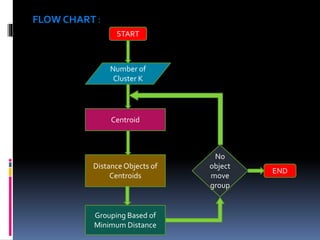
This document discusses K-means clustering, an unsupervised machine learning algorithm. It begins with an introduction to clustering and describes K-means clustering as assigning data points to K number of centroids, or cluster centers. The document outlines the K-means clustering procedure, which iteratively assigns data points to the closest centroid and recomputes centroids until centroids do not change. Advantages include faster computation than hierarchical clustering for large datasets, while disadvantages include difficulty selecting the optimal K value. Applications include wireless sensor networks, city planning, search engines, and email filtering.