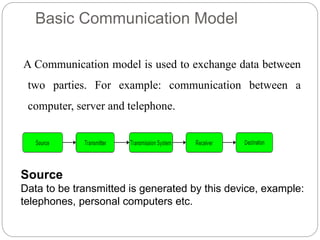
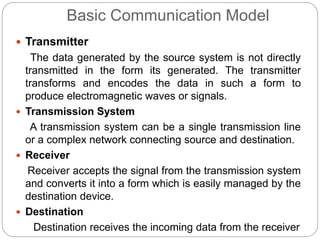
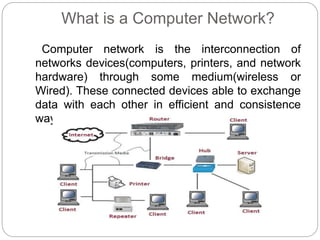
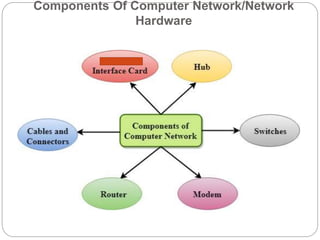
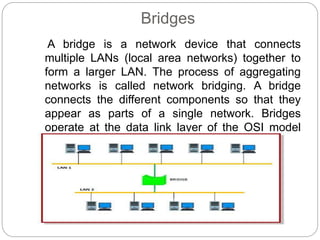
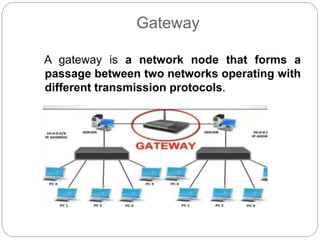
This document provides an overview of basic data communication concepts and components of computer networks. It discusses the basic communication model including a source that generates data, a transmitter that encodes the data, a transmission system that connects the source and destination, and a receiver that converts the signal for the destination. It also defines key terms like message, sender, receiver, medium, and protocols. The document then describes common network hardware components like network interface cards, hubs, modems, switches, bridges, routers, gateways, and repeaters. It concludes by discussing network software functions like user management, file management, access control, and security.