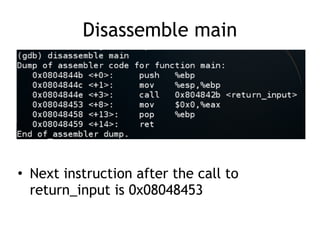
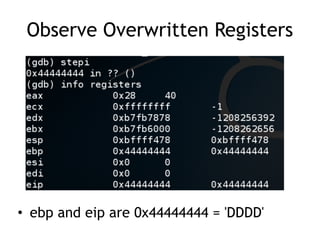
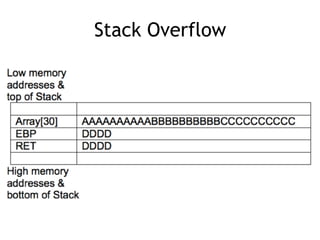
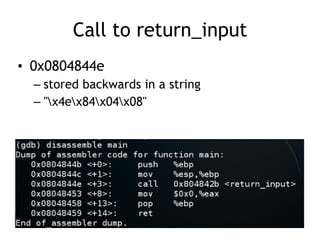
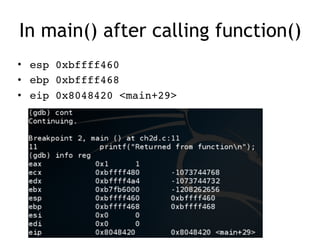
The document discusses stack-based buffer overflows in Linux, detailing the mechanics and significance of this exploitation method, which is one of the most well-understood. It includes examples of using the GNU debugger (gdb) to illustrate how memory can be manipulated and how functions interact with the stack. The text emphasizes the stack's role in efficient function calls and provides a walkthrough of exploiting buffer overflows and controlling the instruction pointer (EIP).


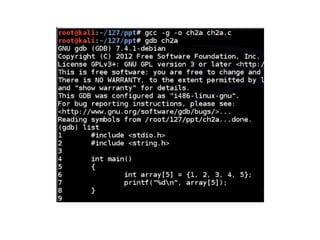
![C and C++ Lack Bounds-Checking
• It is the programmer's responsibility to ensure
that array indices remain in the valid range
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
int array[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
printf("%dn", array[5]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch2-170127044459/85/CNIT-127-Ch-2-Stack-overflows-on-Linux-3-320.jpg)


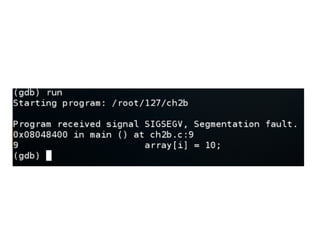
![Reading Past End of Array
• array[5] = 0xb7fb63c4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch2-170127044459/85/CNIT-127-Ch-2-Stack-overflows-on-Linux-7-320.jpg)





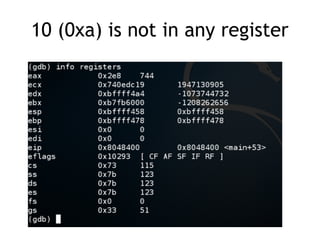

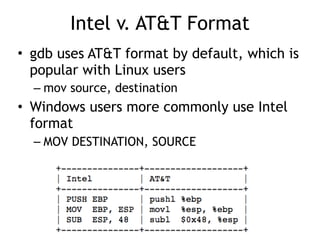



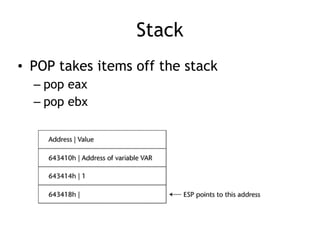
![EBP (Extended Base Pointer)
• EBP is typically used for calculated
addresses on the stack
– mov eax, [ebp+10h]
• Copies the data 16 bytes down the stack
into the EAX register](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch2-170127044459/85/CNIT-127-Ch-2-Stack-overflows-on-Linux-22-320.jpg)




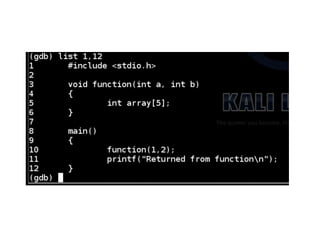


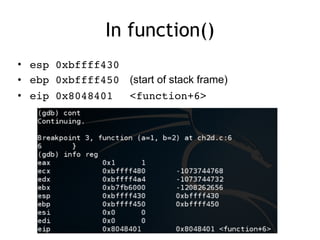

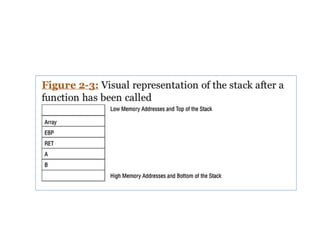

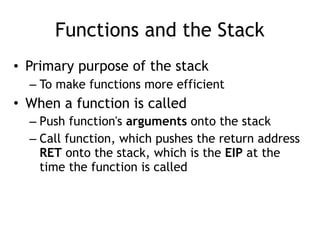

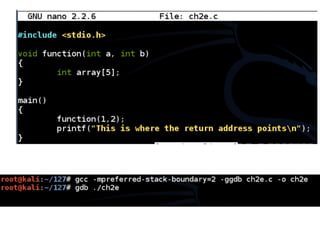
![Functions and the Stack
#include <stdio.h>
void function(int a, int b)
{
int array[5];
}
main()
{
function(1,2);
printf("This is where the
return address pointsn");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch2-170127044459/85/CNIT-127-Ch-2-Stack-overflows-on-Linux-37-320.jpg)