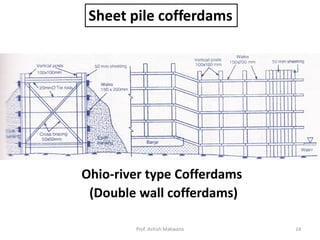
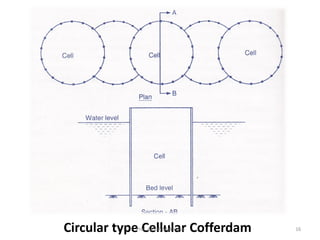
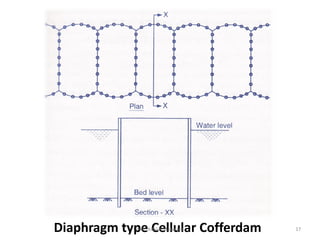
The document outlines the definition, uses, types, and design features of cofferdams, which are temporary structures used to remove water from excavation areas to facilitate construction. It discusses factors influencing the selection of cofferdams, such as water depth, excavation area, material availability, and environmental conditions. Various types of cofferdams are described, including earth fill, rock fill, timber crib, and sheet pile cofferdams, along with considerations for design and potential erosion.