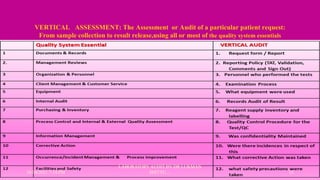
The document outlines the importance and processes of laboratory audits conducted by Dr. Lukman Shittu in the Department of Chemical Pathology. It details various types of audits, including internal and external audits, their objectives, methodologies, and significance in ensuring compliance with quality management systems. The document emphasizes that thorough audits help in identifying issues, improving laboratory processes, and maintaining accreditation standards.



























![INTERNAL AUDIT…
ESTABLISH A SCHEDULE.
• ISO 15189:2007 [4.14.2] states:
The main elements of the quality management system should normally be subject to internal audit
once every twelve months
• In general, audit regularly
• consider three to six-month intervals between audits.
• If audits reveal specific problems, it may be necessary to include more frequent audits.
30/04/2021 7:14 PM
LABORATORY AUDIT BY DR LUKMAN
SHITTU.... 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laboratoryauditls-210430233517/85/Laboratory-audit-ls-30-320.jpg)











