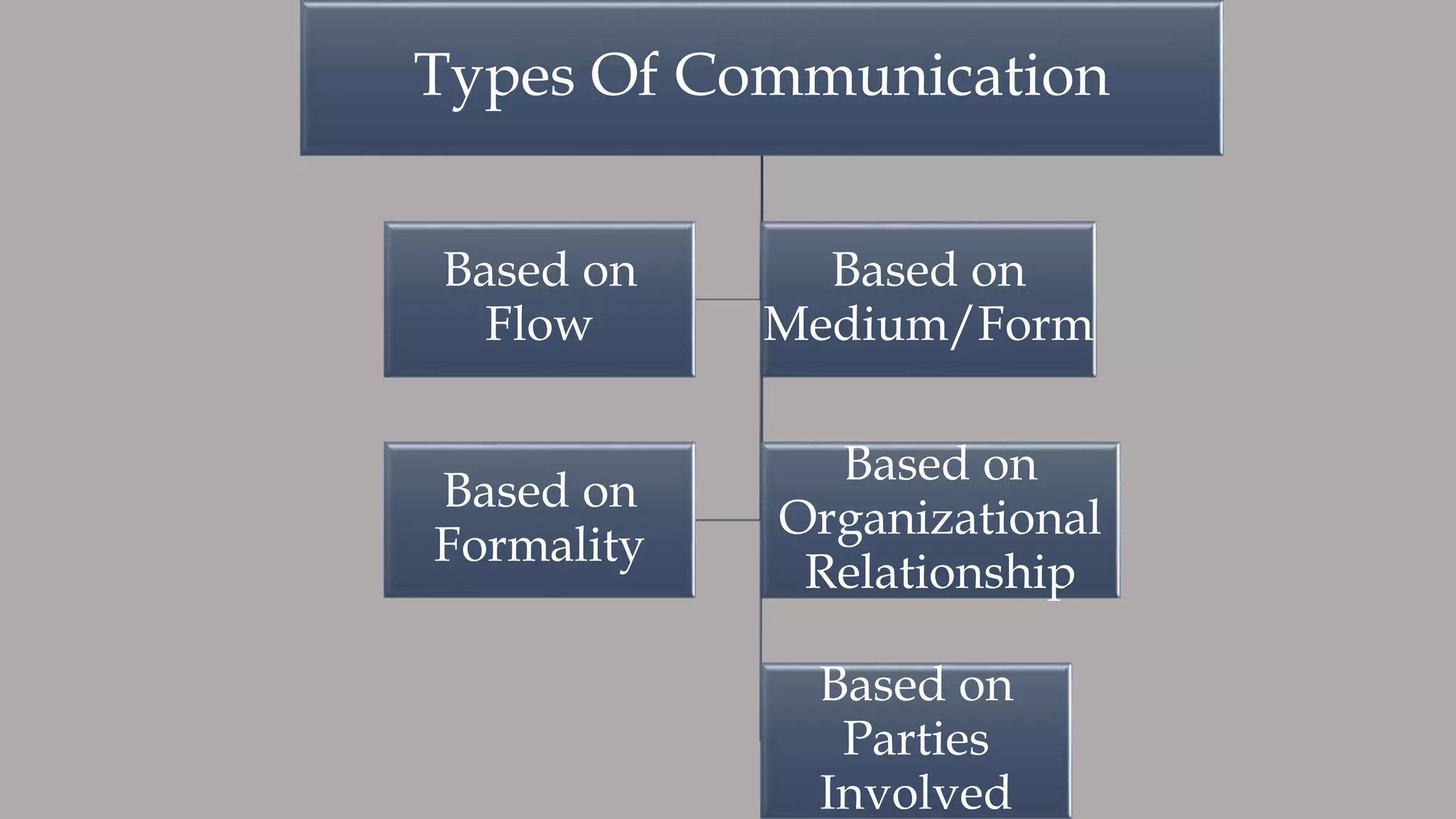
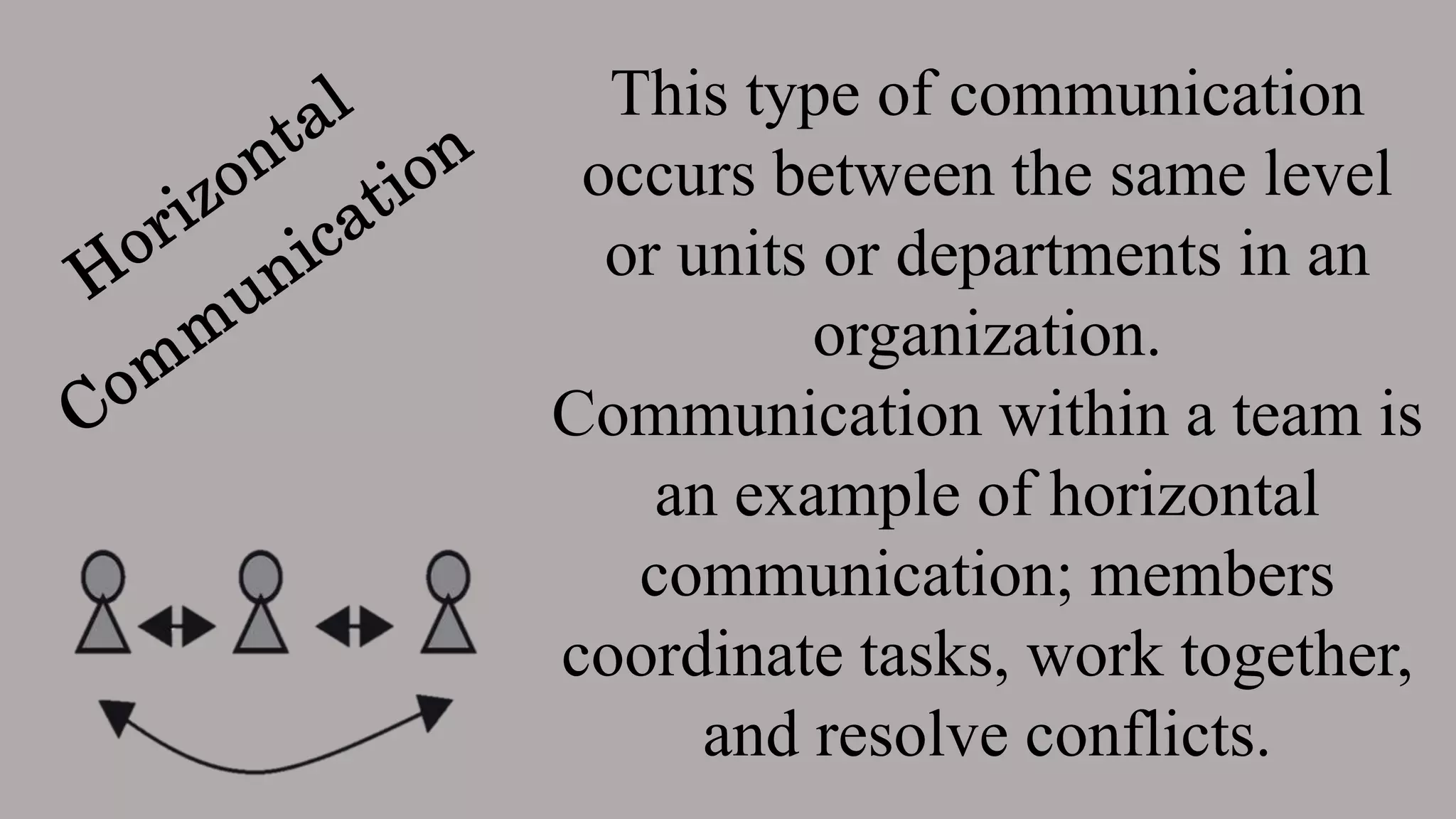
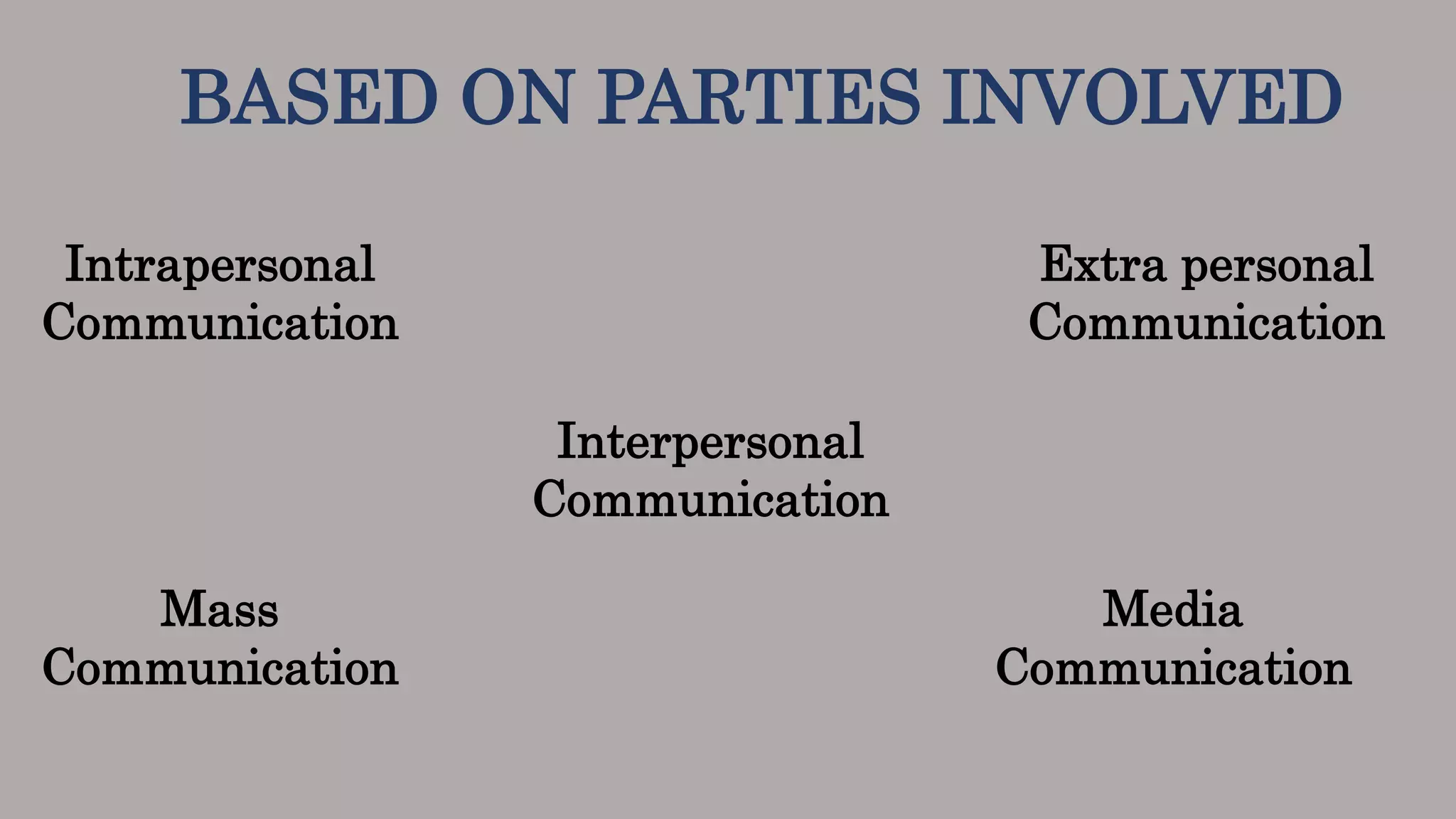
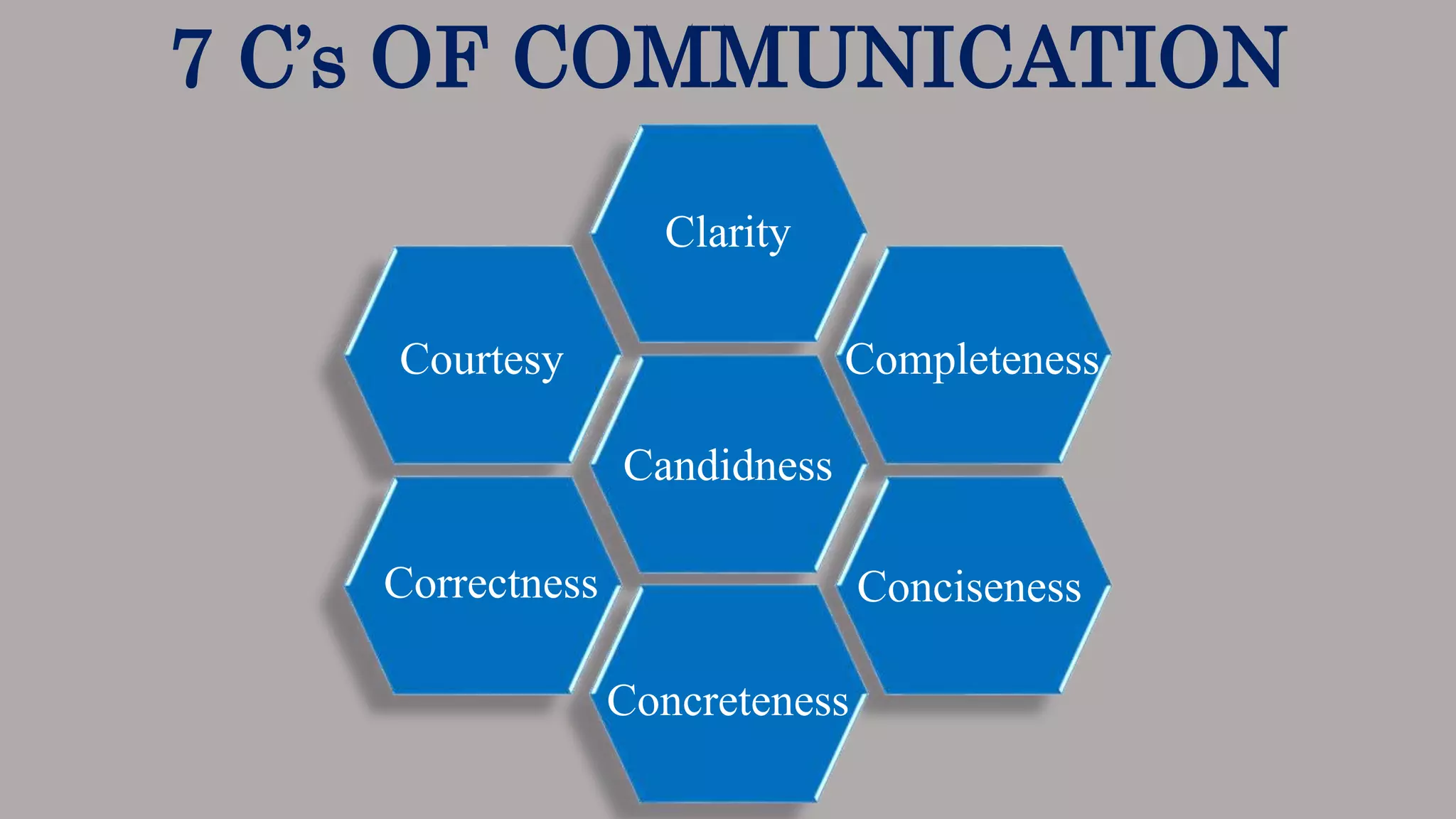
The document outlines various types of communication, categorizing them by medium, flow, organizational relationship, formality, and parties involved. It explains verbal and non-verbal communication, including oral, written, and body language, as well as formal and informal channels within internal and external contexts. Additionally, it discusses barriers to effective communication and the principles of the 7 Cs of communication.