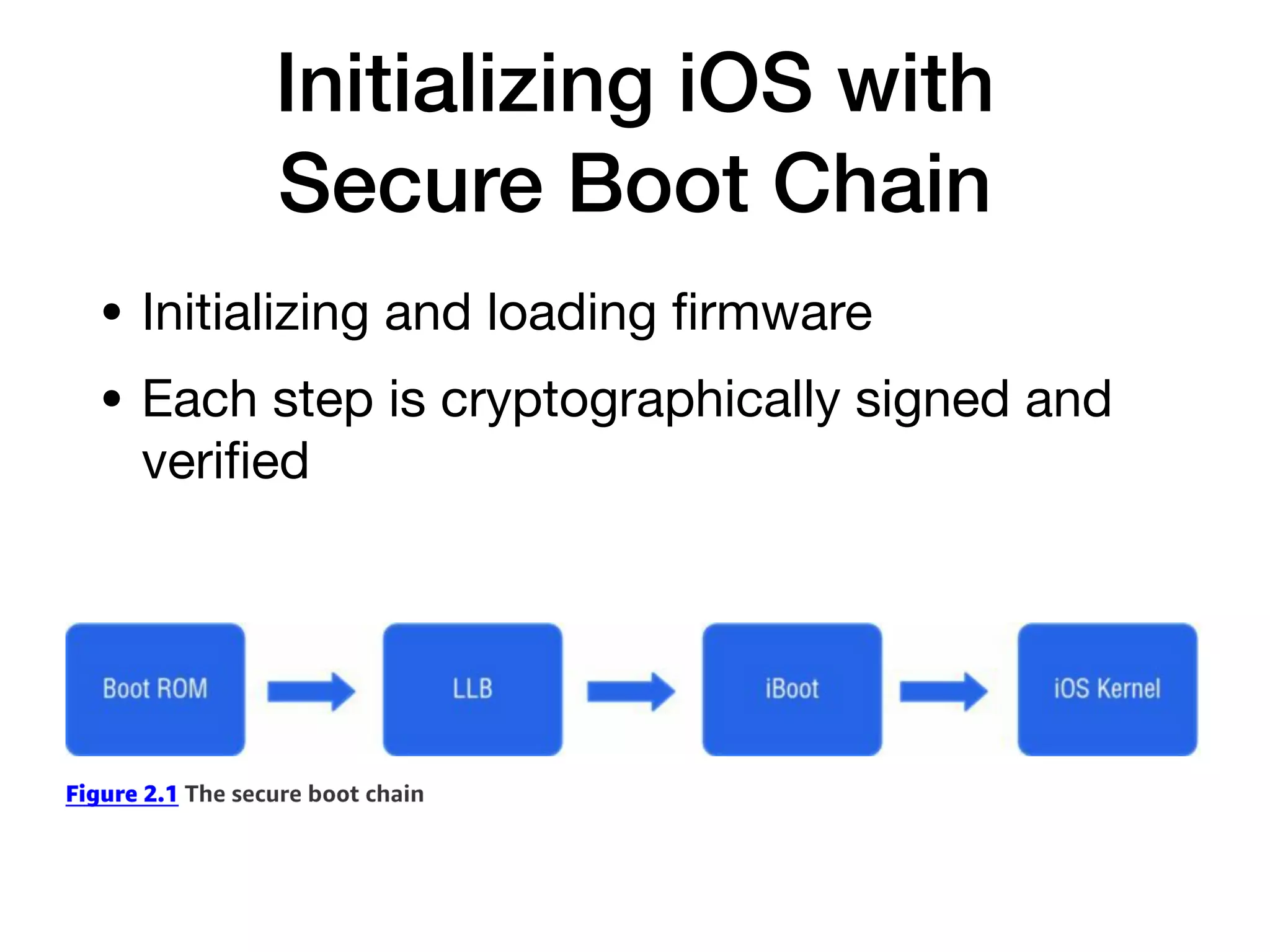
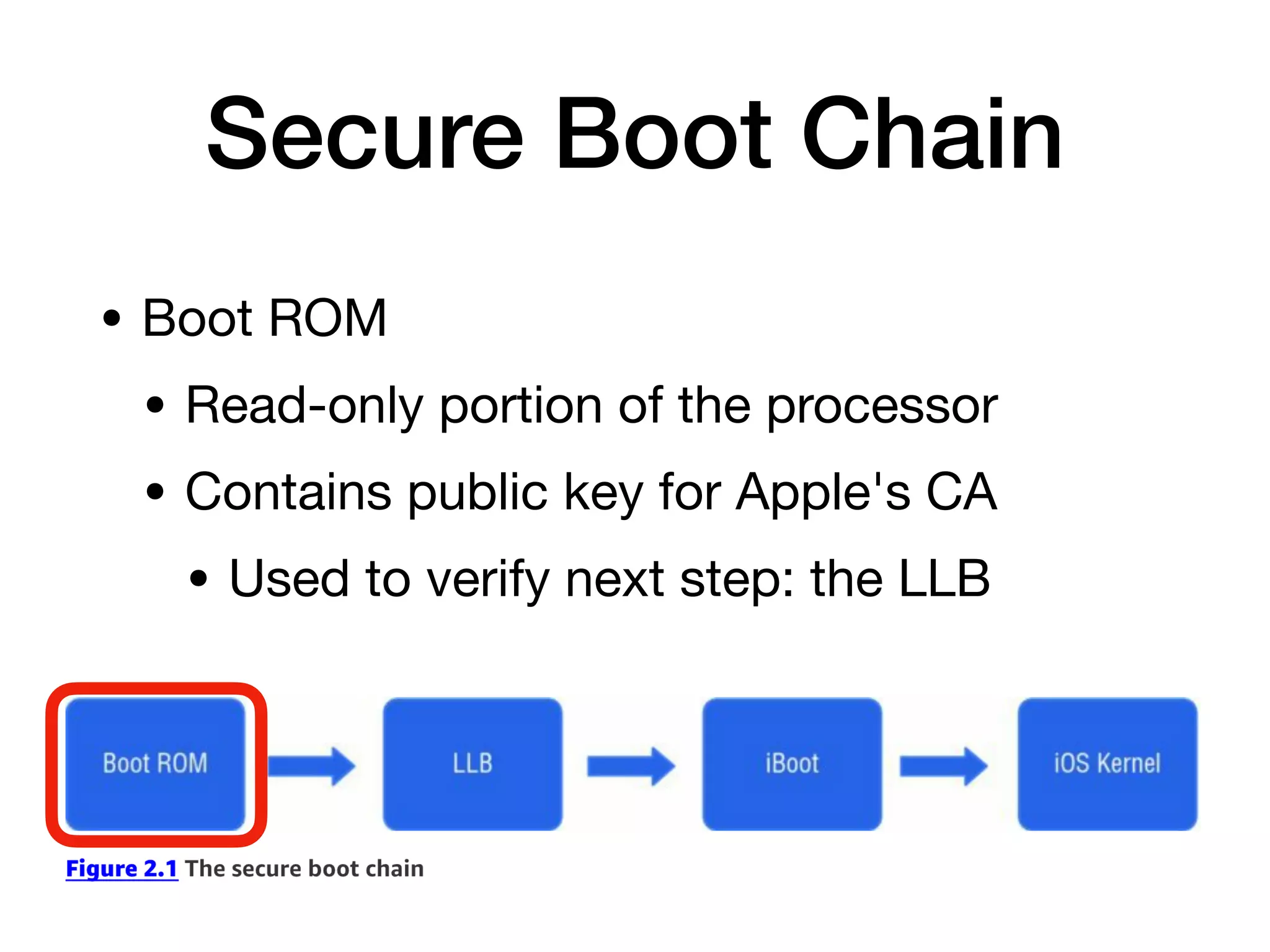
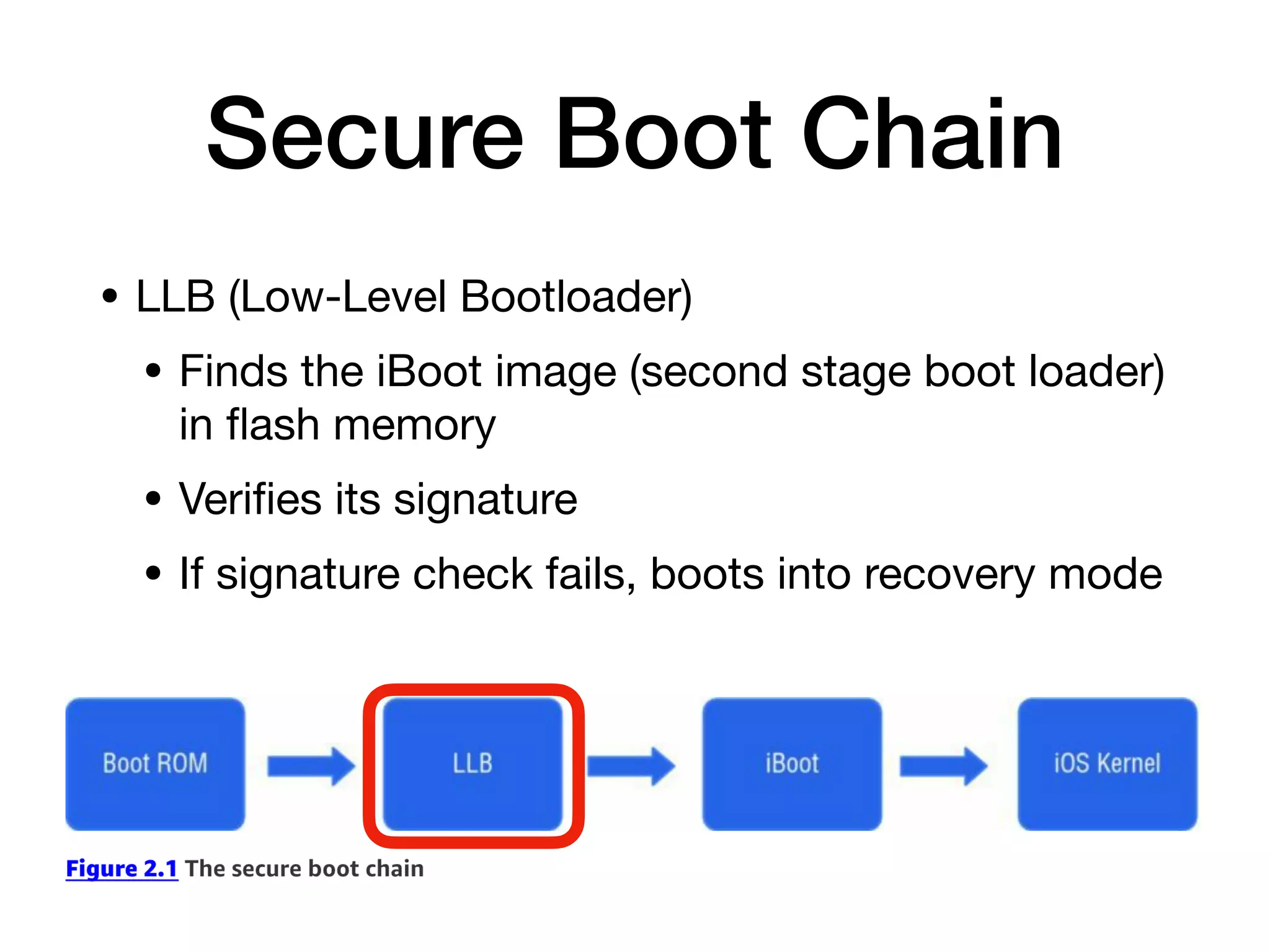
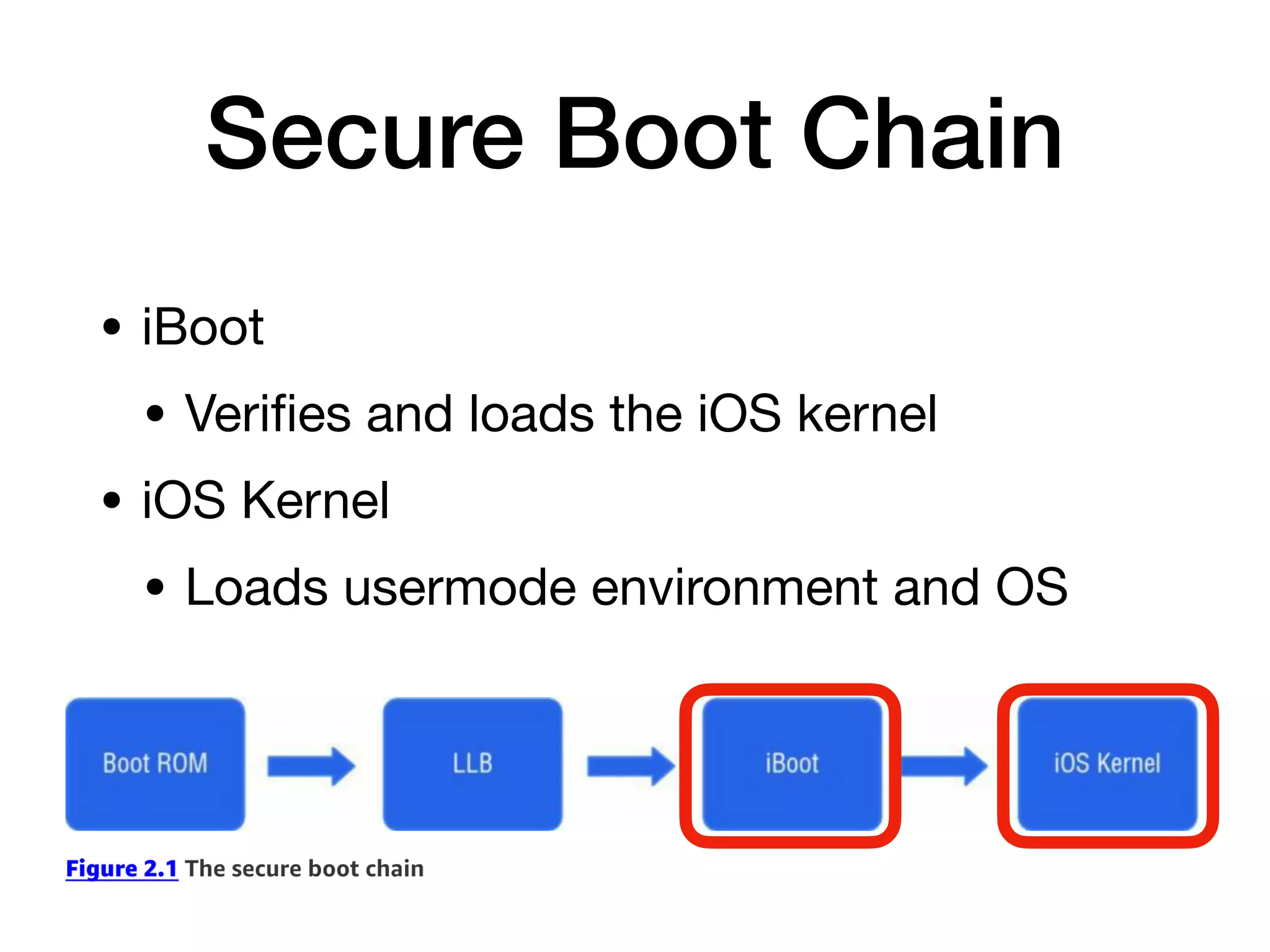
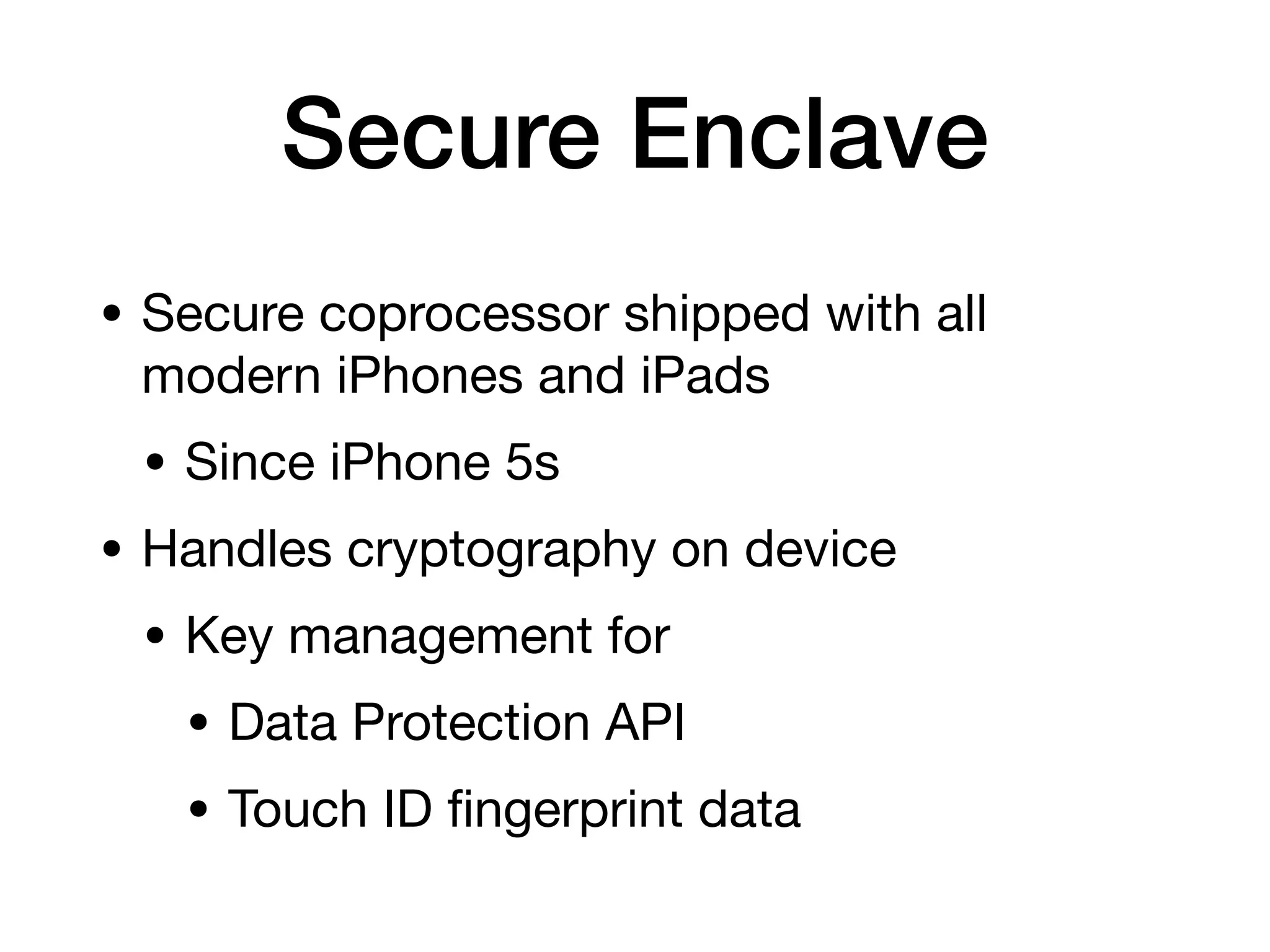
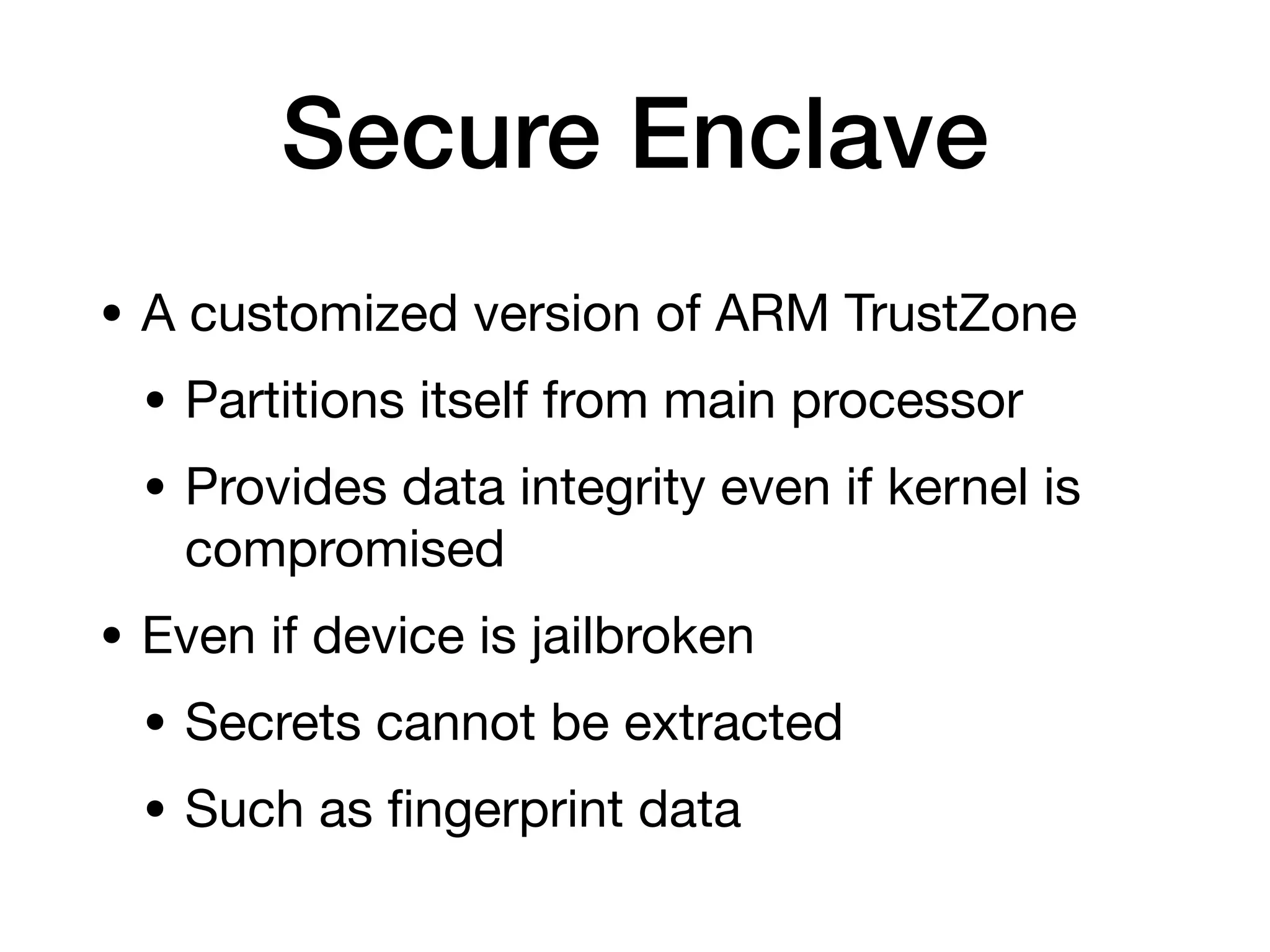
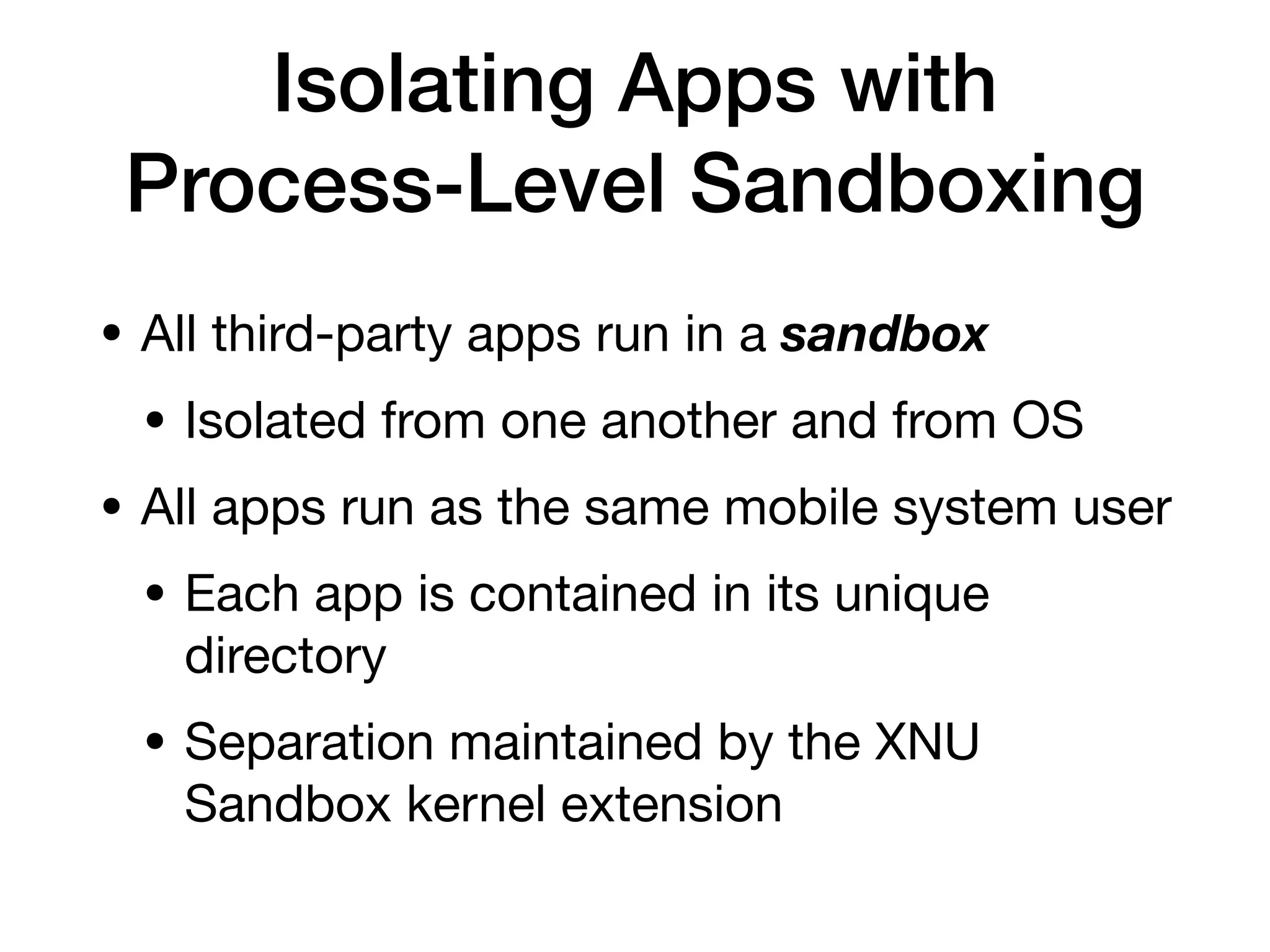
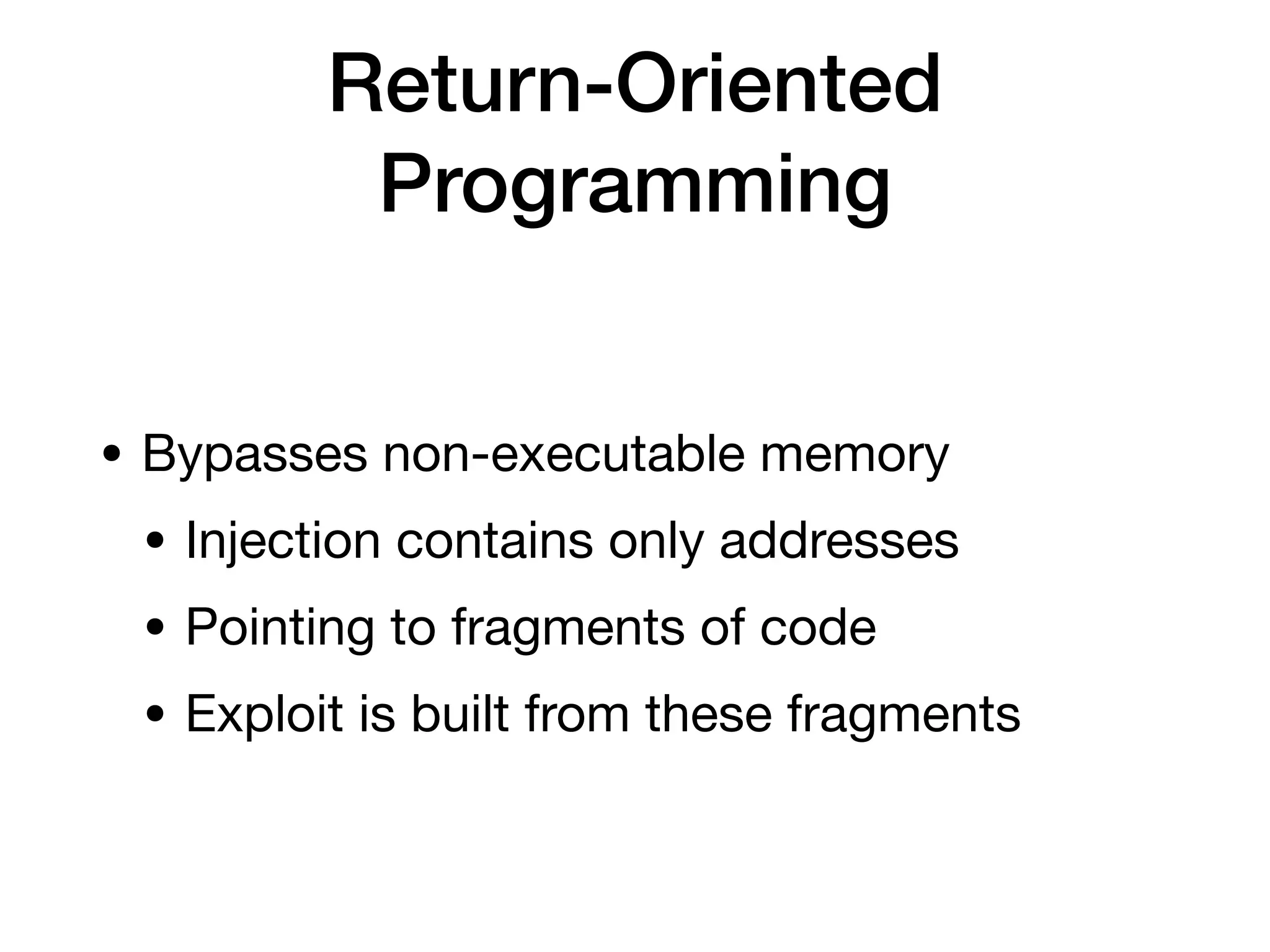
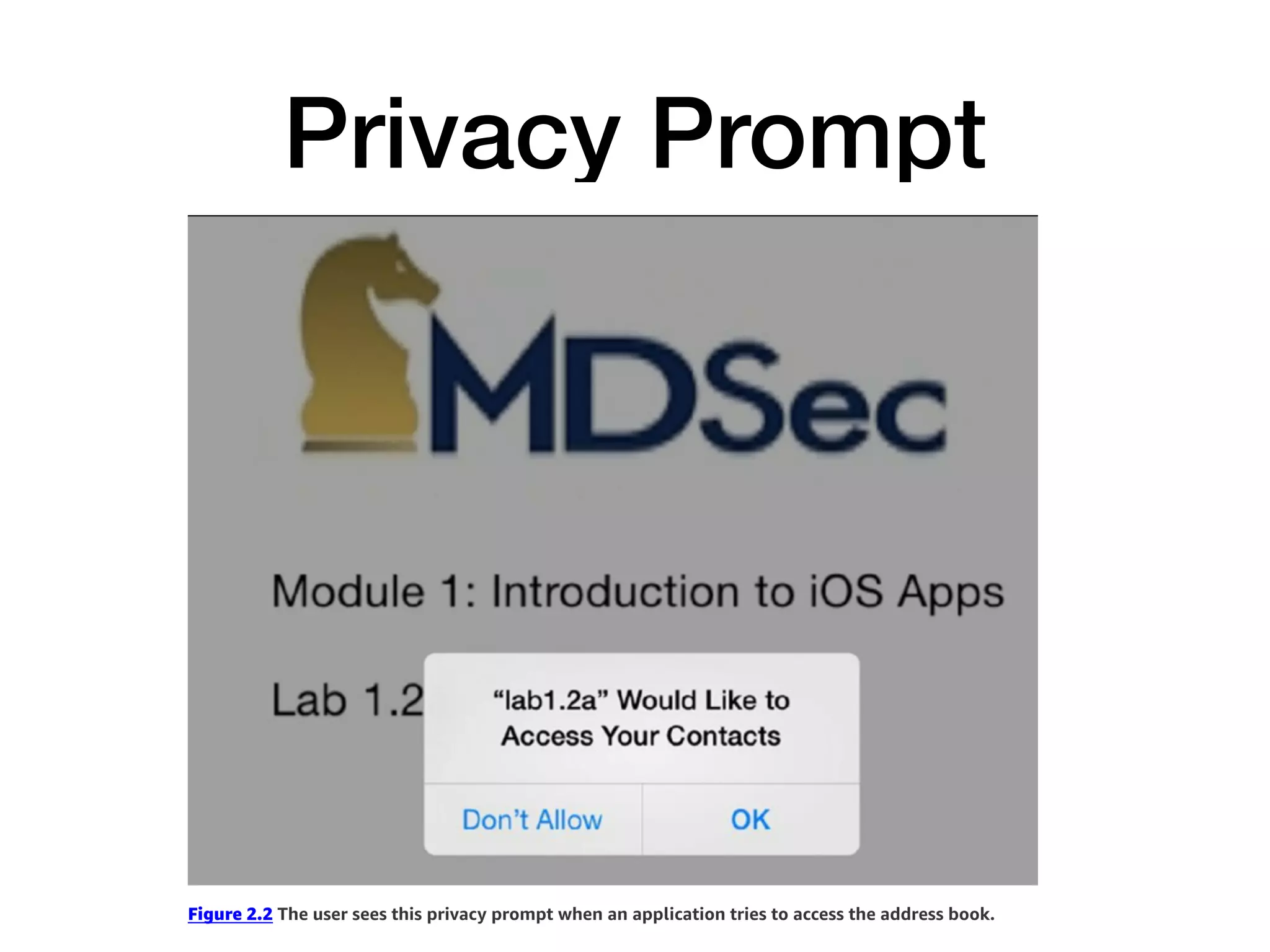
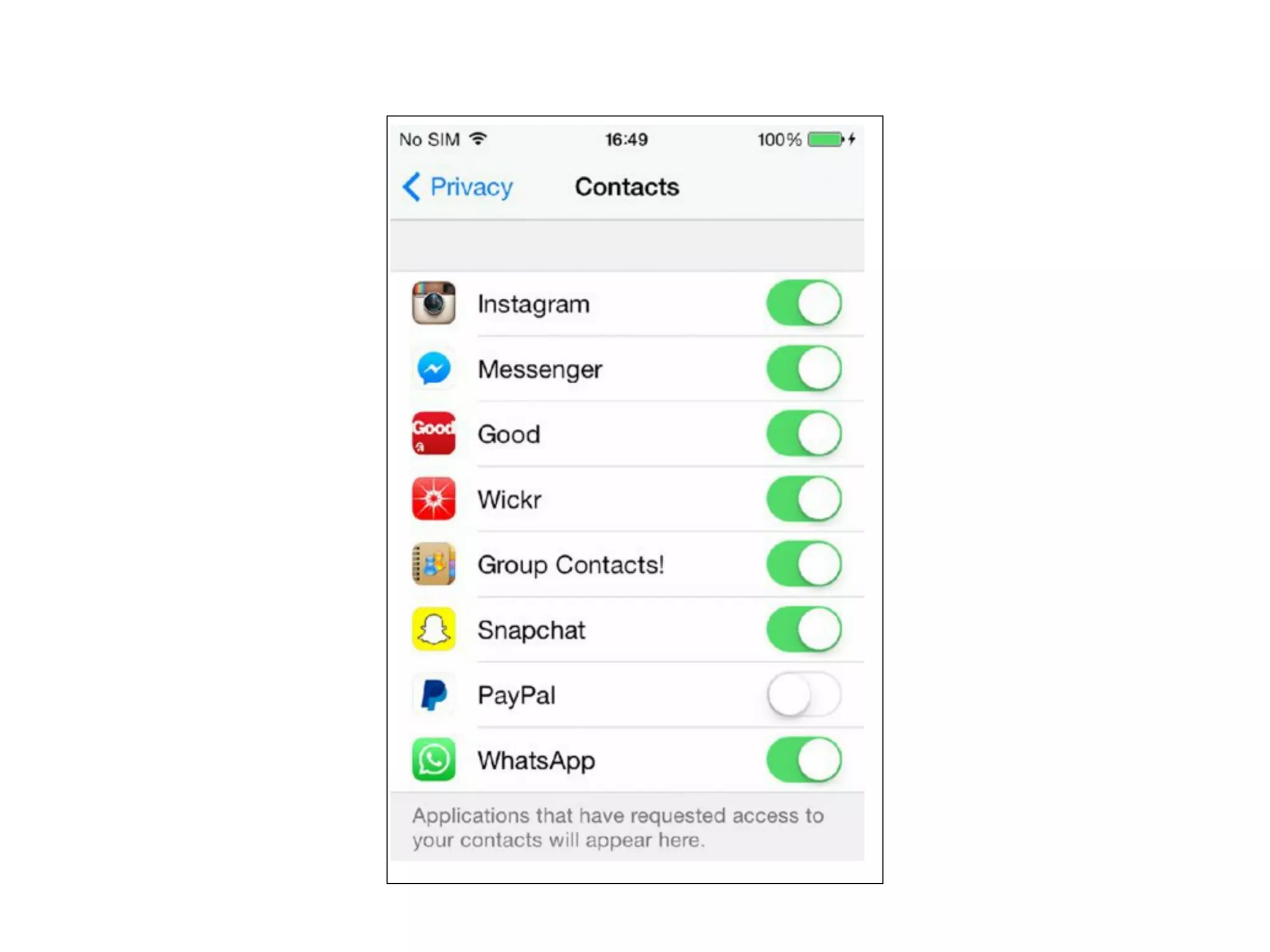
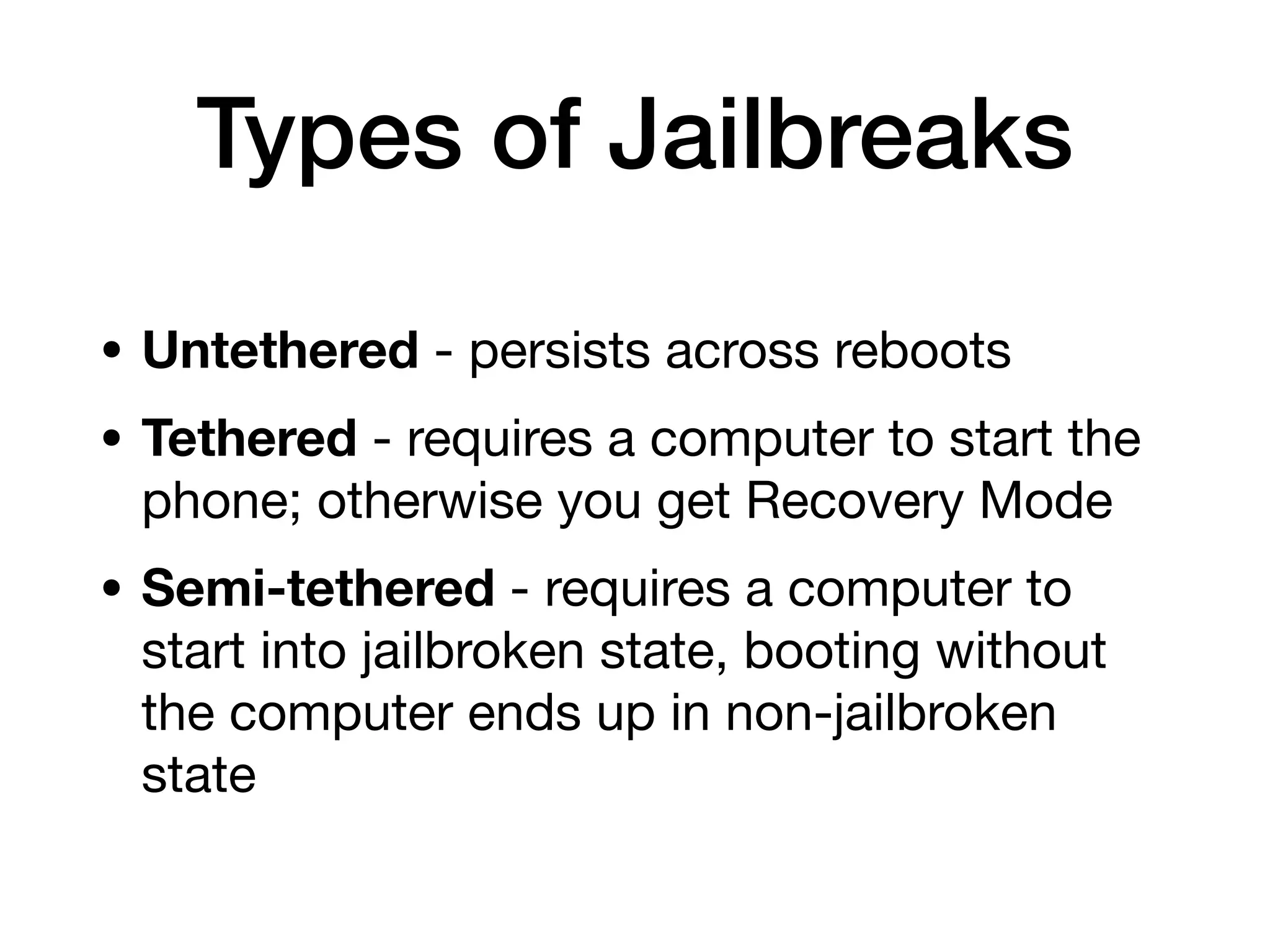
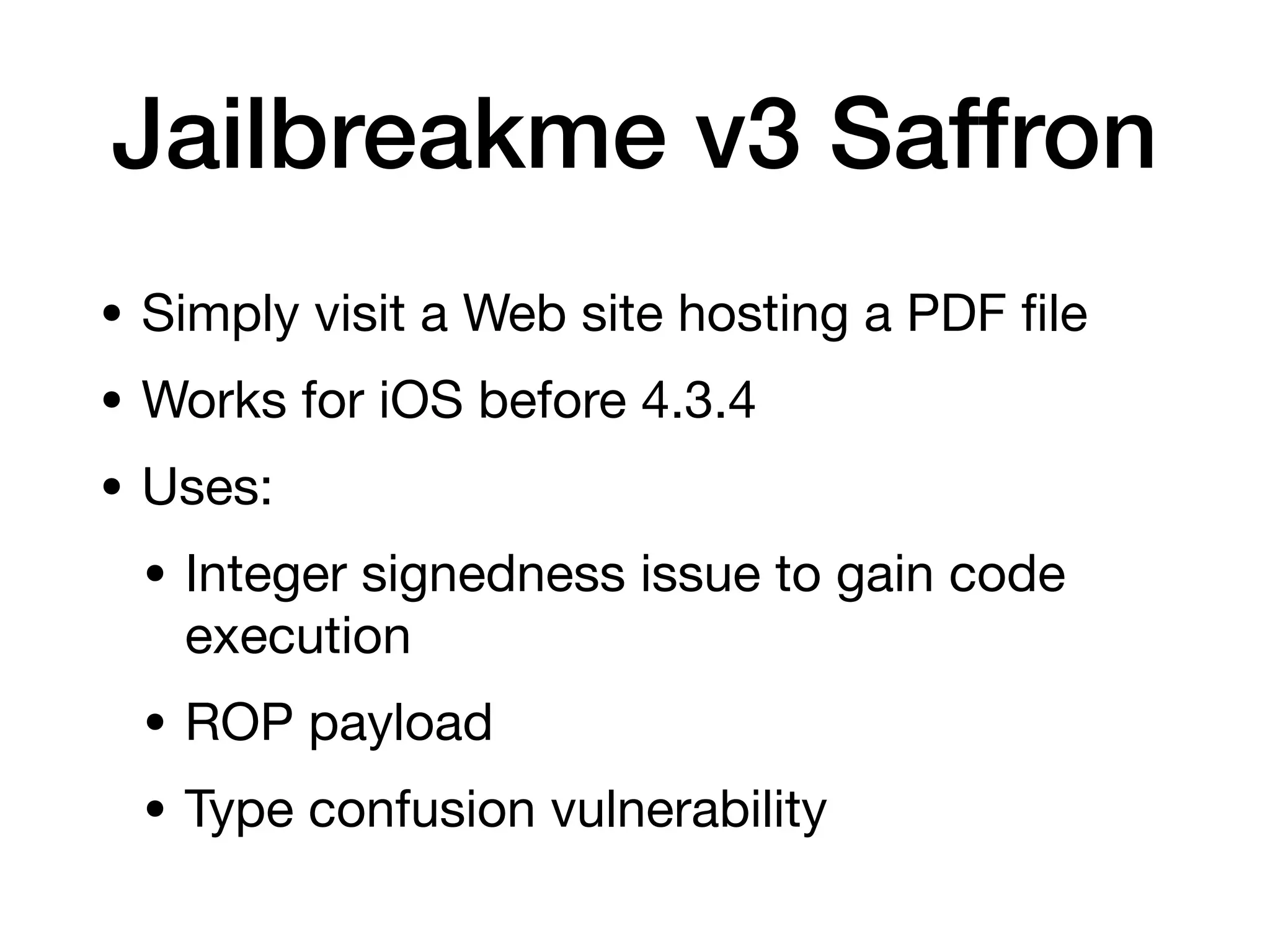
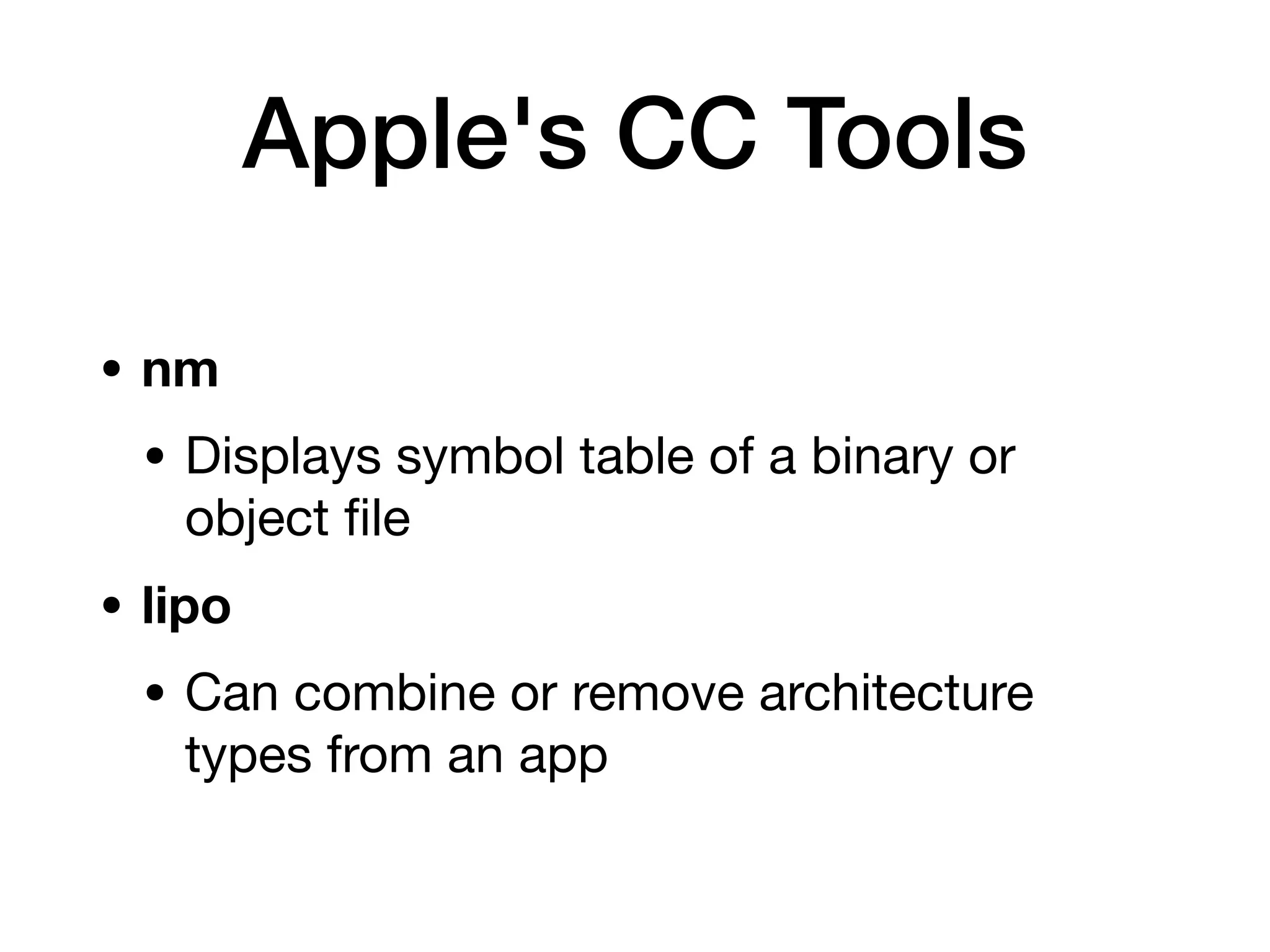
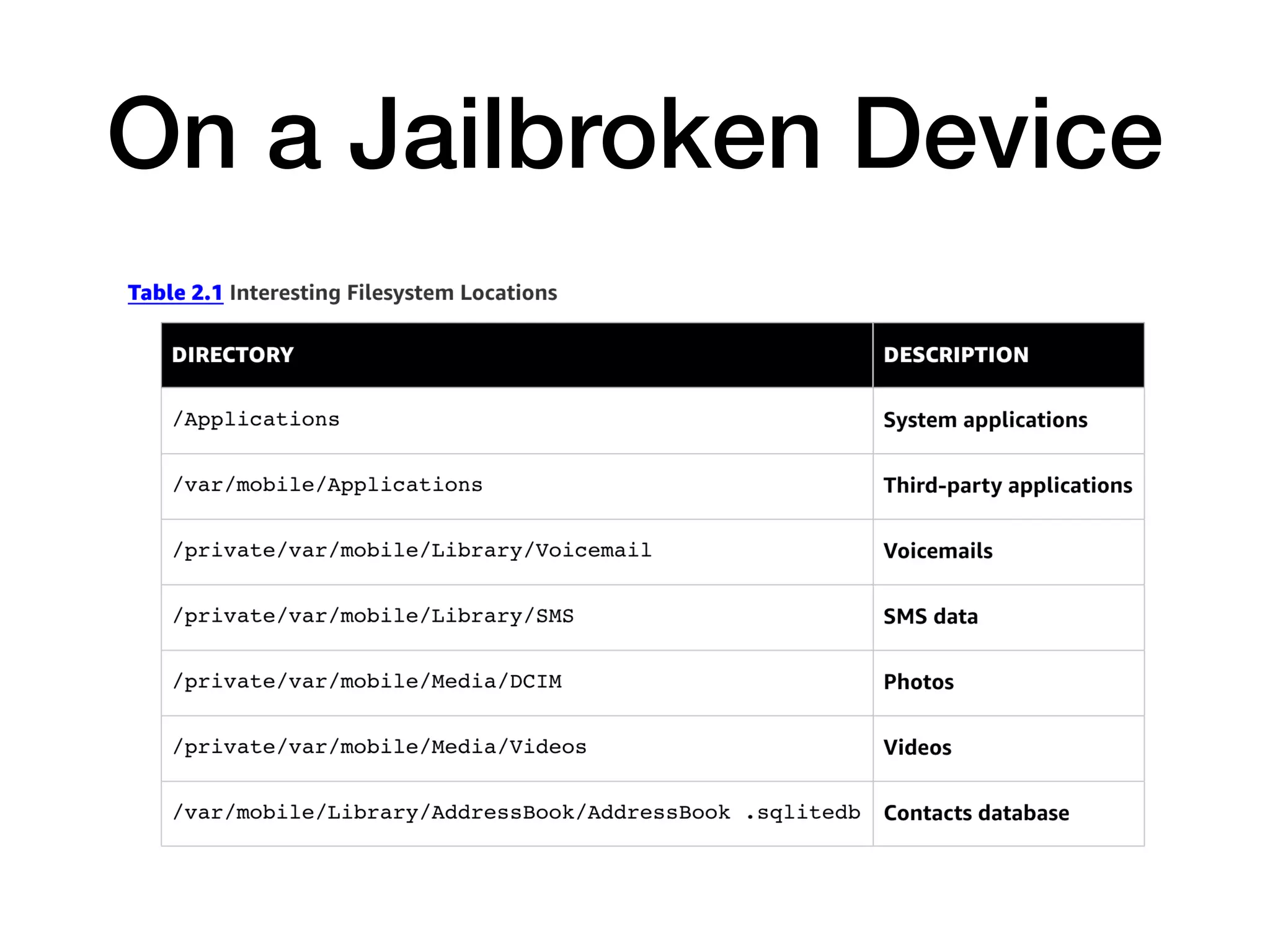
This document provides an overview of analyzing iOS apps, including jailbreaking mobile devices. It discusses iOS security features like code signing and sandboxing. It explains how to set up a test environment for analyzing apps by jailbreaking a device and using Unix tools. Key files like property lists and databases that can be explored are also outlined.