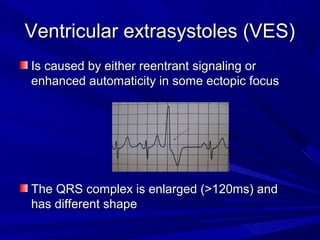
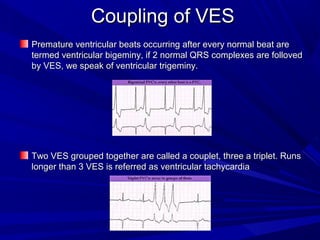
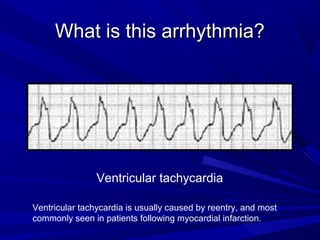
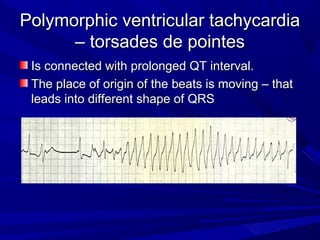
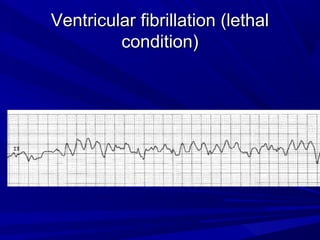
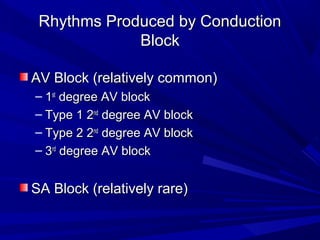
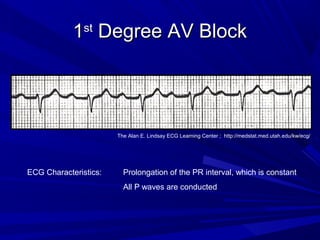
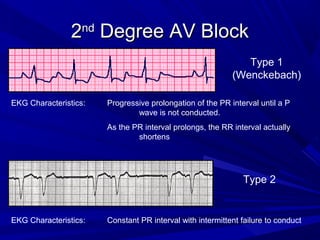
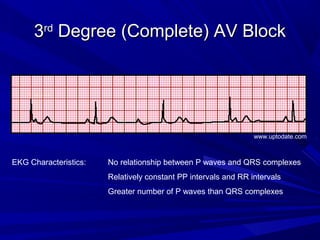
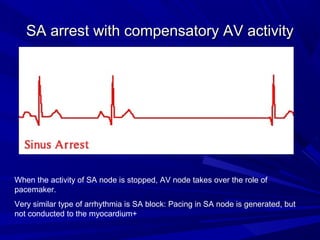
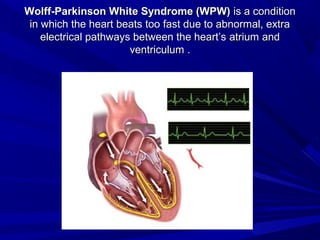
This document discusses various types of ventricular conduction disorders and rhythms produced by conduction block. It describes ventricular extrasystoles which are caused by reentrant signaling or enhanced automaticity in some ectopic focus, leading to an enlarged QRS complex. Ventricular tachycardia is usually caused by reentry and seen after myocardial infarction. Atrioventricular block is a delay or failure in transmission of the cardiac impulse from atrium to ventricle and can be first, second or third degree. Premature contractions refer to non-sinus beats and include atrial and ventricular premature contractions which have various etiologies and presentations. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a condition in which the heart beats too fast