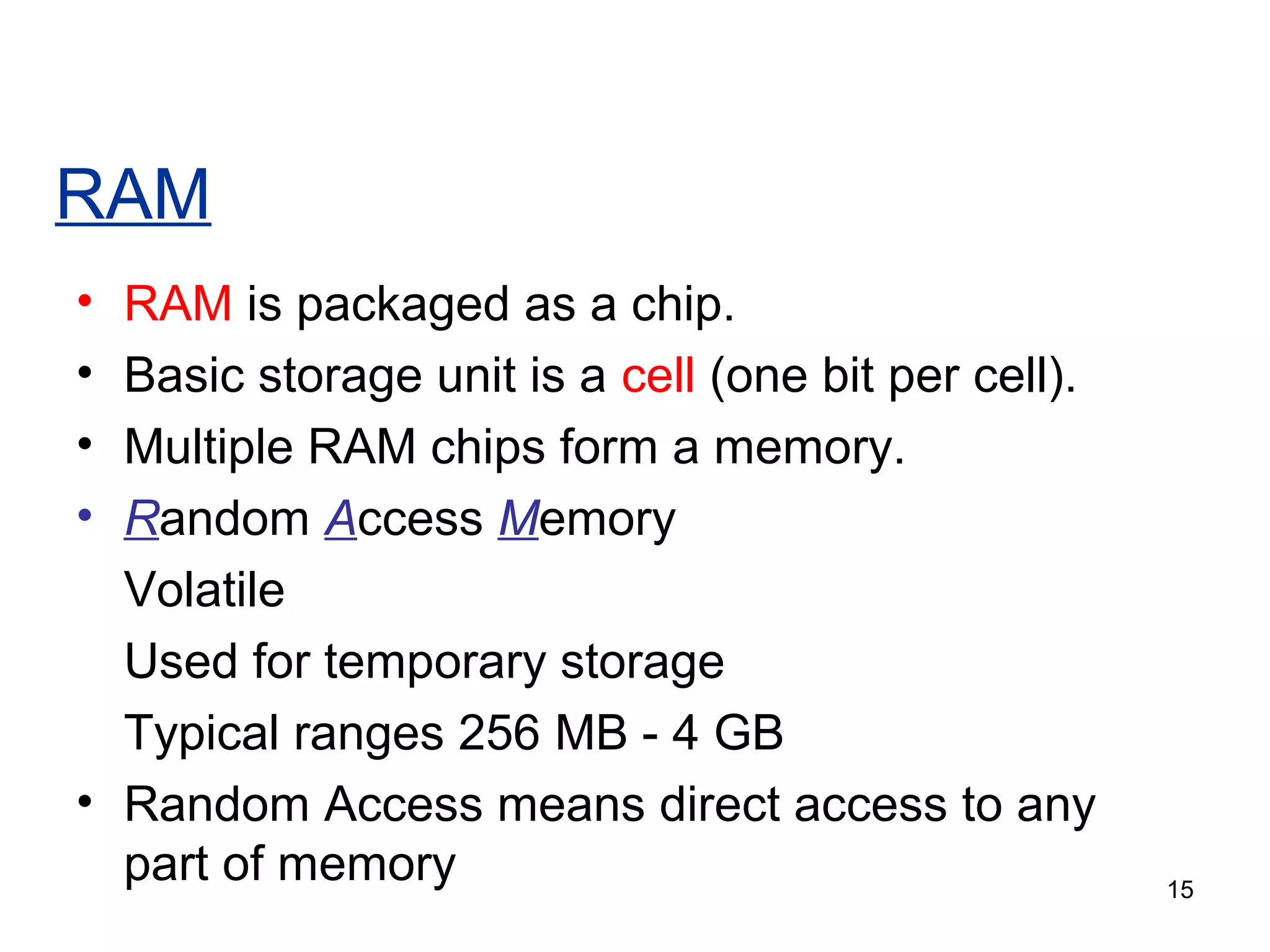
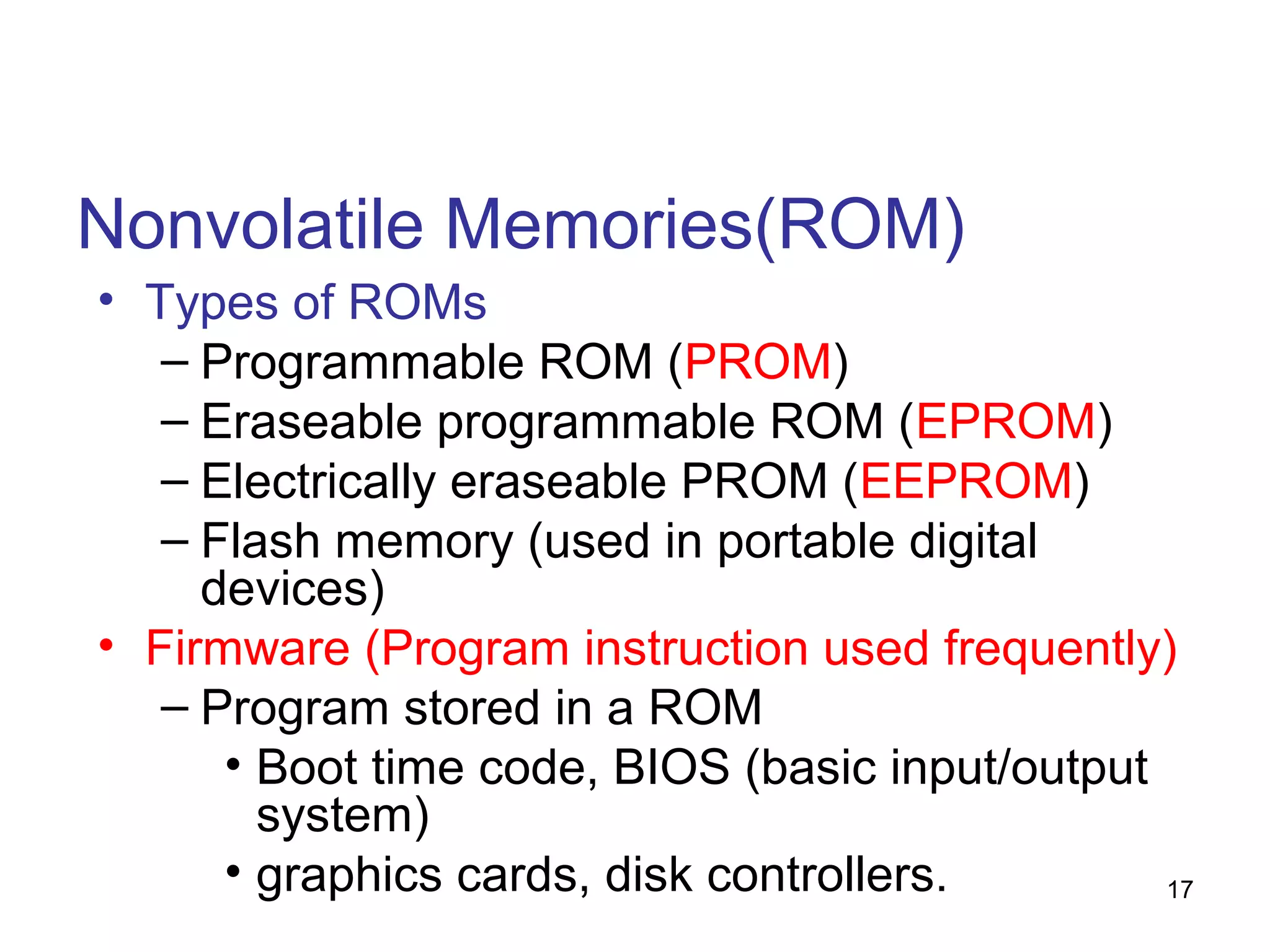
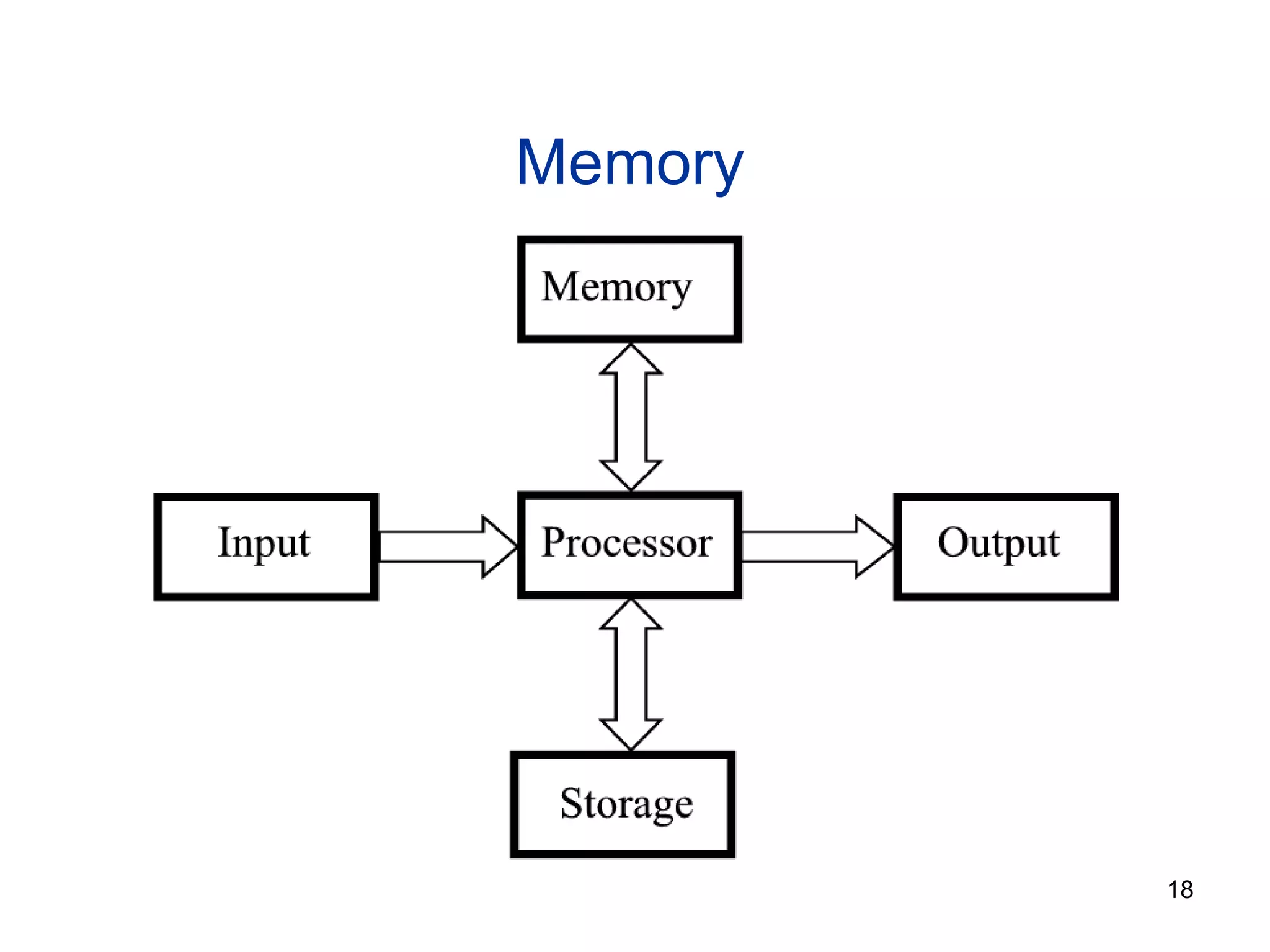
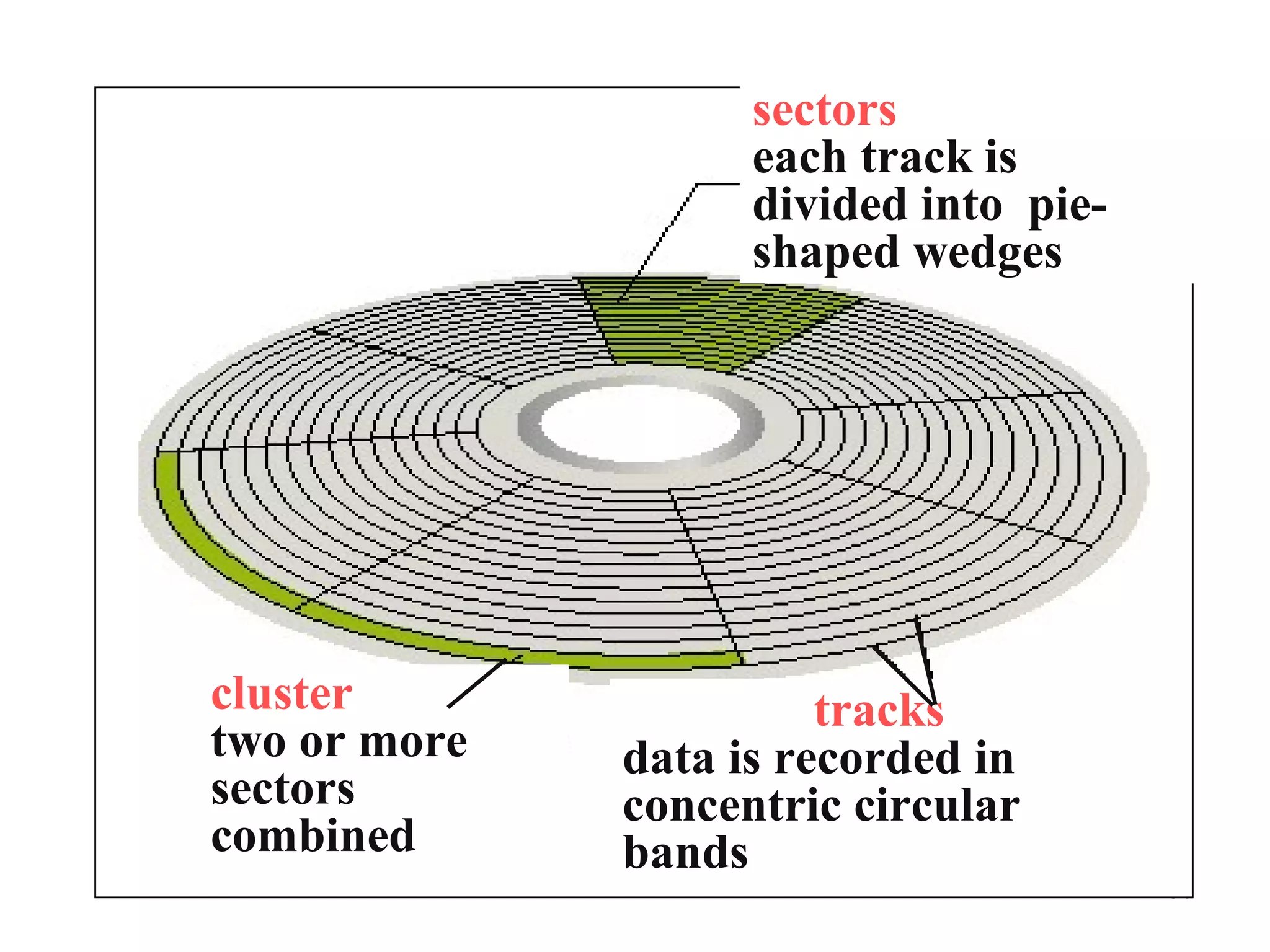
This document provides an overview of computer memory and storage devices. It discusses the main types of memory, including RAM, ROM, PROM, and EPROM. It also describes various storage devices such as magnetic tapes, hard disks, floppy disks, and optical disks like CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. The document explains the characteristics, units of measurement, capacities and structures of these different memory and storage technologies.