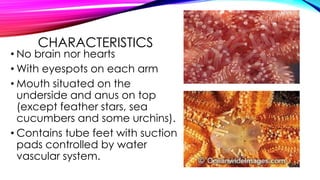
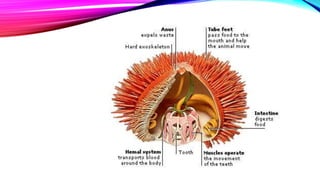
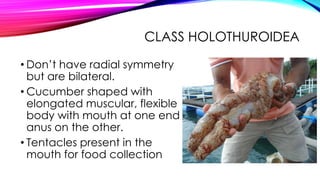
This document discusses the phylum Echinodermata, which includes sea stars, brittle stars, feather stars, sea cucumbers, and sea urchins. It describes their key characteristics such as radial symmetry, multiple arms radiating from a central disc, and a water vascular system. It provides details on the classes within this phylum, including their anatomy, feeding behaviors, locomotion methods, and examples such as crown-of-thorns starfish.