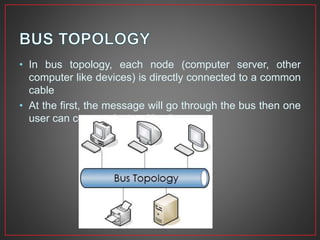
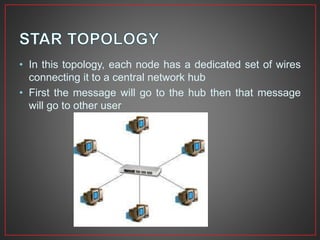
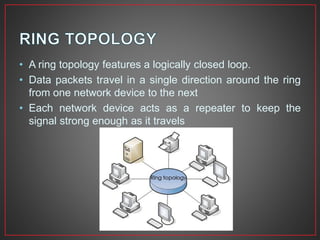
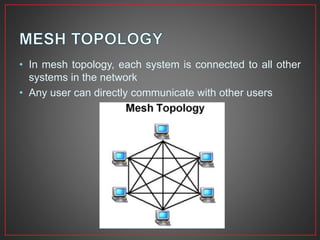
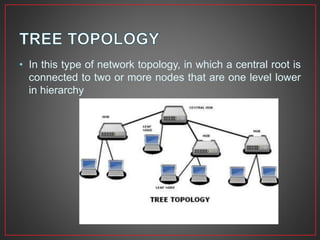
This document provides an overview of computer networks. It defines a computer network as a collection of connected computers that can communicate and exchange information. It describes different types of network connections including simplex, half duplex, and full duplex. It also outlines common network topologies like bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree. Additionally, it explains important networking hardware and standards including network interface cards, switches, routers, Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, IEEE 802 standards, and more.