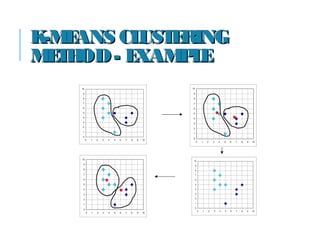
Cluster analysis is used to group objects that are similar to each other within the same cluster and dissimilar to objects in other clusters. It has various applications in marketing, land use, insurance, and city planning. There are different types of data that can be used for cluster analysis, including interval-scaled, binary, ordinal, and ratio variables. Major clustering methods include partitioning methods like k-means clustering and hierarchical clustering. K-means clustering partitions objects into k clusters by assigning objects to the cluster with the nearest centroid.