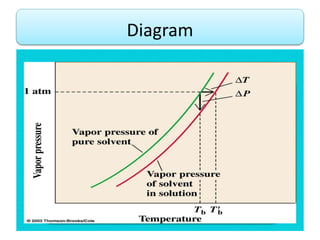
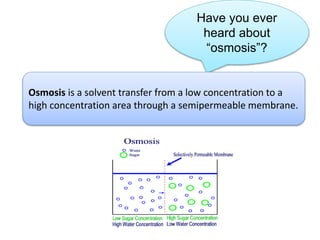
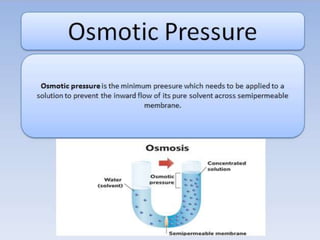
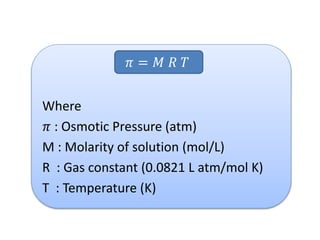
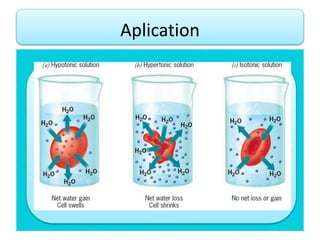
- Vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor above its liquid in a sealed container where vapor and liquid are in dynamic equilibrium.
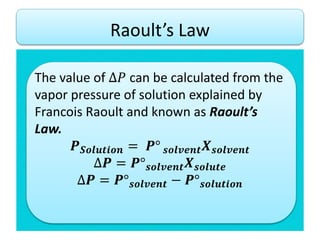
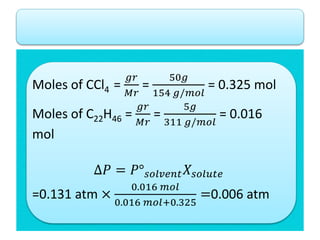
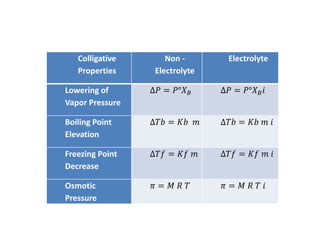
- According to Raoult's law, the vapor pressure of a solution is lower than the vapor pressure of the pure solvent. This lowering of vapor pressure (ΔP) can be calculated using Raoult's law.
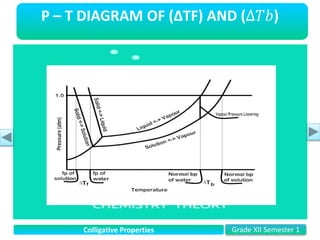
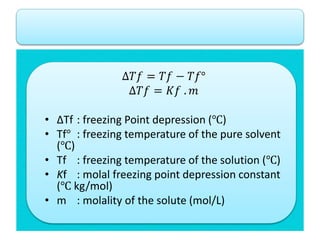
- Freezing point depression (ΔTf) and boiling point elevation (ΔTb) are colligative properties that depend on the number of solute particles in solution. ΔTf and ΔTb increase with increasing molality of the solute.