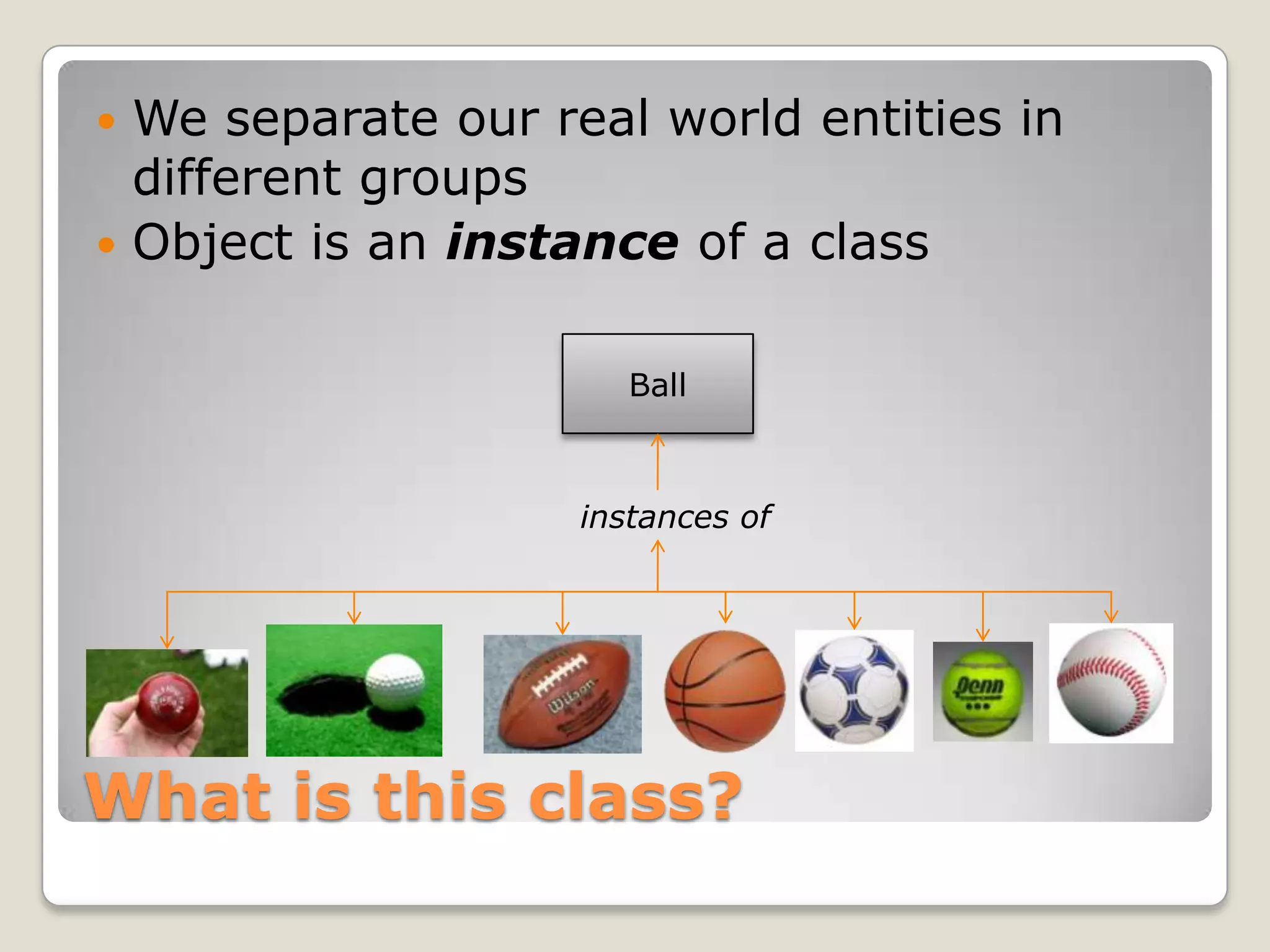
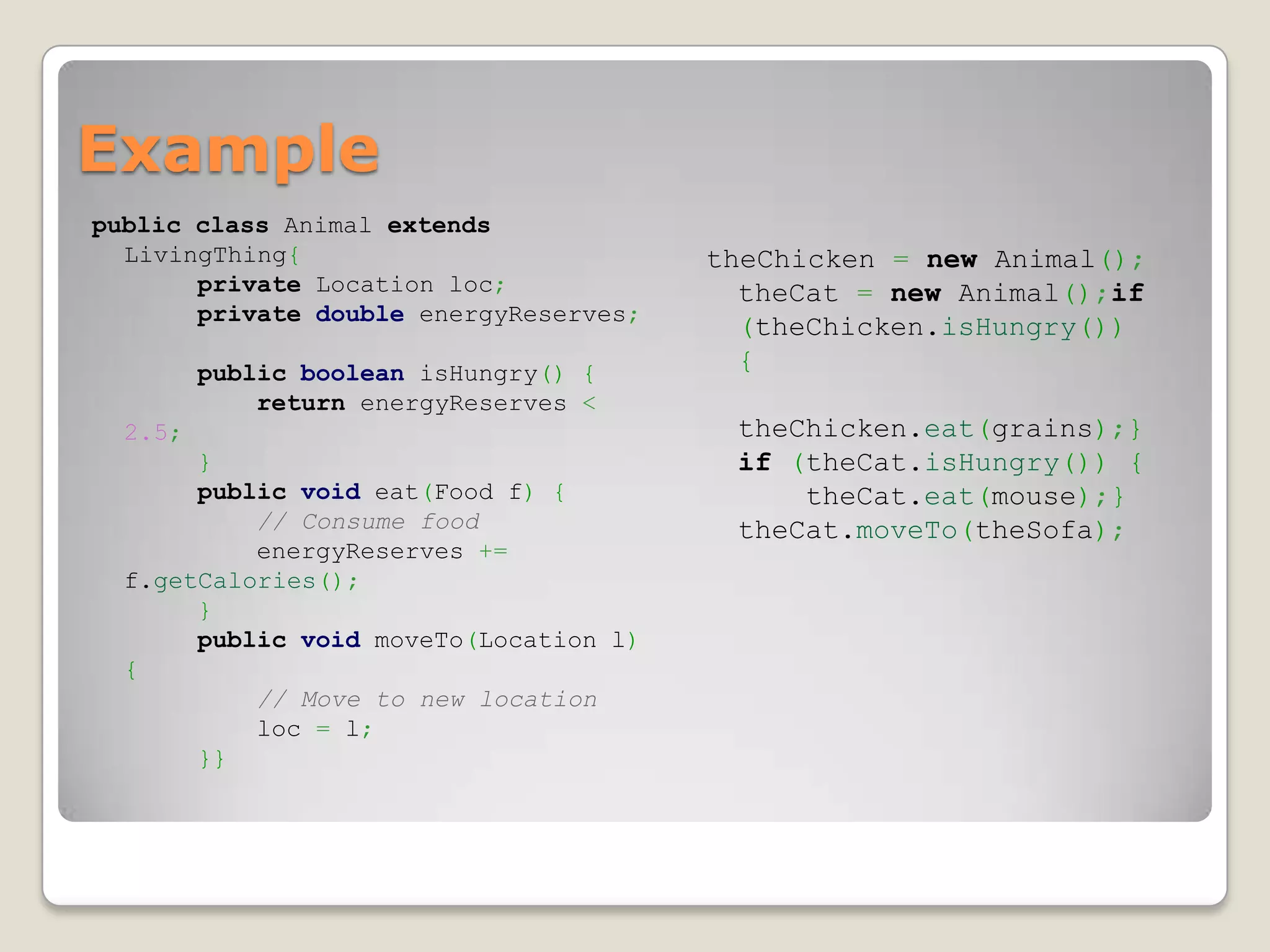
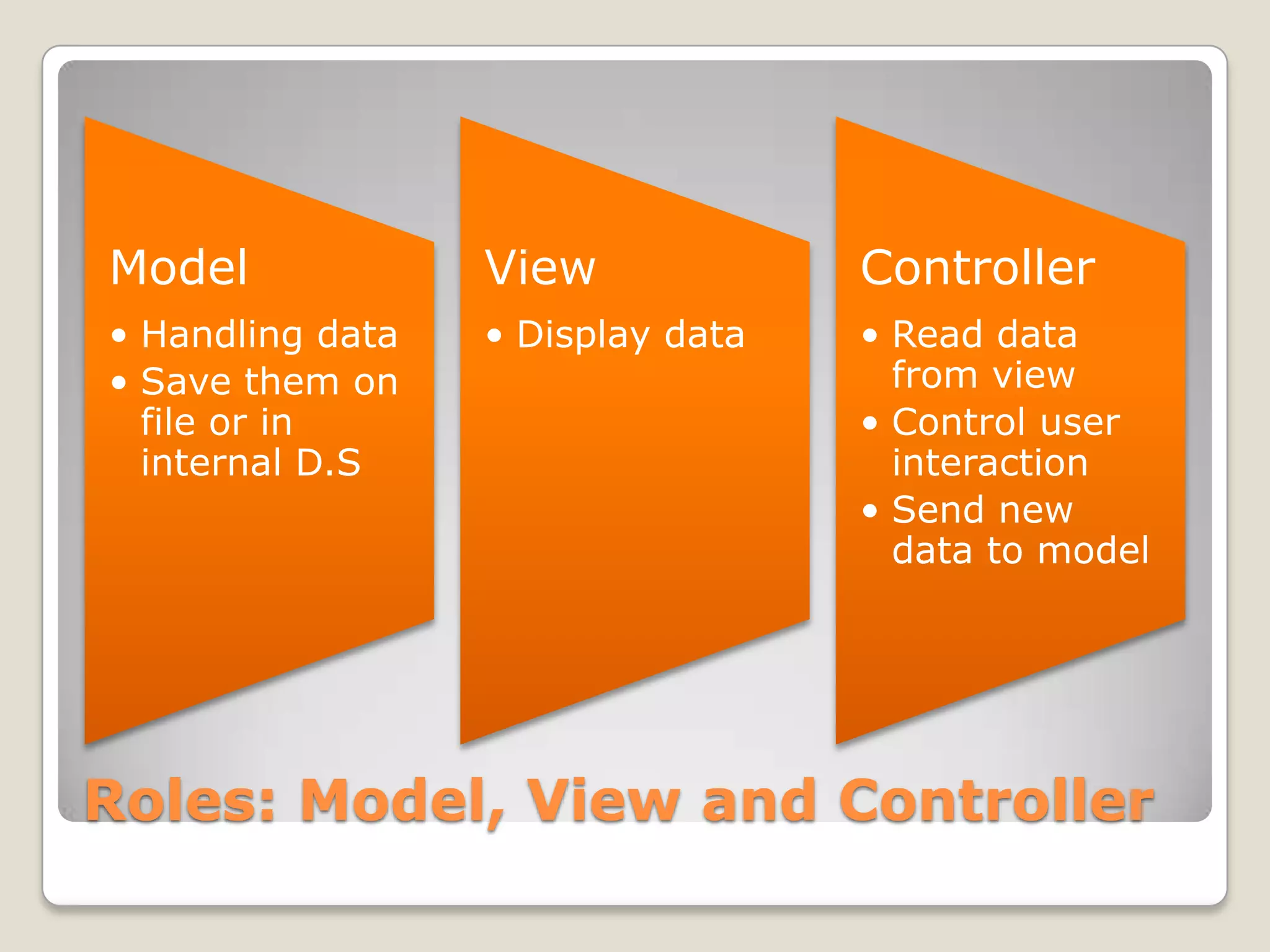
The document discusses converting real-world entities into programming objects, focusing on object-oriented programming concepts such as classes, objects, inheritance, and abstraction. It highlights API design principles, the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, and emphasizes the importance of organizing code effectively. The content is aimed at enhancing understanding and practical application of these programming paradigms and methodologies.






























![Model
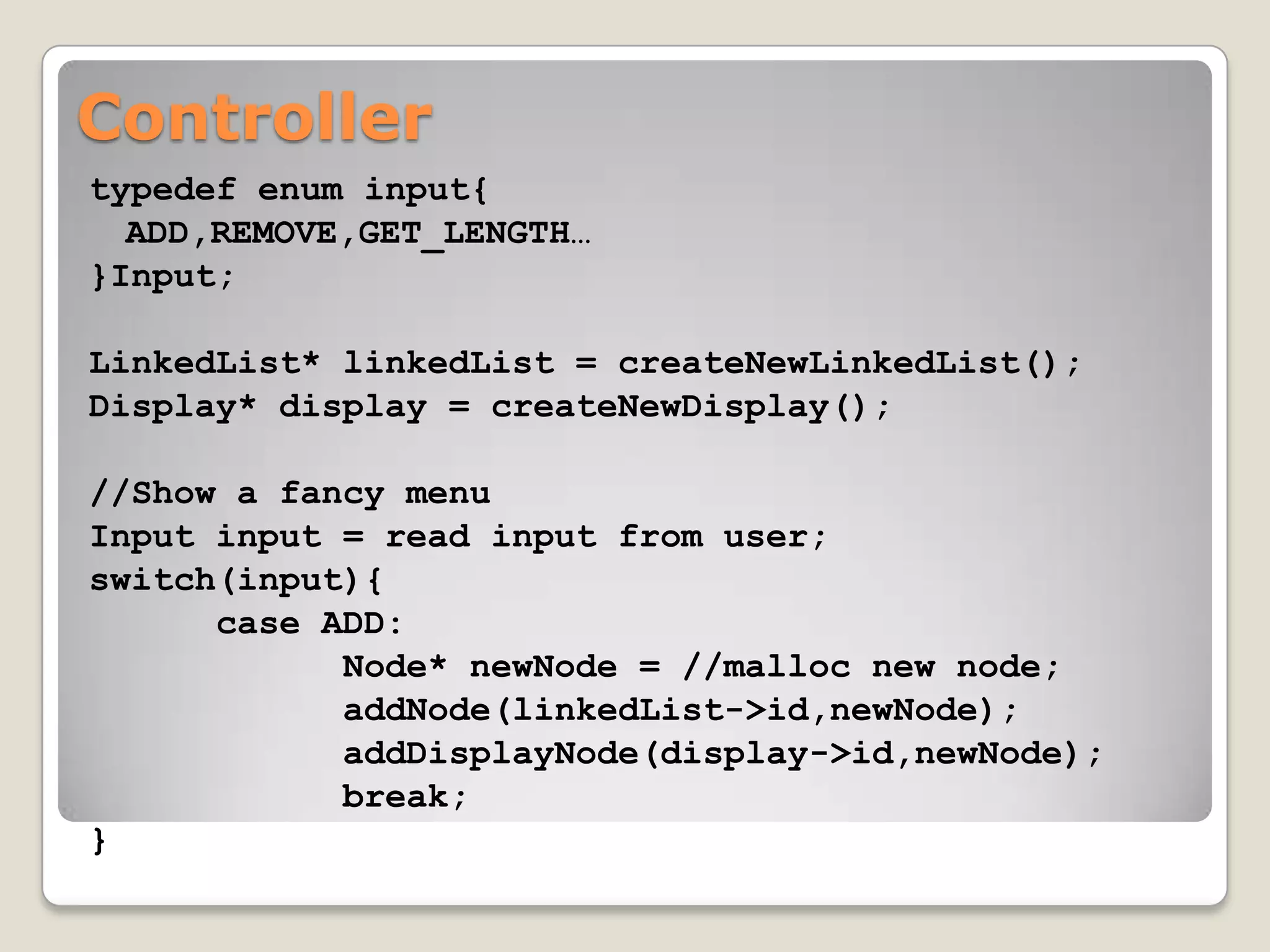
typedef struct node{ C++ or other
struct node* nextNode;
int id; OOP languages
… make finding the
}Node;
int globalId = 0;
context easy
typedef struct linkedList{
Node * headNode;
int id;
int listLength;
}LinkedList;
LinkedList *linkedListPool[];
void addNode(int linkedListId, int index, Node *newNode){
…
}
void removeNode(int linkedListId, Node *node){
…
}
LinkedList* createNewLinkedList(){
LinkedList* newll = (LinkedList*) malloc(sizeof(struct linkedList));
newll->id = globalId++;
newll->headNode = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newll->length = 0;
linkedListPool[globalId] = newll;
return newll;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oop-120910095902-phpapp01/75/OOP-API-Design-and-MVP-40-2048.jpg)
![View
typedef struct viewNode{
struct viewNode* nextViewNode;
int xLocation, int yLocation;
String color; //#FF3e2A (in hex)
…
}ViewNode;
//Similar to Model create another struct
typedef struct display{
ViewNode* head;
int id;
int length;
}Display;
Display *displayNodeList[];
void addDisplayNode(int viewNodeId, int index, Node *newNode){
//create new ViewNode
//Render UI
…
}
//create new display node like Model](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oop-120910095902-phpapp01/75/OOP-API-Design-and-MVP-41-2048.jpg)