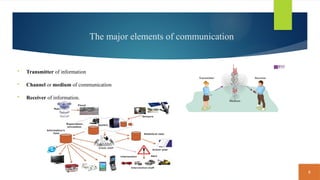
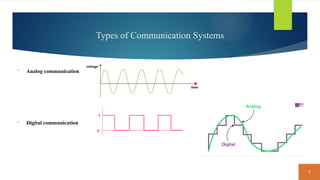
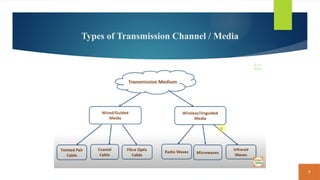
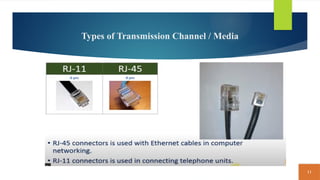
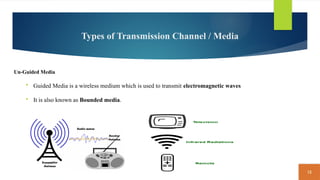
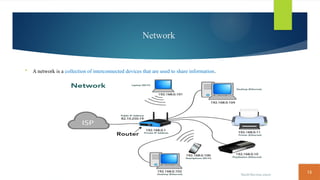
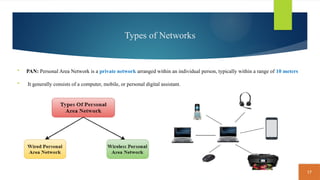
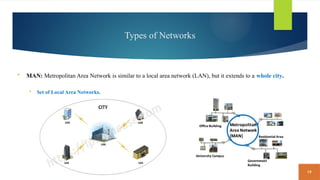
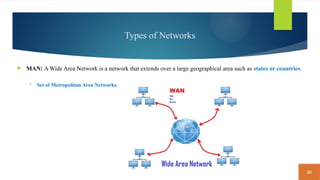
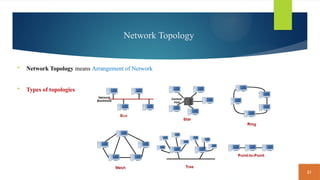
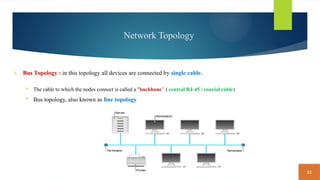
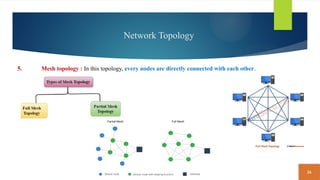
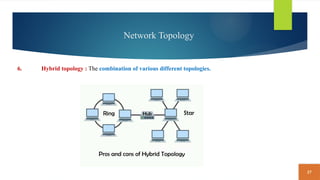
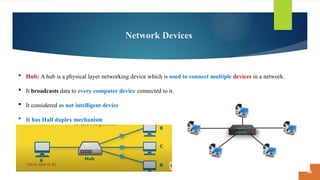
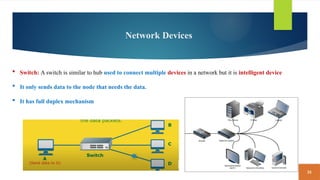
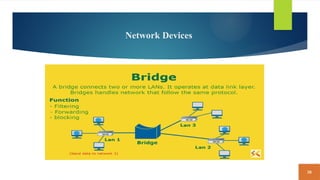
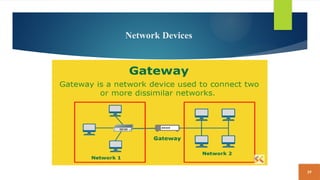
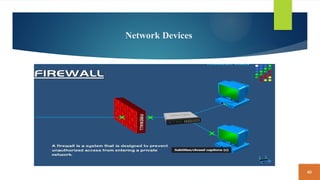
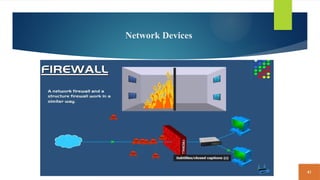
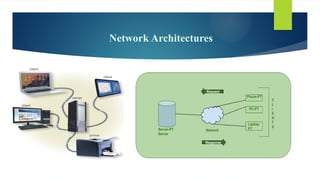
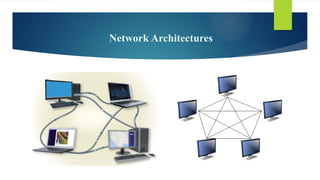
This document covers fundamental concepts related to digital communication and networking, including types of communication systems, devices, and various network types such as LAN, MAN, WAN, and their topologies. It details the roles of communication devices like modems, routers, and switches, and the importance of protocols like TCP/IP and Ethernet in facilitating data transmission. Additionally, it discusses network architectures, comparing client/server models to peer-to-peer systems, and the advantages and disadvantages of each.