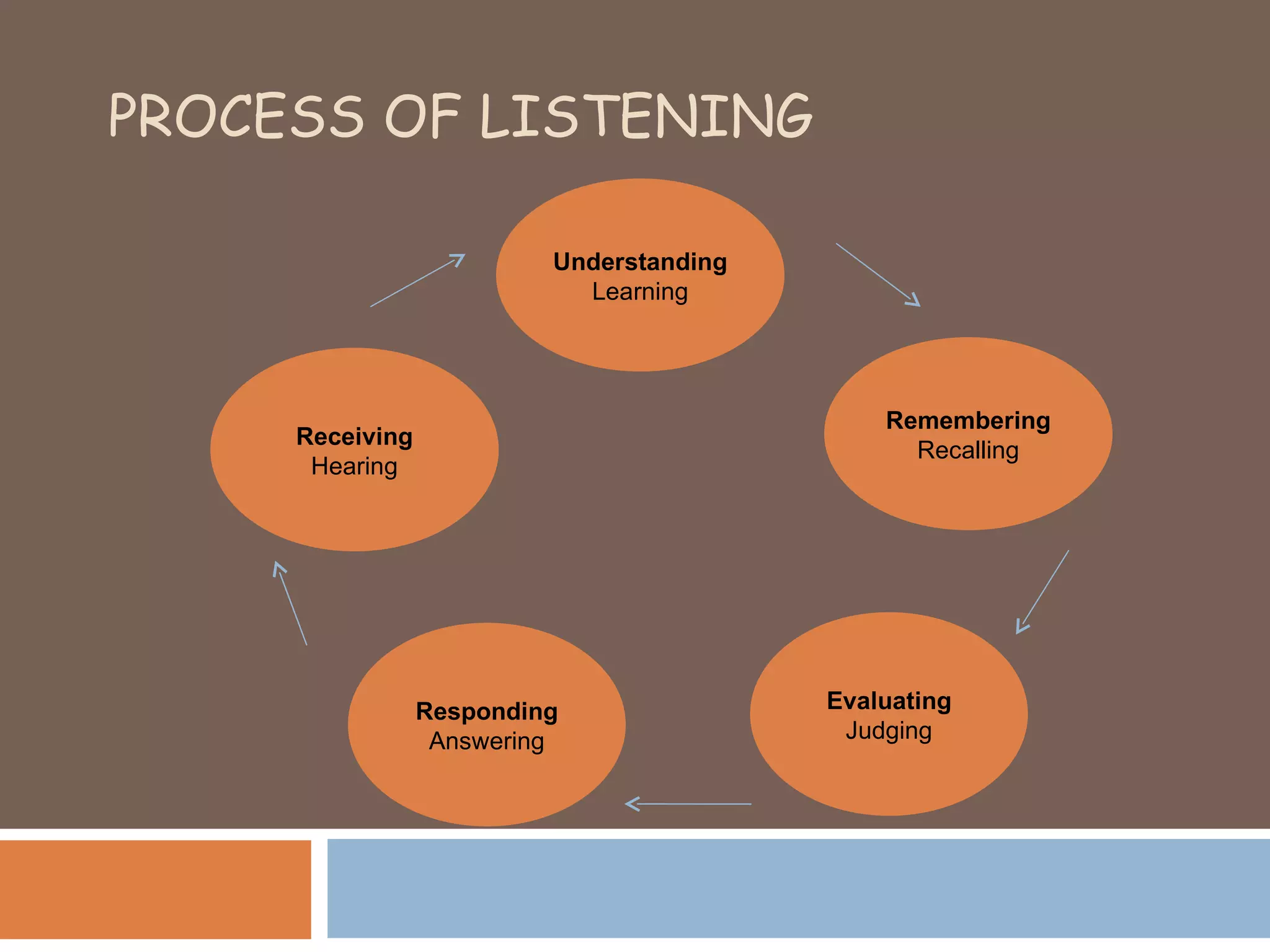
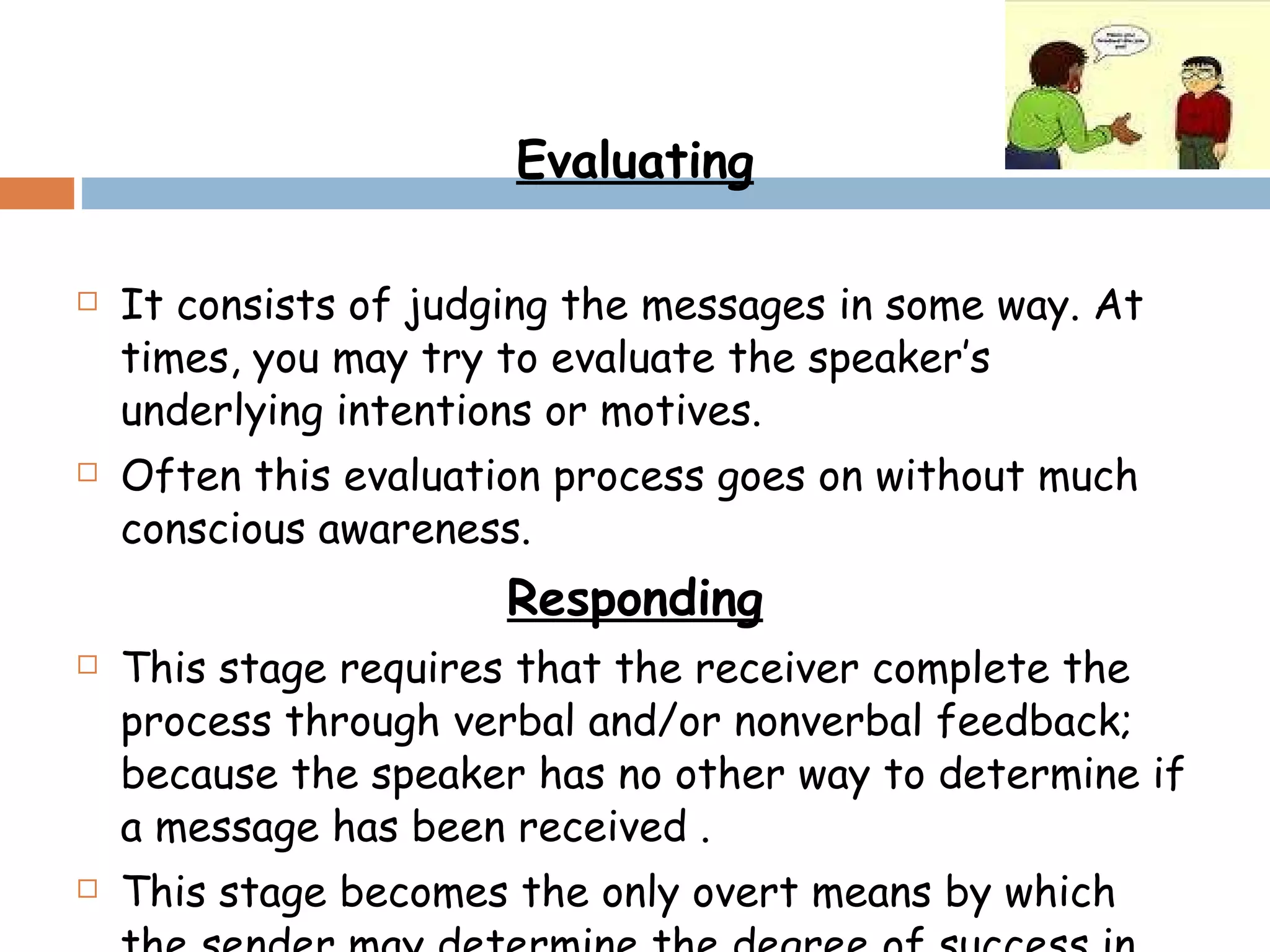
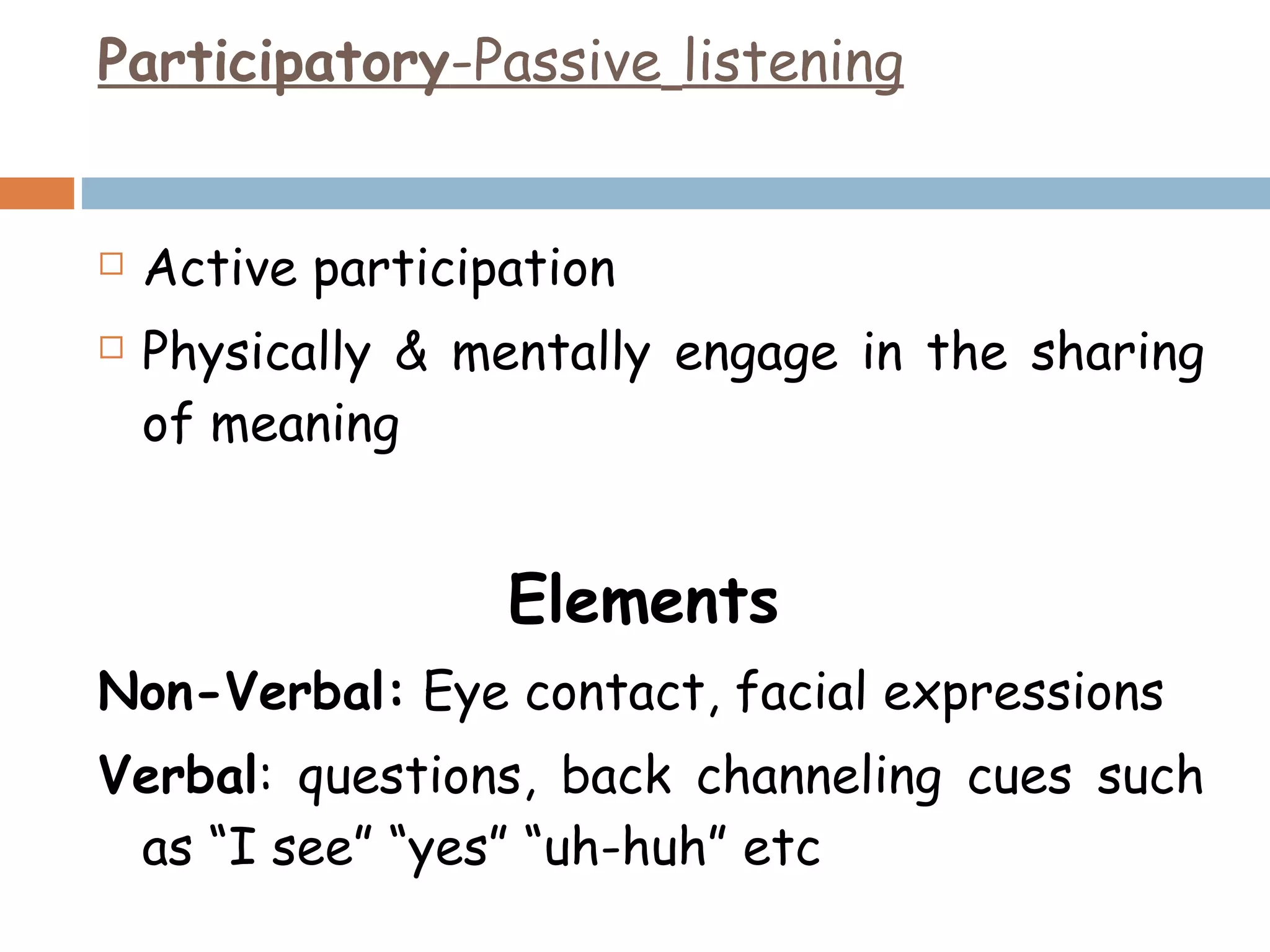
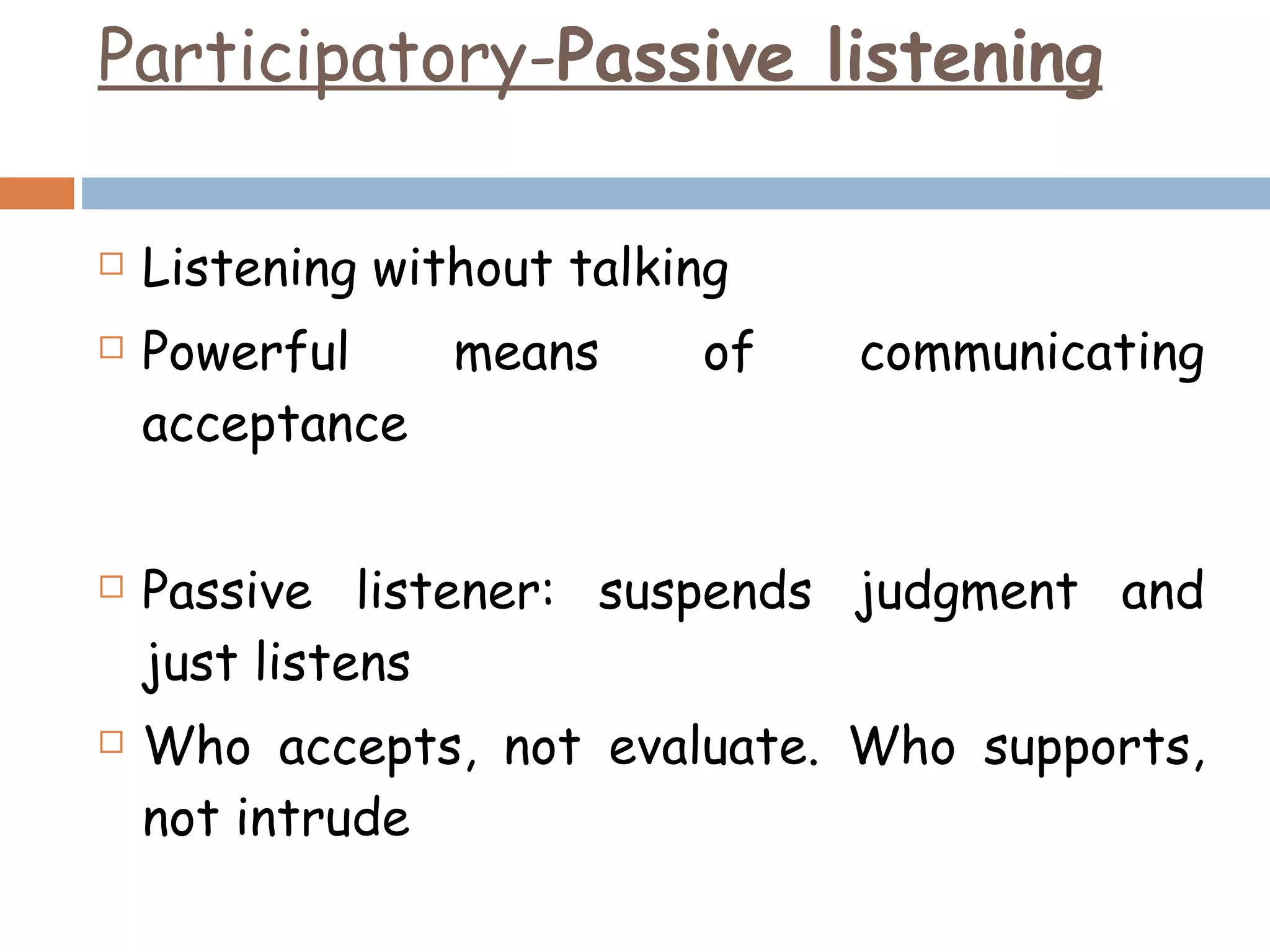
The document discusses listening as an important communication skill. It defines listening as a psychological process that involves receiving, constructing meaning from, and responding to spoken messages. In contrast, hearing is defined as a physiological process. The document also highlights that 85% of what we know comes from listening, but people typically only recall 20% of what they hear. It then describes different styles of effective listening, including participatory, empathic, non-judgmental, surface-level versus in-depth listening. Active listening techniques like paraphrasing and asking questions are also outlined to ensure the listener understands the speaker.