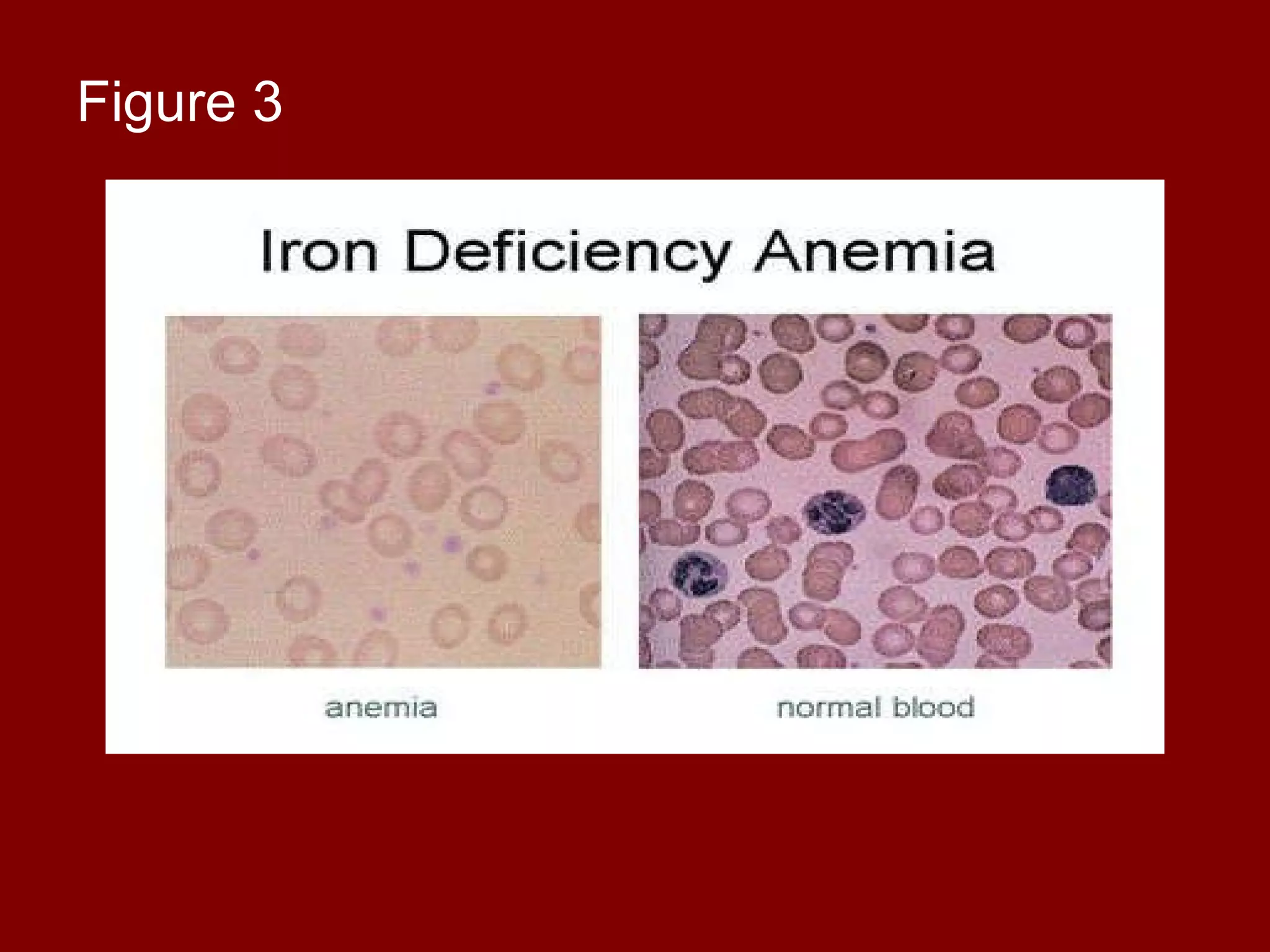
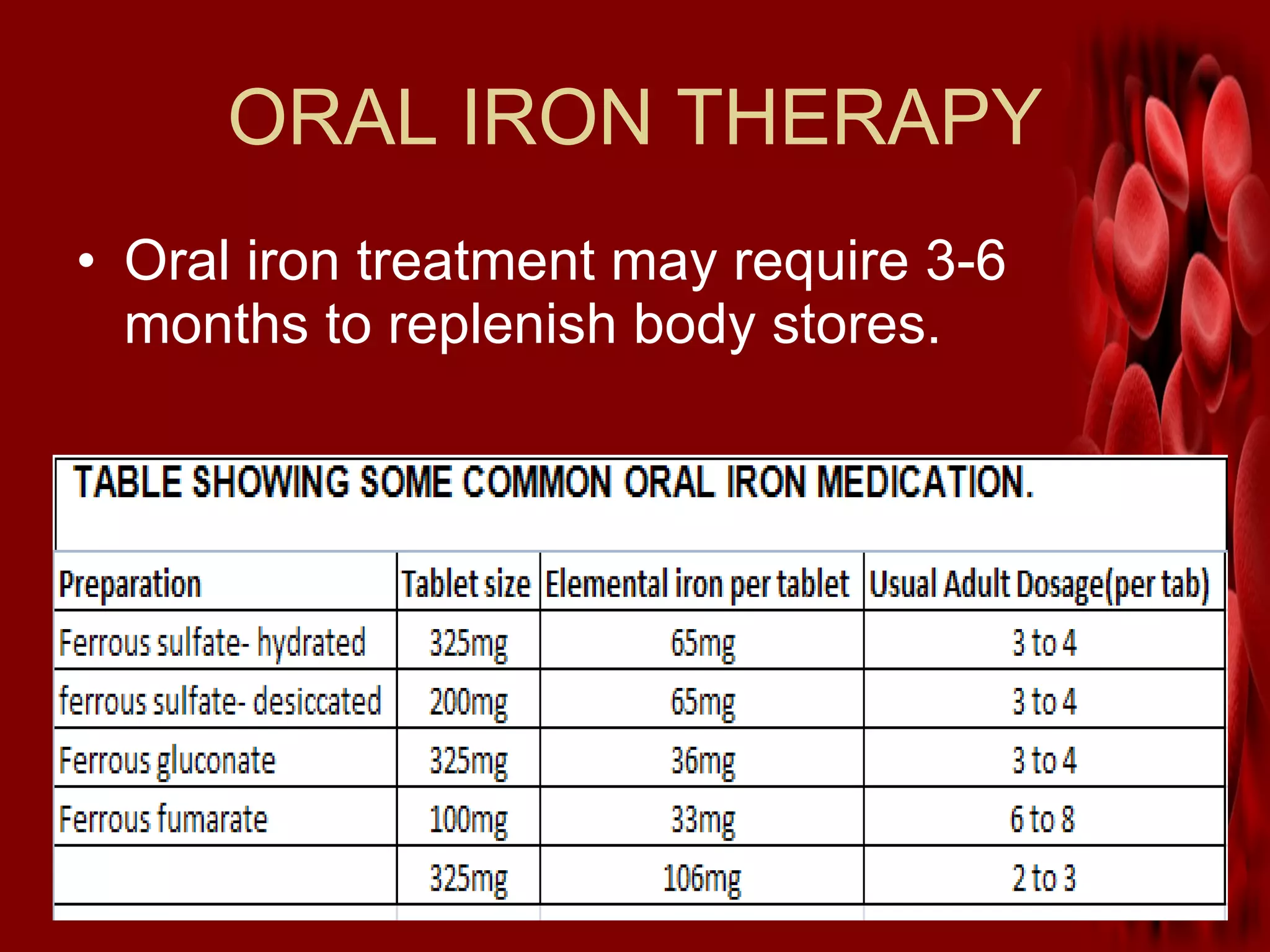
Iron deficiency anemia is a common condition characterized by a lack of red blood cells due to insufficient iron, affecting the body's ability to transport oxygen. Causes include blood loss, poor diet, and inability to absorb iron, leading to symptoms like fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath. Treatment typically involves iron supplements, dietary changes, and monitoring for potential adverse effects and contraindications.