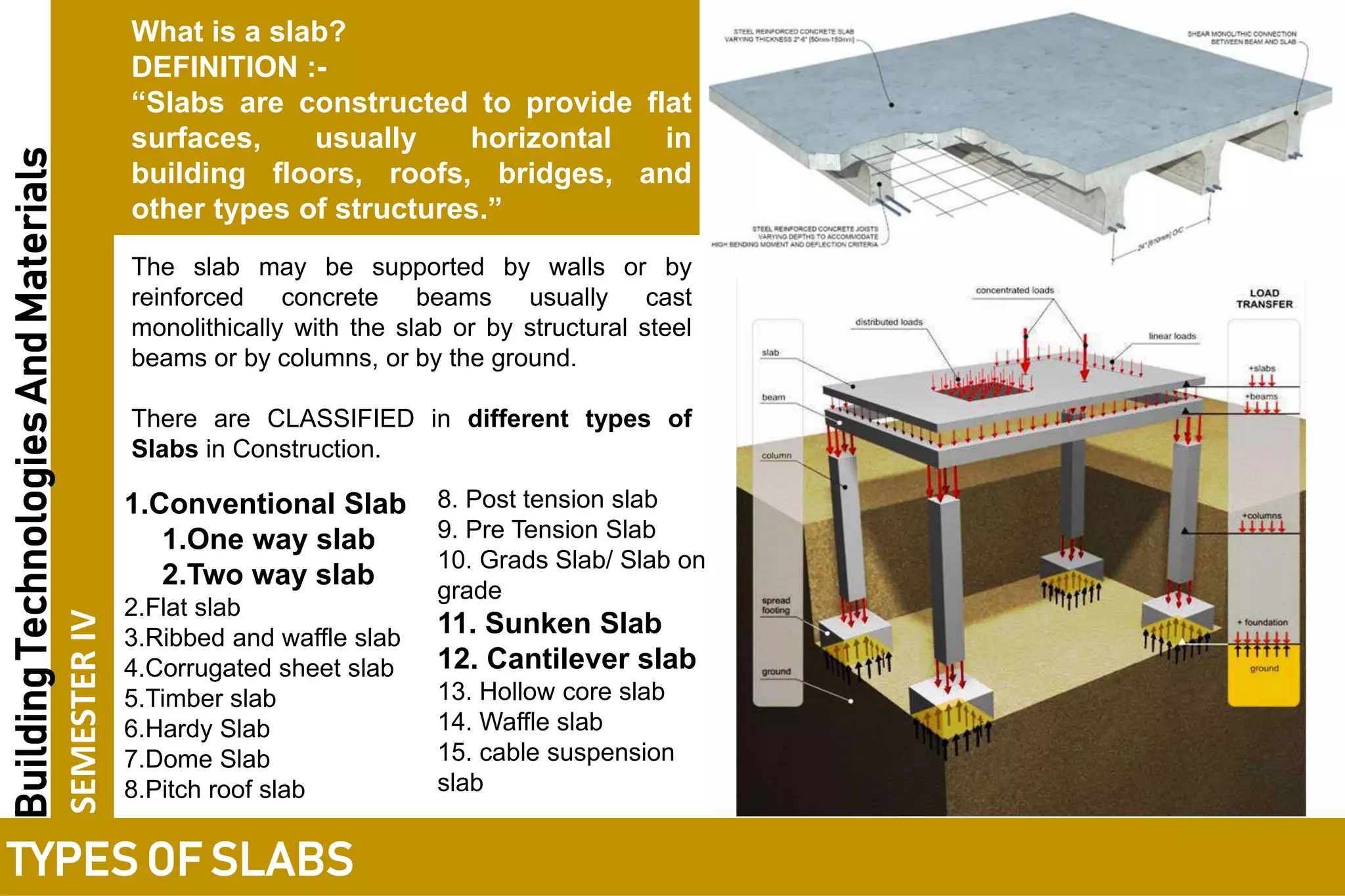
1. There are many types of slabs used in construction including conventional slabs, flat slabs, ribbed slabs, waffle slabs, corrugated sheet slabs, timber slabs, and more.
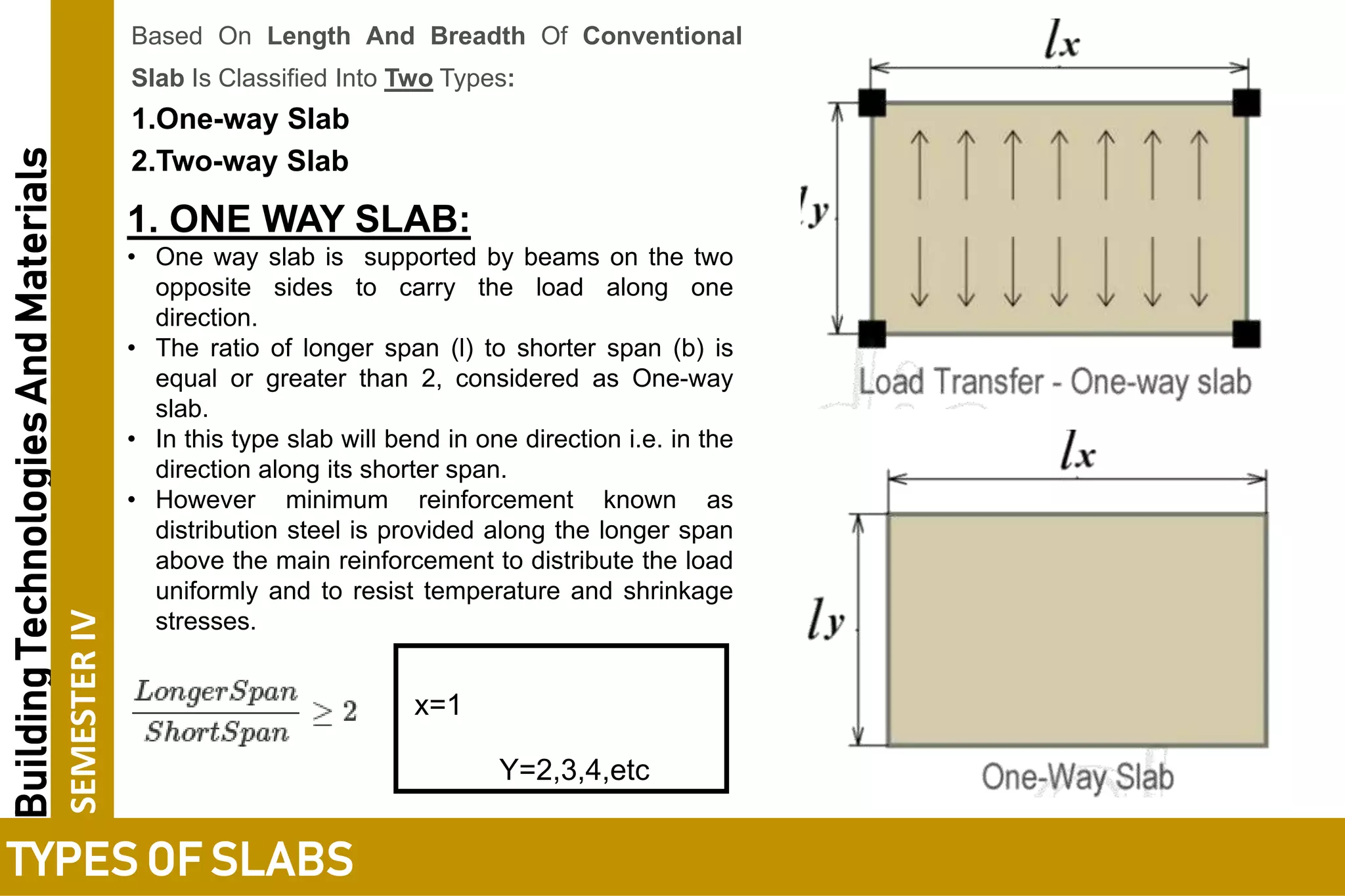
2. Conventional slabs are classified as one-way or two-way slabs depending on their length to width ratio and the direction of load transfer.
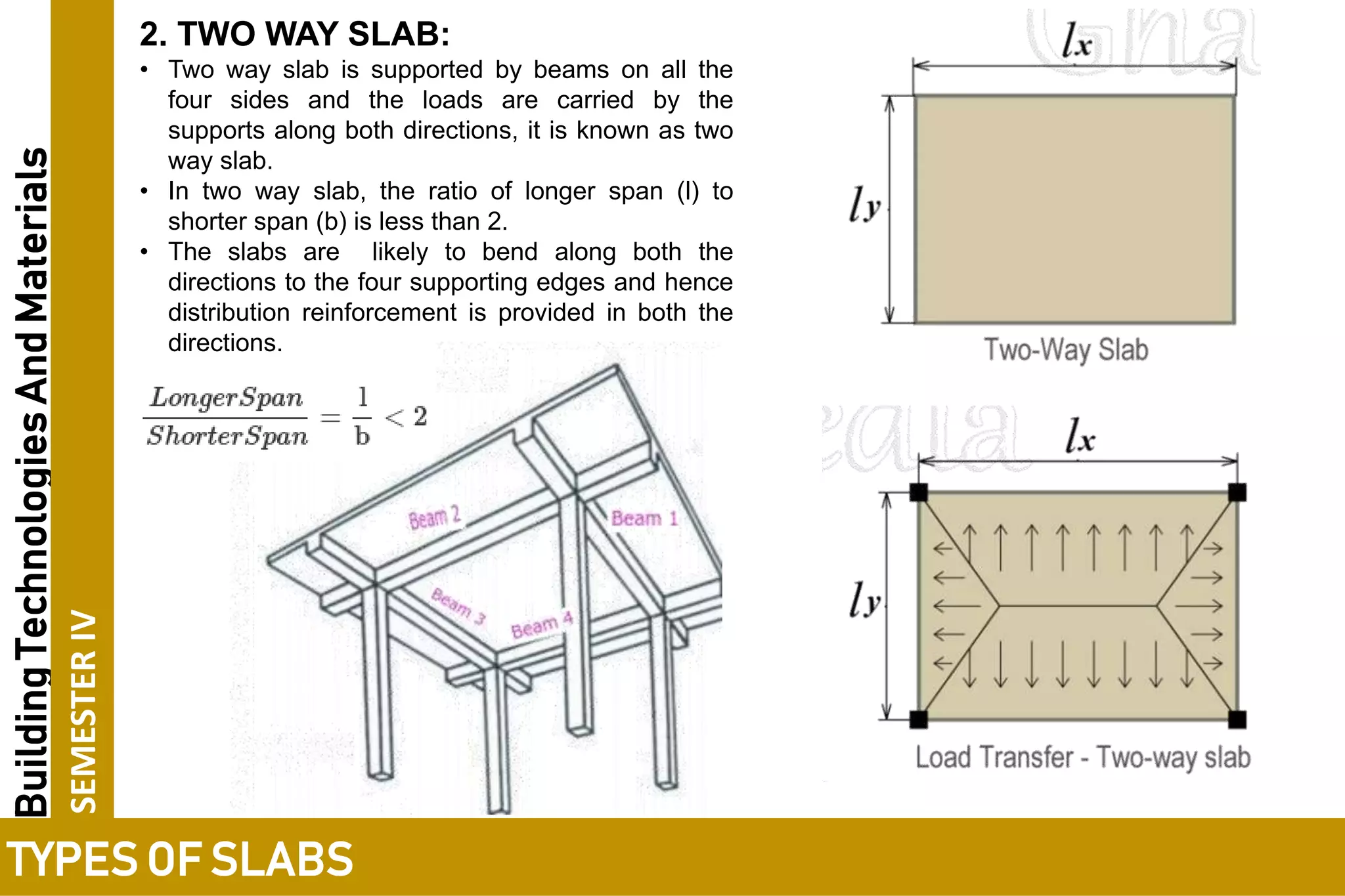
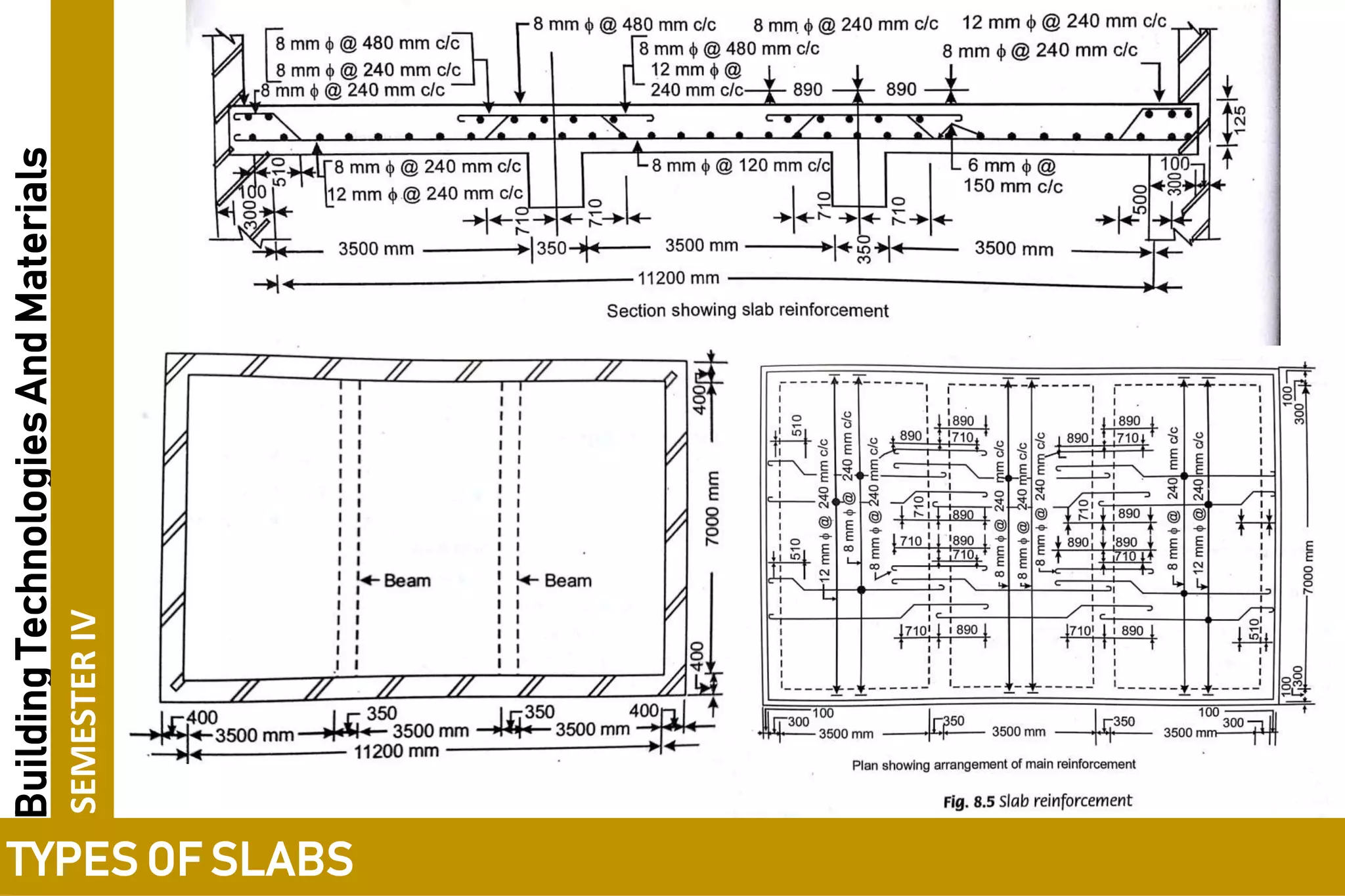
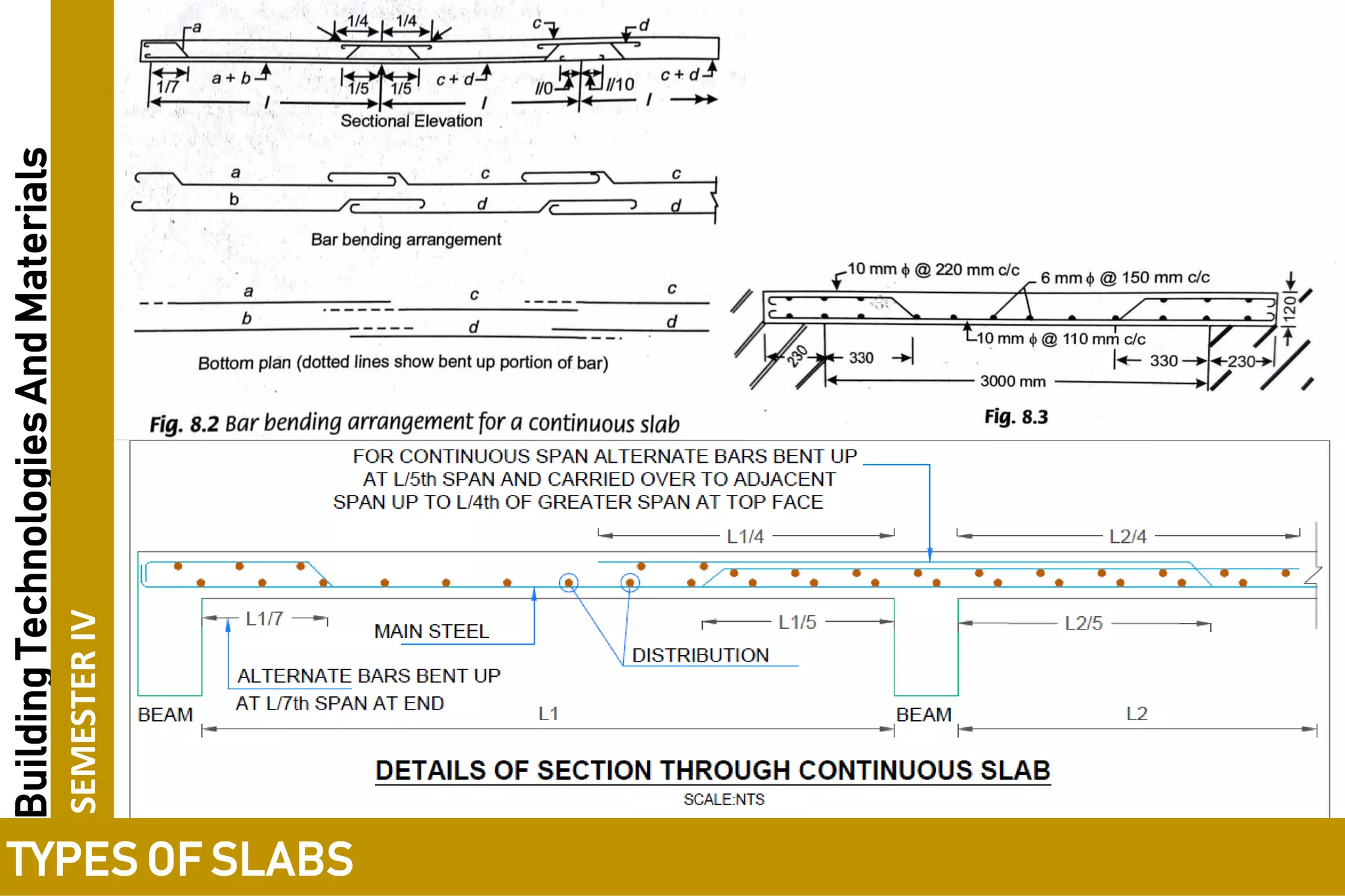
3. One-way slabs have a length to width ratio of 2 or greater and transfer load along the shorter span, while two-way slabs have a ratio of less than 2 and transfer load along both spans.