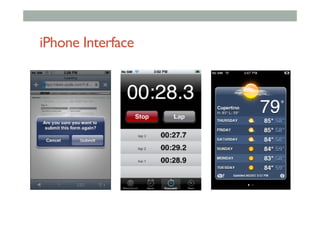
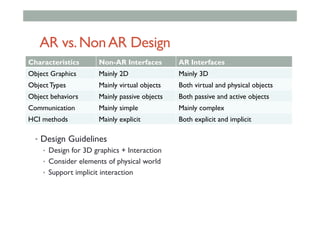
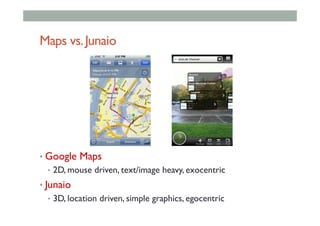
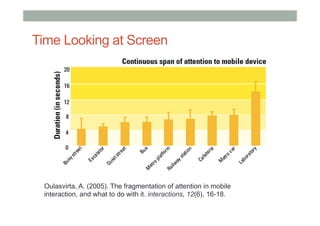
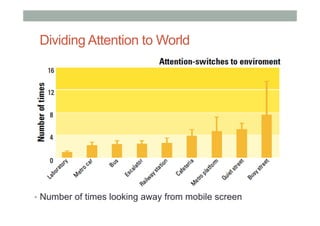
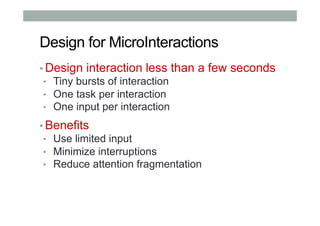
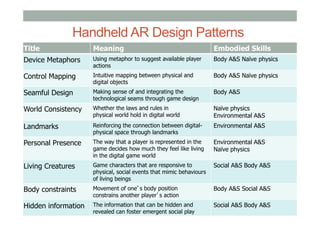
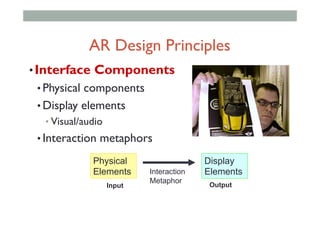
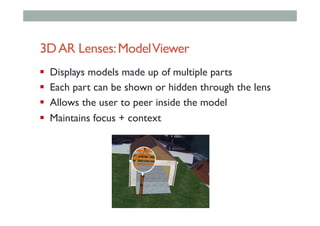
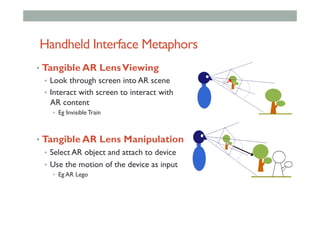
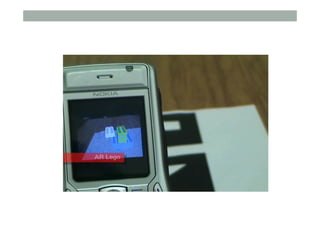
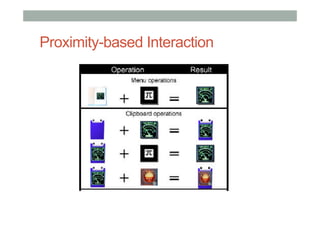
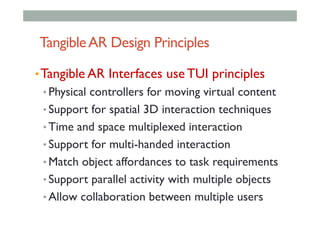
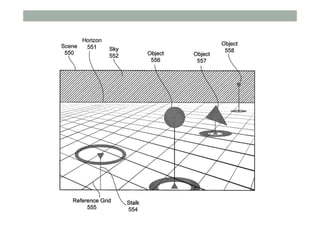
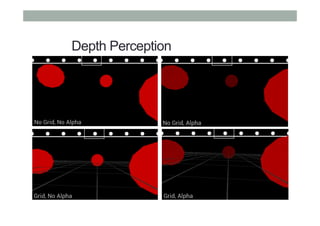
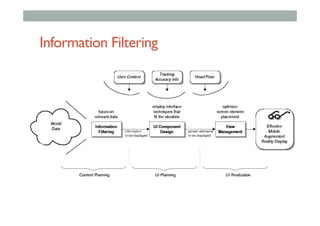
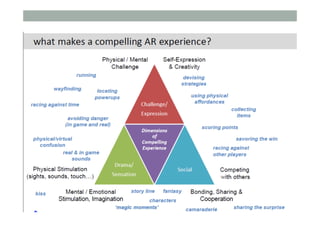
The document provides guidelines for designing mobile augmented reality (AR) interfaces, focusing on user-centered design and good human-computer interaction (HCI) principles. It emphasizes the importance of adapting existing interface guidelines for mobile environments, considering factors like device constraints, user context, and micro-interactions. Additionally, it introduces design patterns and principles for effective AR experiences, highlighting the integration of physical and virtual elements.