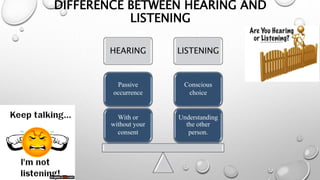
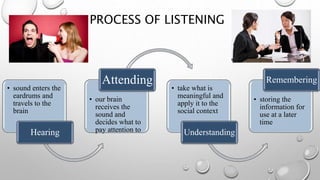
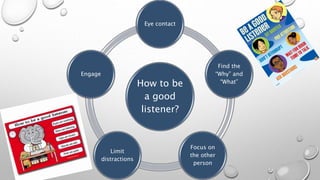
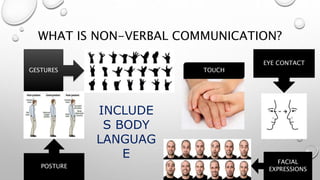
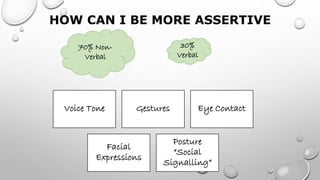
The document outlines a skills training program focused on communication, differentiating between hearing and listening, and emphasizing effective listening techniques. It discusses the importance of verbal and non-verbal communication, offers insights into assertiveness, and provides guidance on saying 'no' and 'yes' confidently. Additionally, it includes practical scenarios for self-reflection and evaluation of learning outcomes from the training.