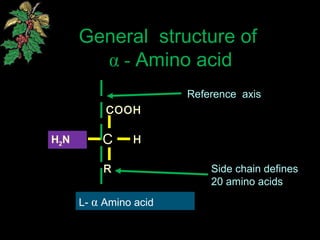
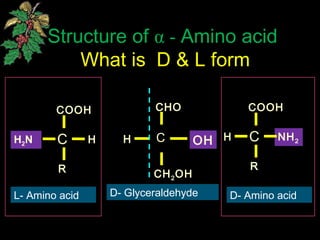
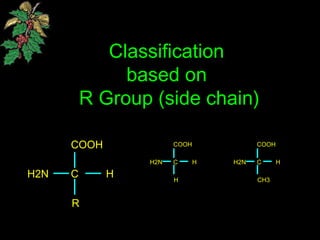
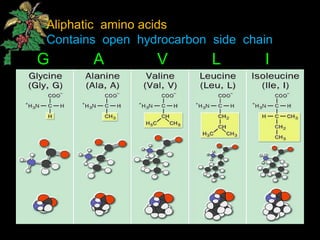
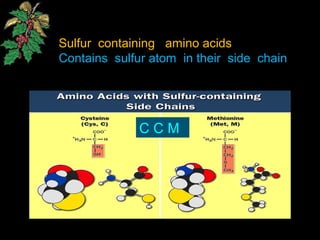
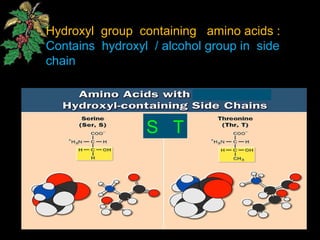
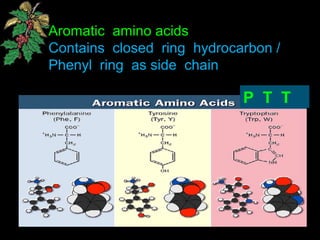
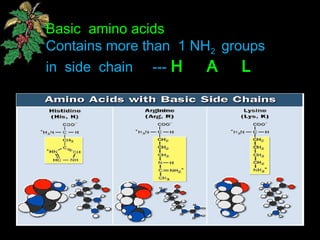
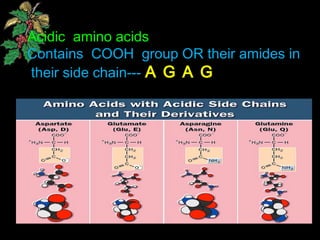
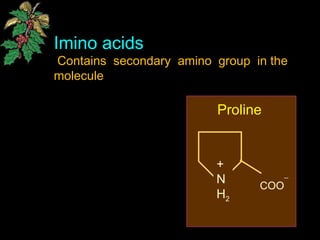
The document discusses amino acids, which are organic compounds that are the building blocks of proteins. It defines amino acids and explains their general structure, which includes an alpha carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain that differs between the 20 standard amino acids. The document also classifies amino acids based on their structure, including whether they contain sulfur, hydroxyl groups, aromatic rings, or other functional groups in their side chains. Amino acids serve various functions, including as components of proteins and enzymes, acting as buffers or carriers of oxygen, and involvement in metabolic reactions and synthesis of other biomolecules.