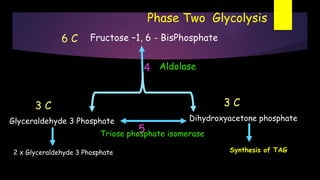
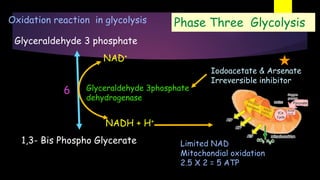
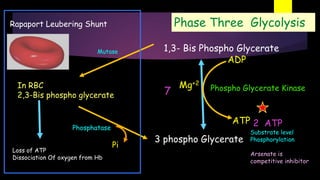
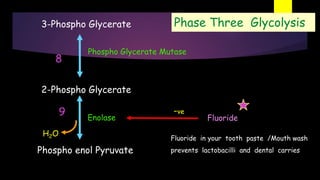
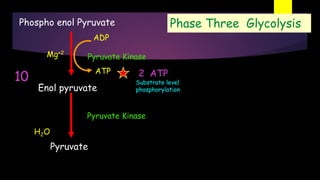
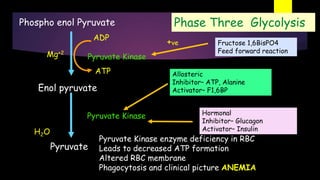
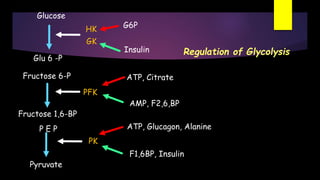
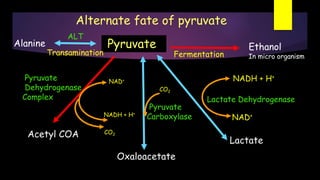
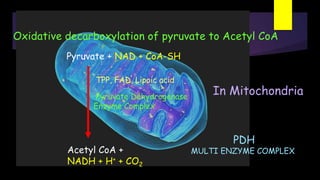
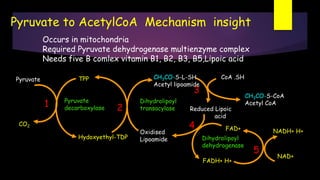
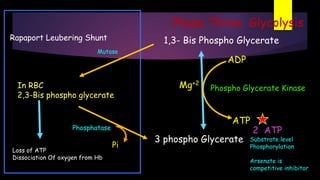
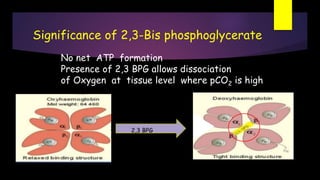
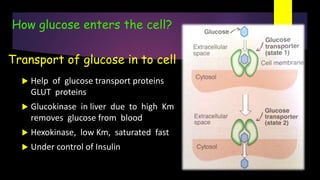
Glycolysis is a key metabolic pathway for glucose and other carbohydrates, functioning both aerobically and anaerobically to produce energy. In aerobic conditions, glucose is converted to pyruvate, while in anaerobic conditions, it is converted to lactate, with various regulatory enzymes and phases governing the process. Glycolysis plays a crucial role in providing energy for tissues, including the brain and muscles, and its malfunction can lead to conditions such as hemolytic anemia and lactic acidosis.








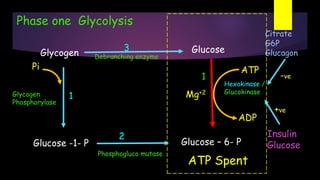
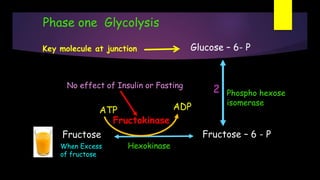
![Phase one Glycolysis
Fructose –1, 6 – Bis Phosphate
Phospho fructokinase 1 [PFK]
3
ADP
ATP
Fructose – 6 - P
• ADP
• Fructose 2,6,BisPO4
• Insulin
+ve
• Glucagon
• Citrate
• ATP-ve
Mg+2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class23glycolysis-161224060500/85/Class-2-3-glycolysis-12-320.jpg)