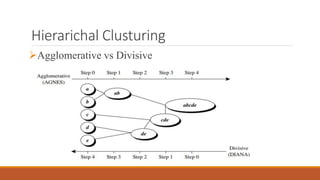
Cluster analysis is a technique used to classify objects into groups called clusters based on their similarities. It has many applications in areas like market research, biology, and image processing. There are different types of clustering methods like partitioning, hierarchical, density-based, and grid-based. The k-means algorithm is a commonly used partitioning method where objects are grouped into k clusters based on their distances from centroid points, which are recalculated in each iteration until cluster memberships stabilize. Cluster analysis helps discover patterns and insights from large datasets.