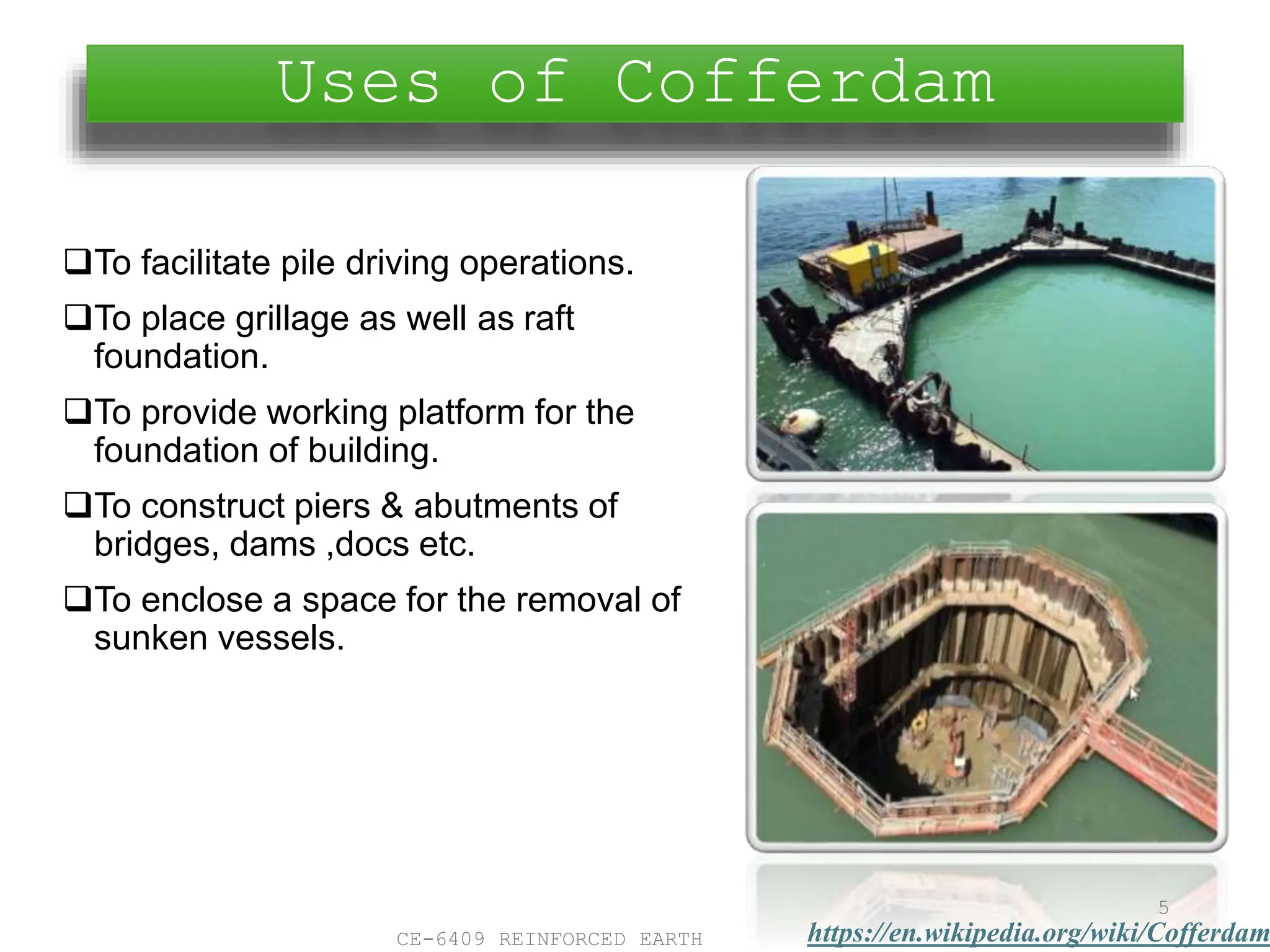
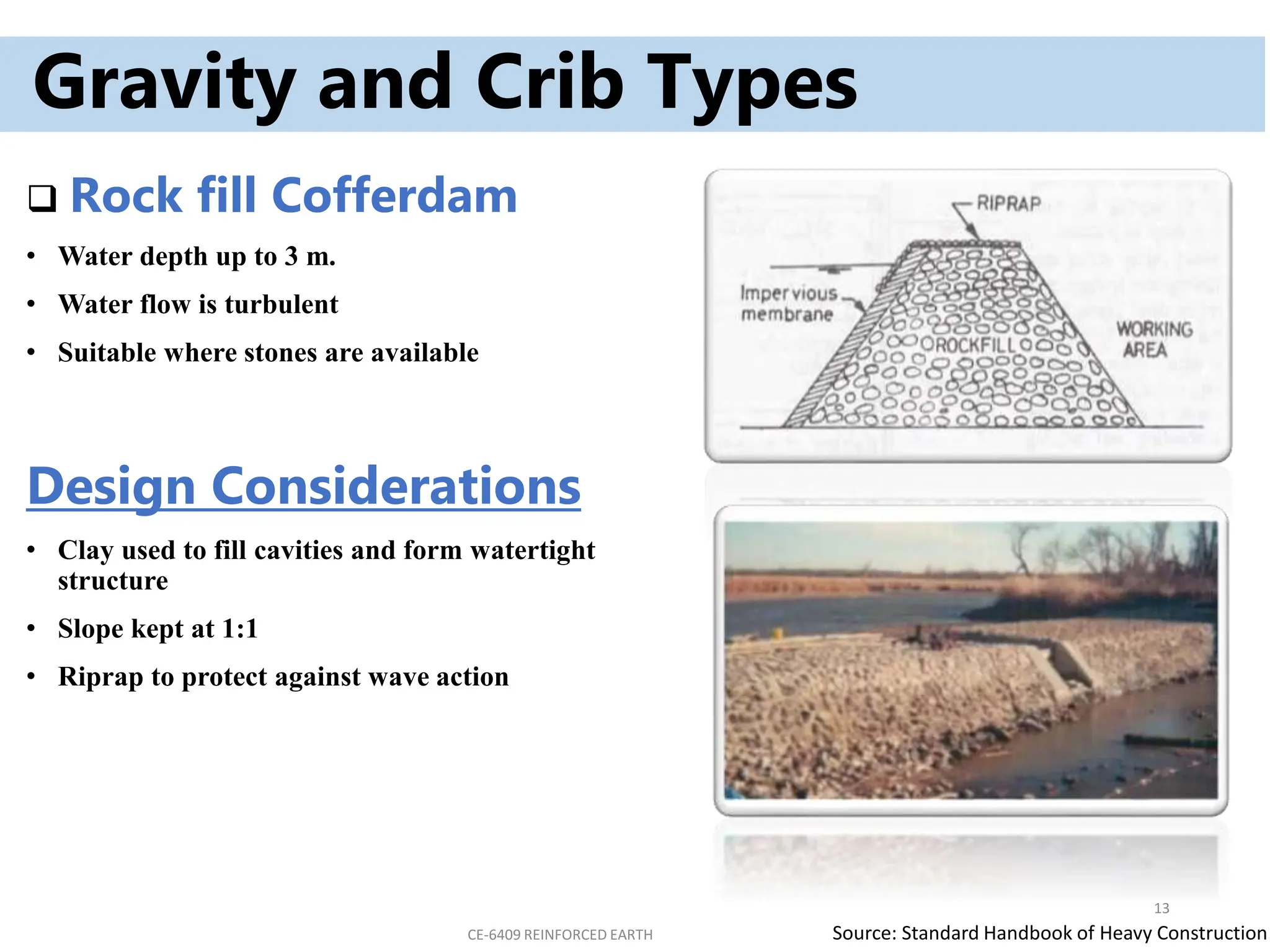
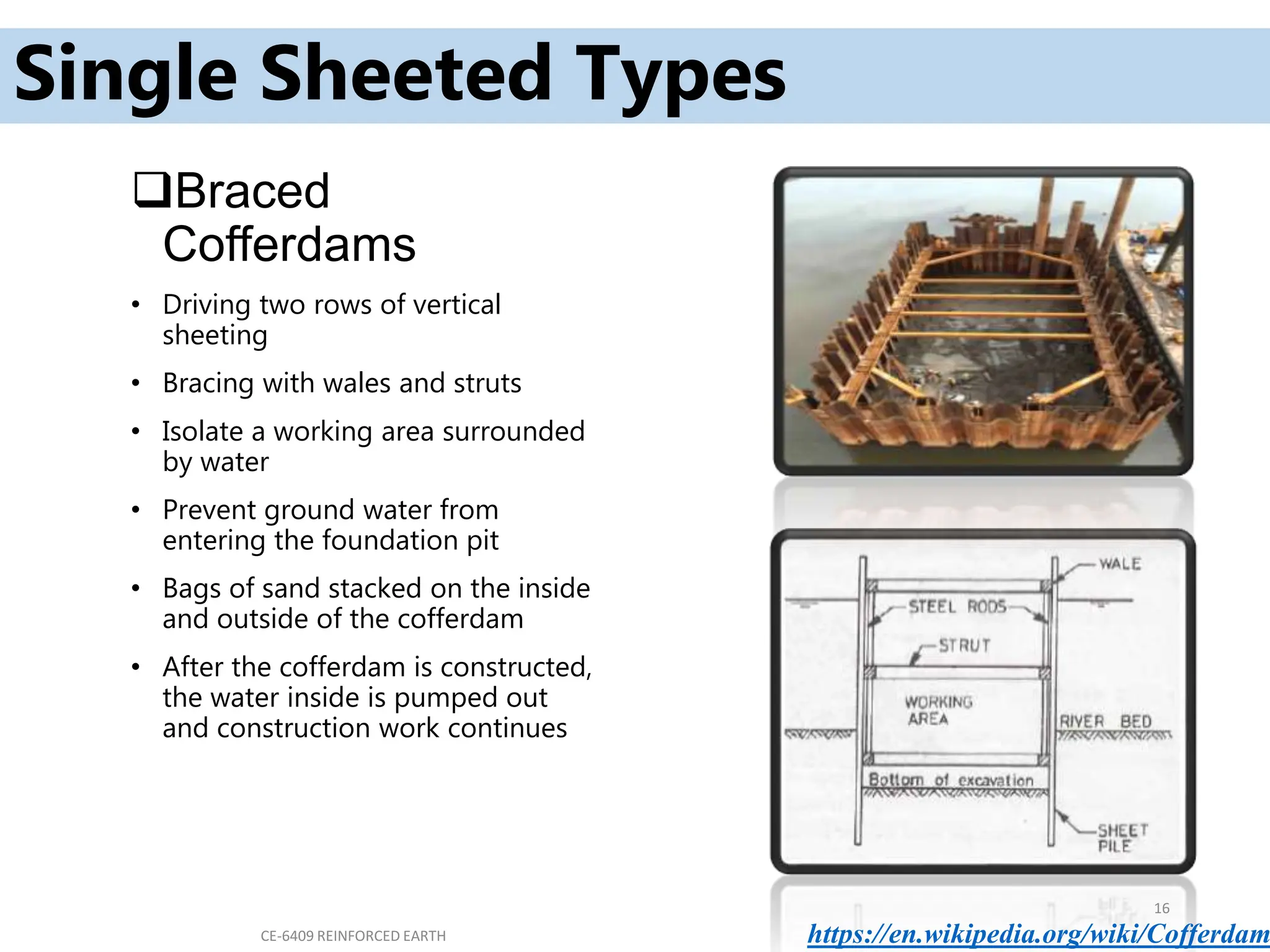
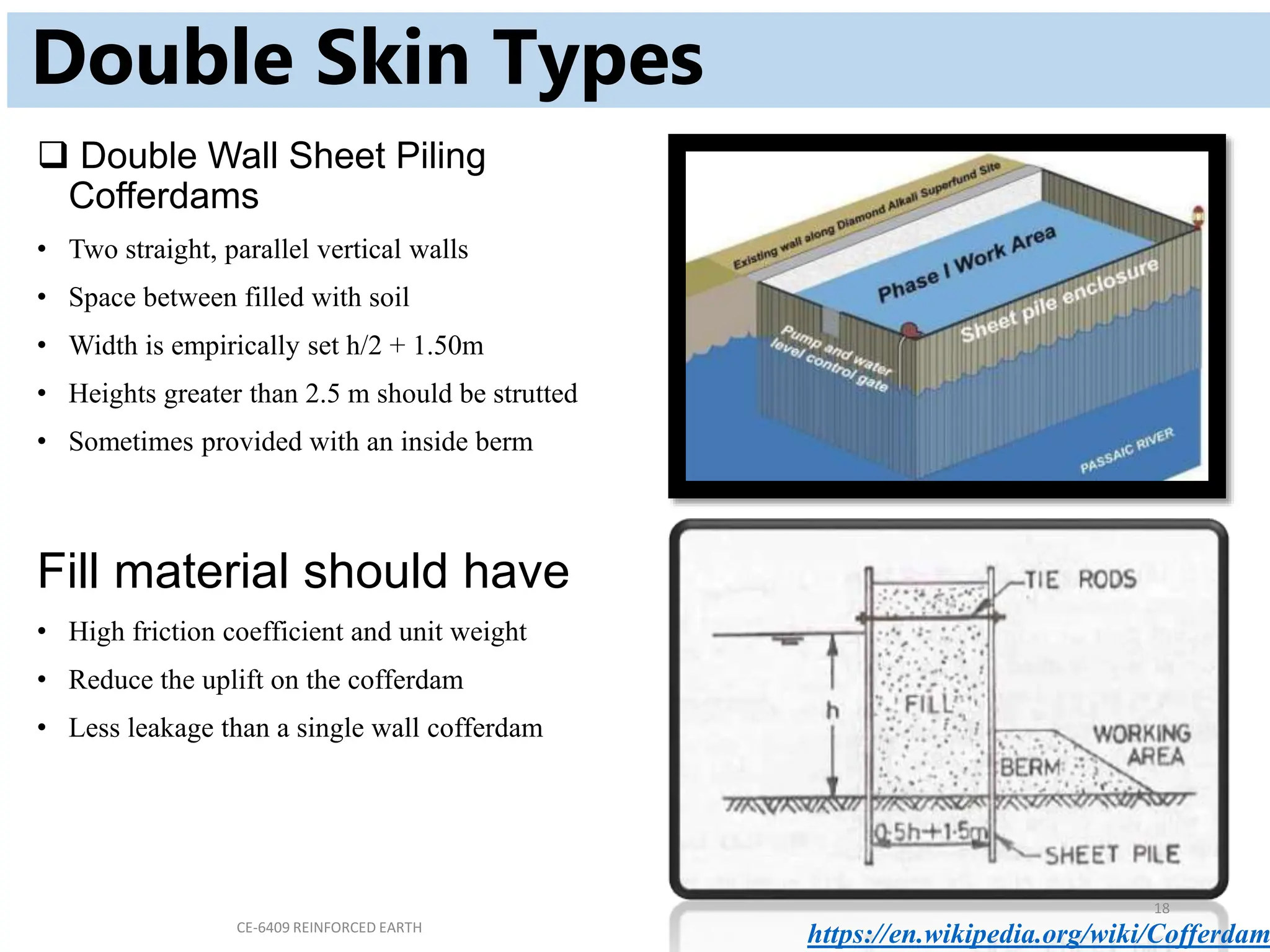
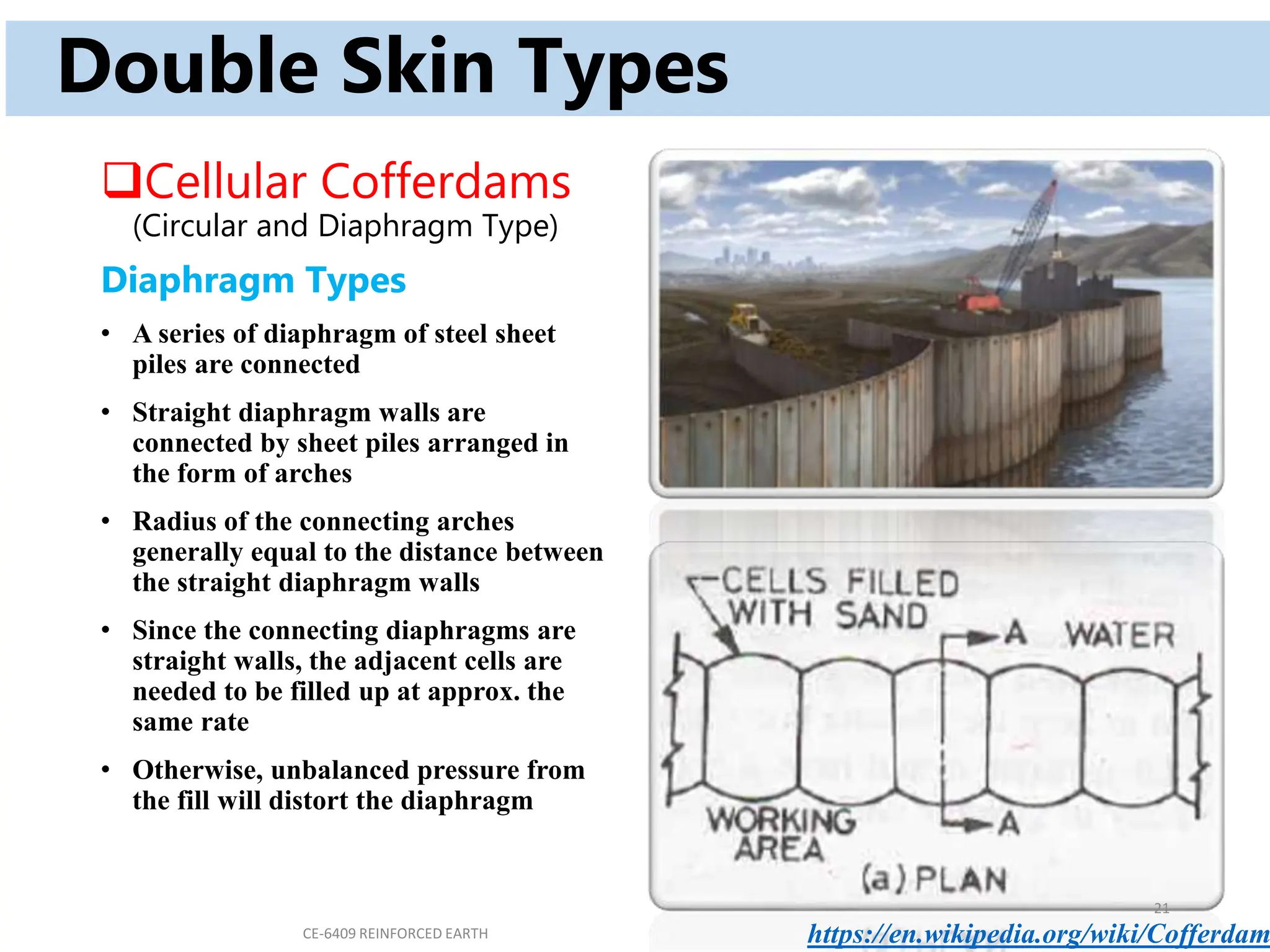
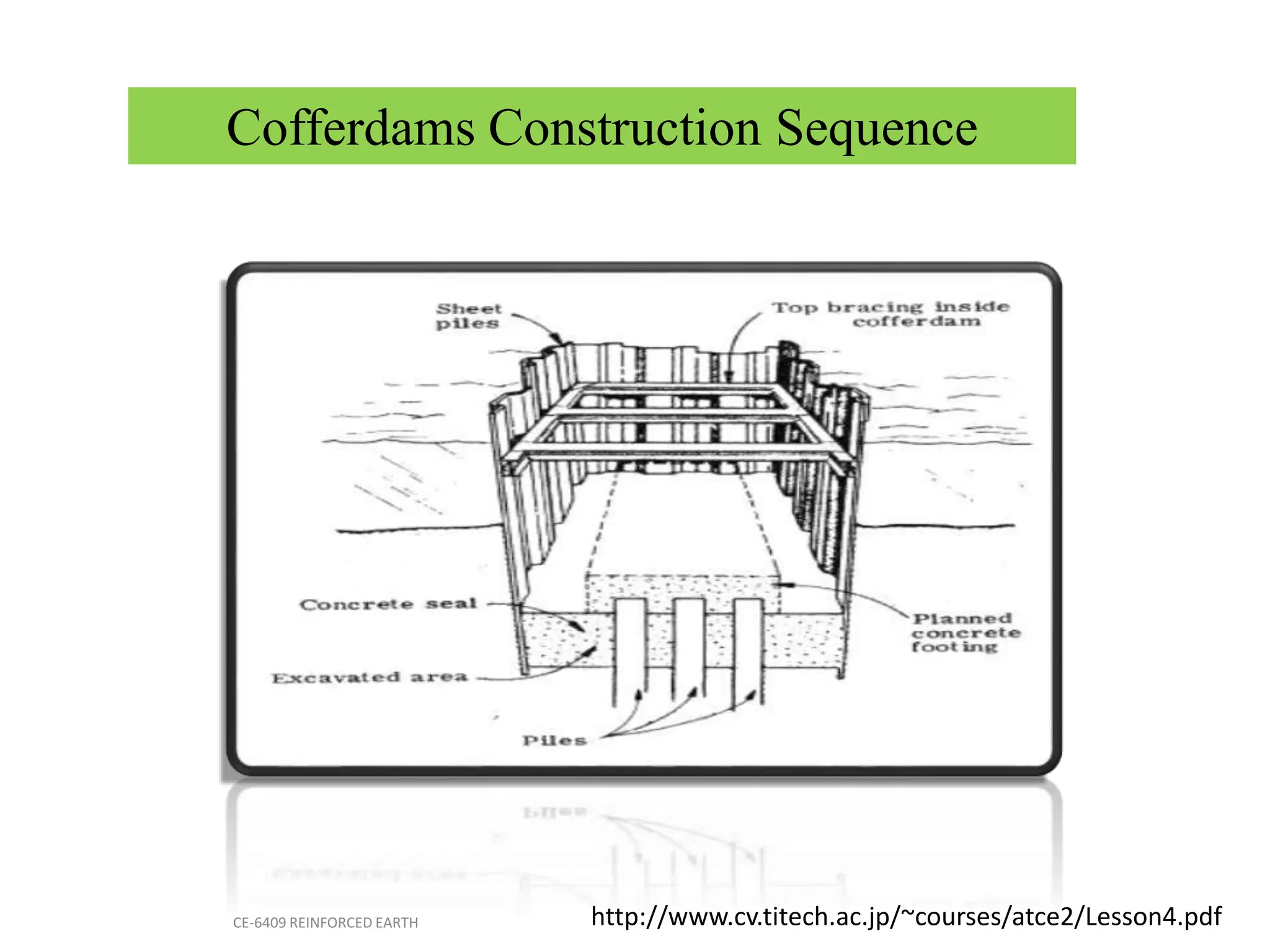
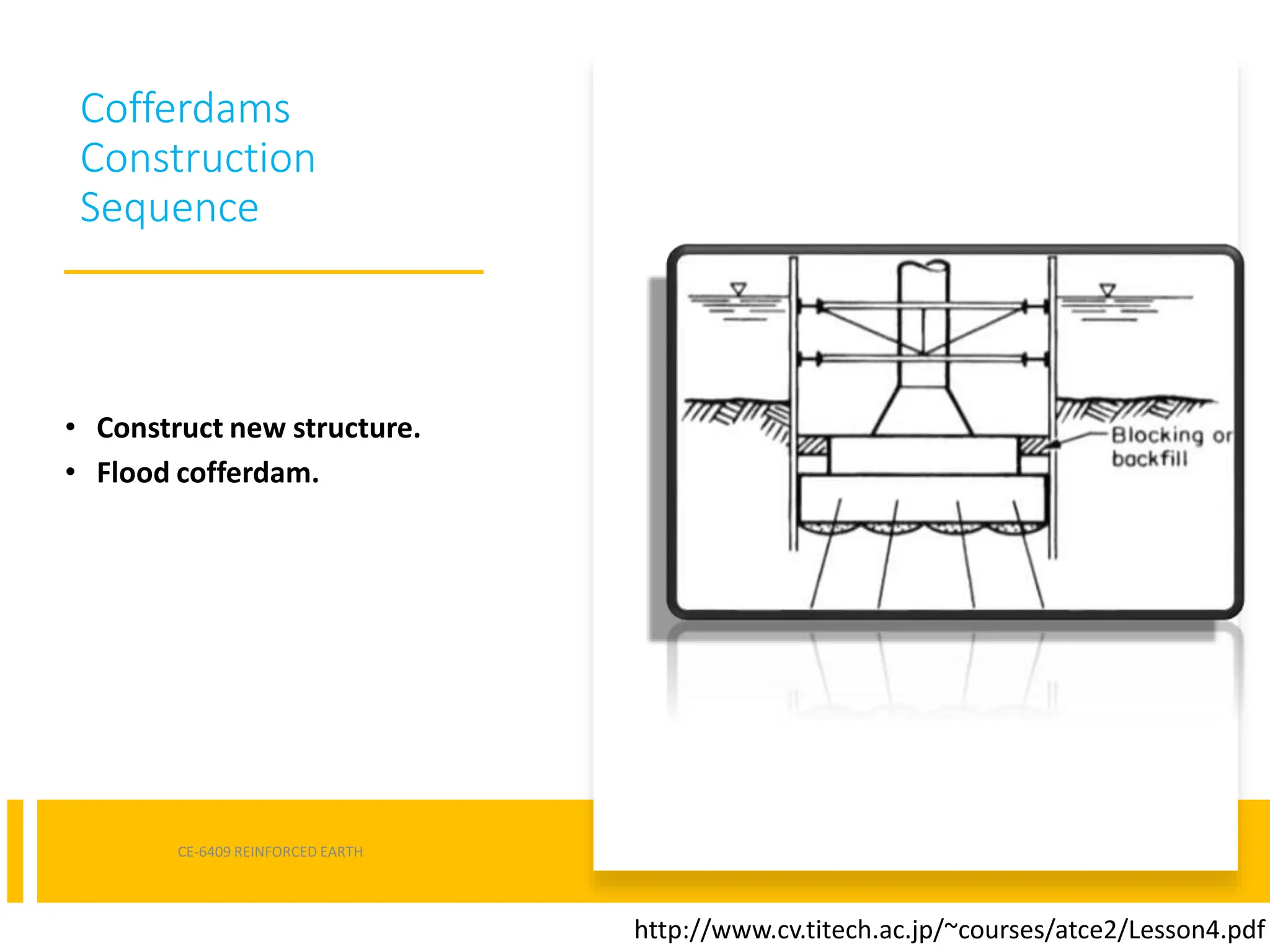
Cofferdams are temporary structures designed to allow construction in areas that would otherwise be submerged. There are several types of cofferdams including gravity, sheeted, and double-skin types. Gravity types use their mass to resist water pressure, while sheeted types use bracing and anchors. Double-skin types form cells using sheet piling. Selection depends on factors like water depth, site area, and soil/flow conditions. Construction involves installing sheet piles or cells, excavating inside, and pumping water before building the structure and removing the cofferdam.