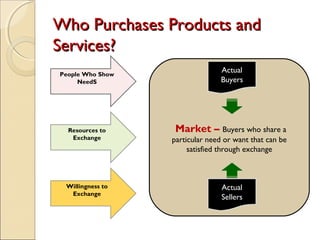
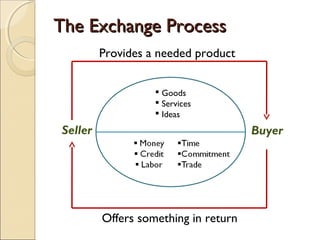
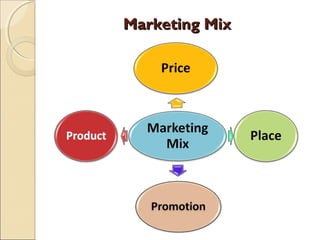
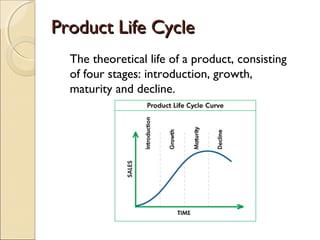
This document discusses marketing strategy and the marketing mix. It defines marketing as determining customer needs and providing goods and services to meet those needs. It also defines a market as a place where buyers and sellers interact to exchange goods and services. The marketing mix is made up of 4 Ps - product, price, place/distribution, and promotion. These tools are used to satisfy the needs of the target market. The document provides details on each of the 4 Ps, including product life cycle stages of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. It also discusses different promotional tools like advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, and publicity.