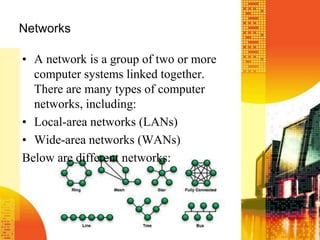
This document discusses various concepts related to data transmission and computer networks. It covers topics such as transmission of data, protocols and handshaking, different types of networks including LANs and WANs, common network topologies, and network access methods. It also describes various hardware components used in networks such as NICs, servers, routers, switches, and transmission media. Finally, it discusses network software concepts like network operating systems and their tasks as well as intranets and extranets.