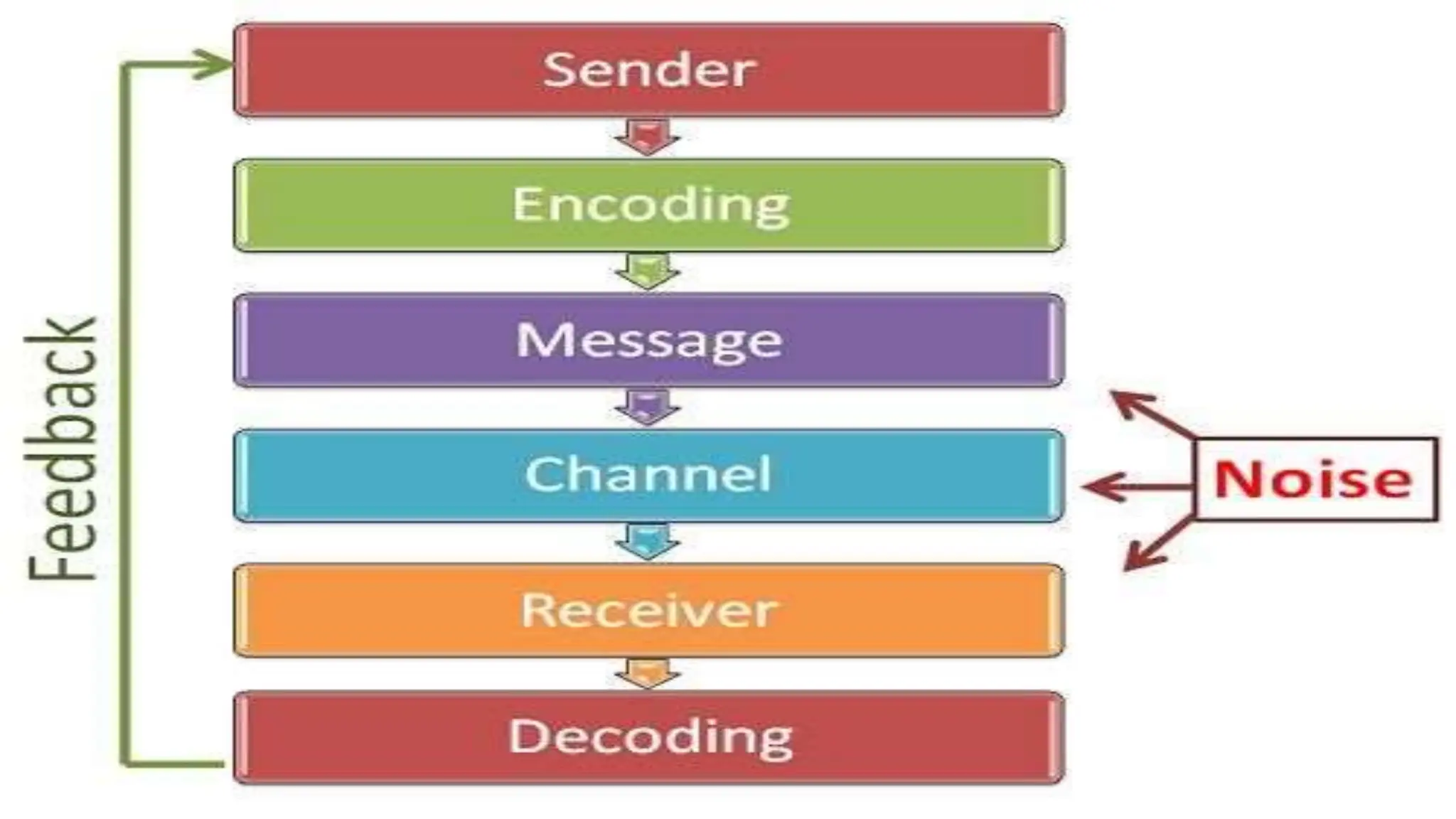
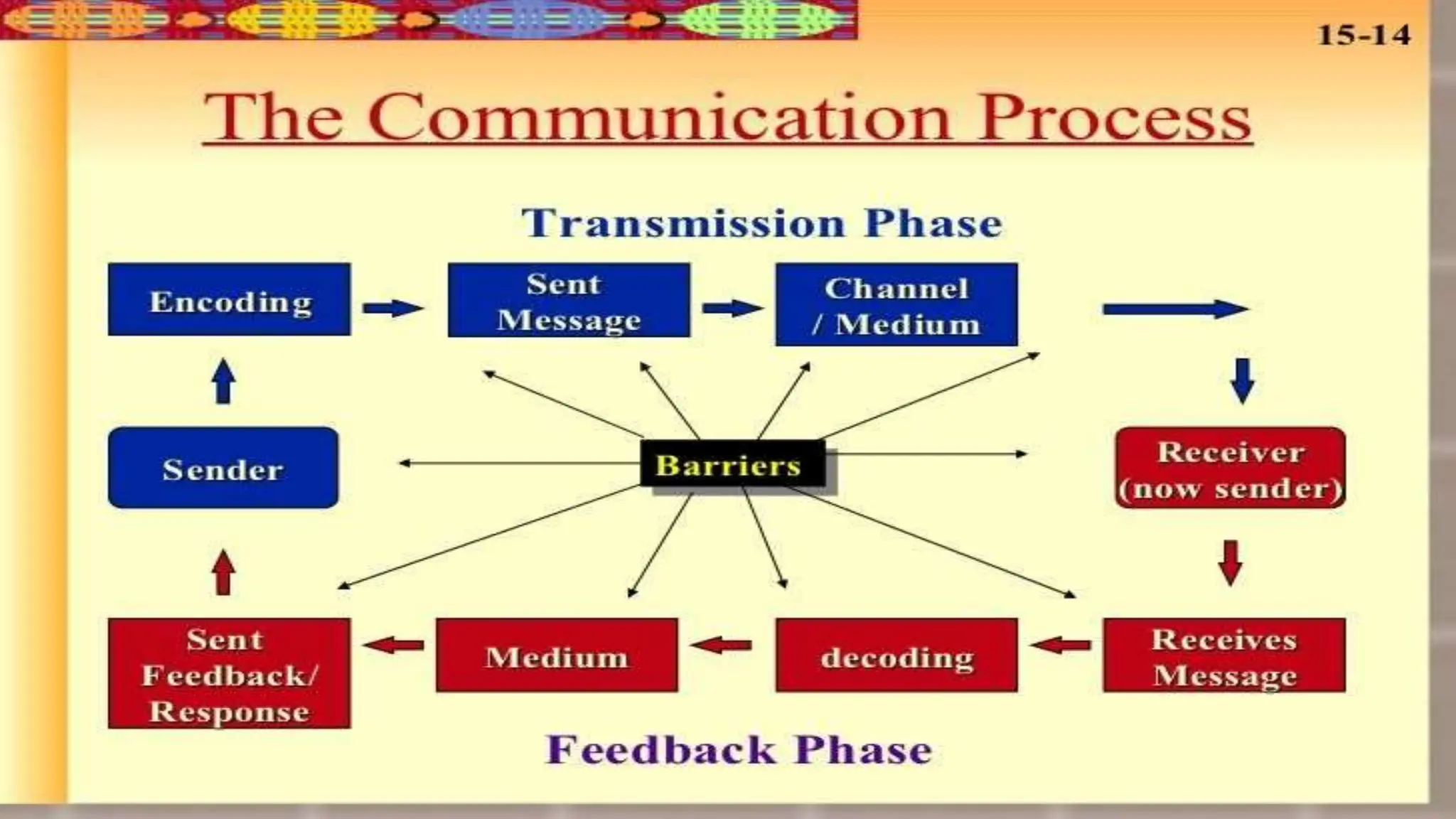
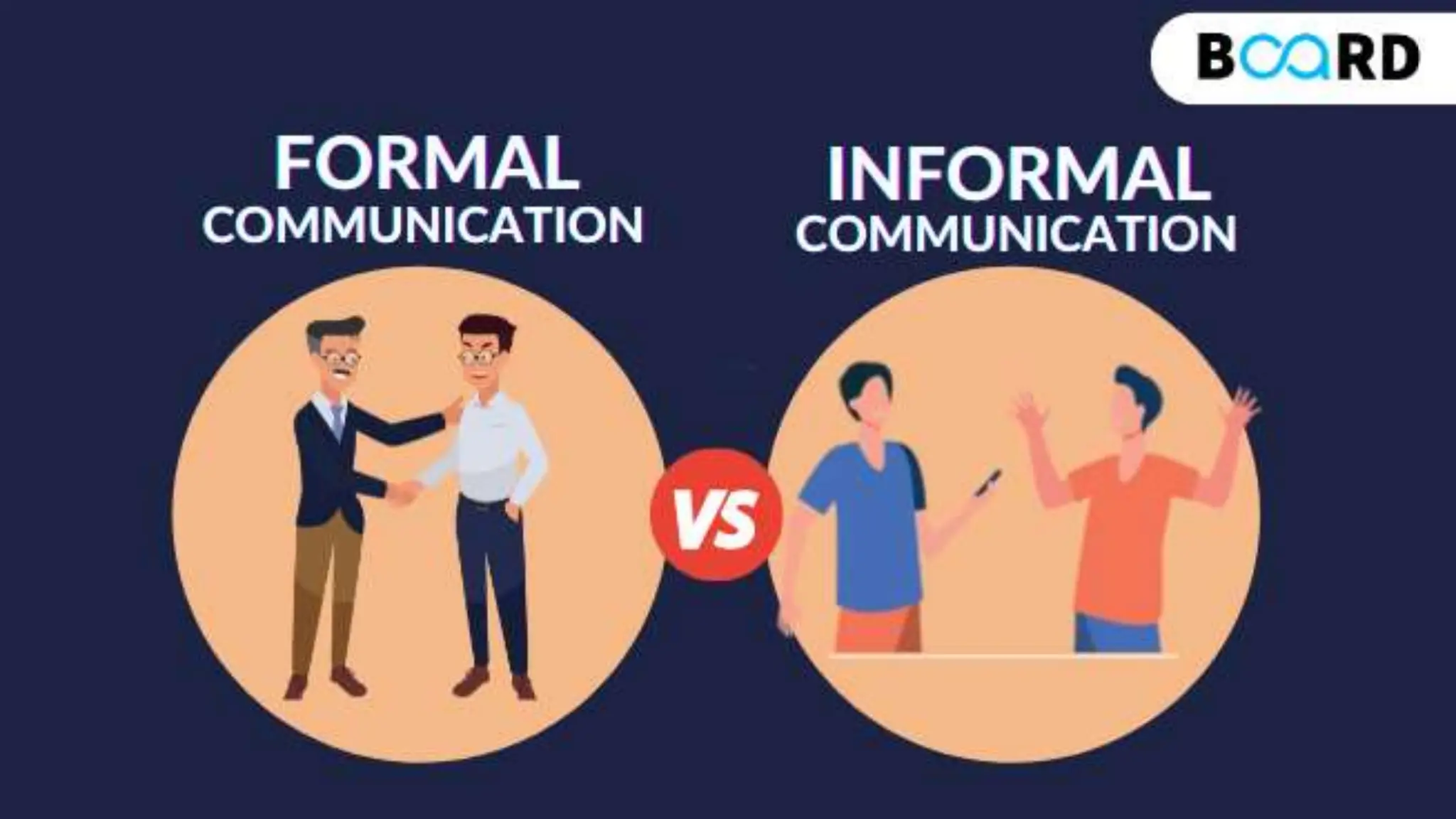
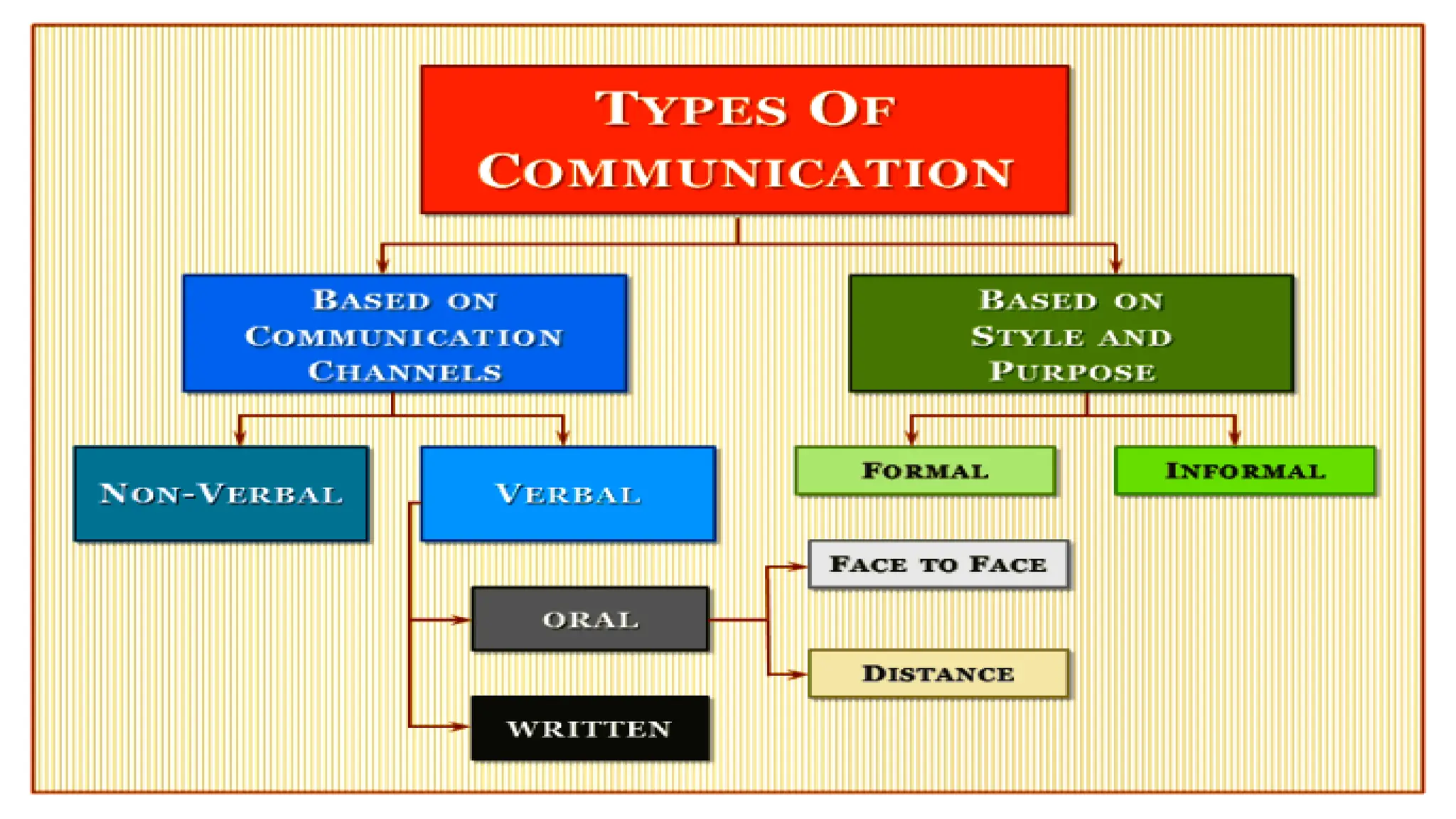
This document discusses communication in healthcare settings. It begins by outlining the objectives of the presentation, which are to define communication, learn about types of communication, understand barriers to communication, and explain channels, modes, factors, and strategies for effective communication. It then defines communication and describes the basic process, which involves a sender encoding and transmitting a message through a channel to a receiver who provides feedback. It outlines different types of communication including formal/informal and verbal/non-verbal. It also discusses barriers to communication such as language barriers, emotional barriers, physical barriers, systemic barriers, and taboos.