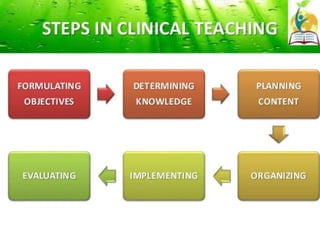
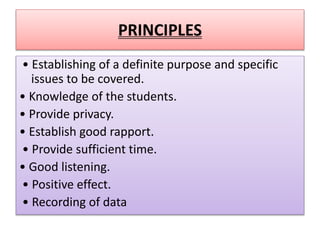
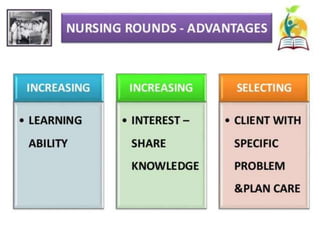
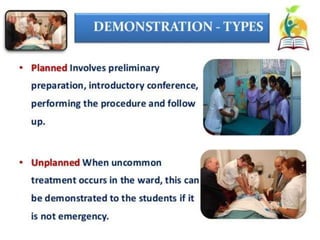
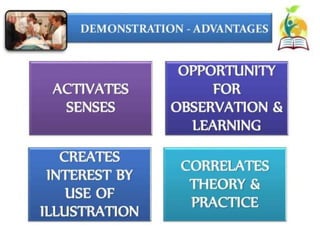
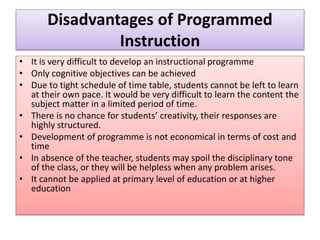
This document discusses clinical teaching methods in nursing. It provides information on essentials for good clinical instruction such as selecting clinical areas that allow students to practice high standards of nursing care. The principles of clinical instruction are establishing clear purpose and issues to be covered, knowing students, providing privacy and time, and having good listening skills. The functions of clinical instructors include setting objectives and standards, developing evaluation tools, and assisting with patient care. Qualities of good clinical instructors are enjoying bedside nursing and having strong communication and teaching skills. Various clinical teaching methods are also outlined such as conferences, bedside clinics, and case studies.