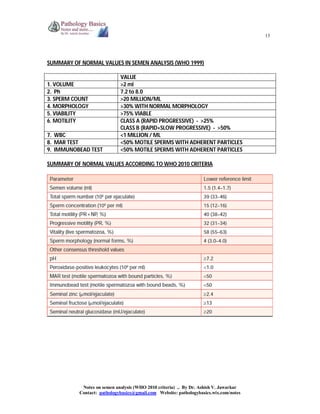
The document provides comprehensive information on semen analysis according to WHO 2010 criteria, including the contents, collection methods, and examination procedures of seminal fluid. It outlines the indications for analysis, such as assessing infertility, paternity testing, and evaluating vasectomy effectiveness, alongside normal value ranges for various parameters like volume, pH, and sperm motility. Additionally, it discusses immunological and biochemical analysis techniques, as well as sperm function tests relevant in clinical and medicolegal contexts.