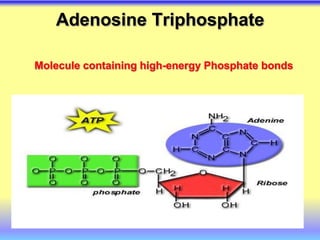
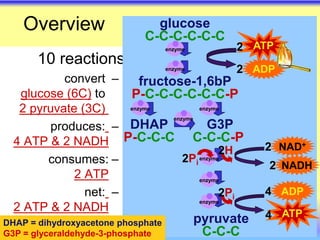
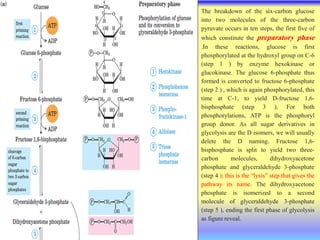
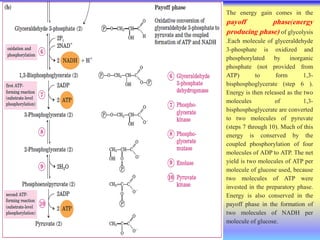
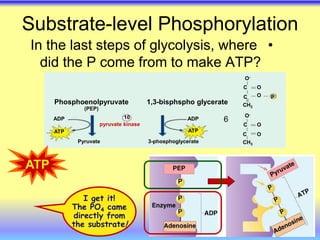
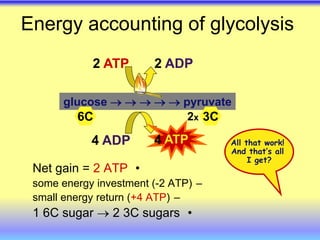
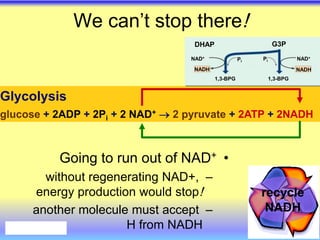
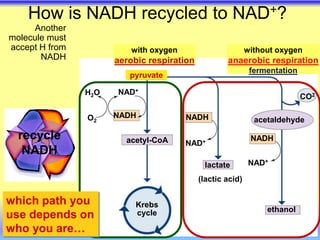
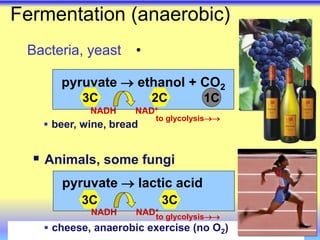
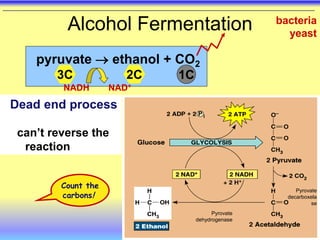
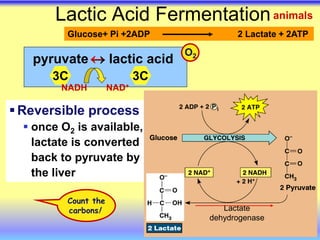
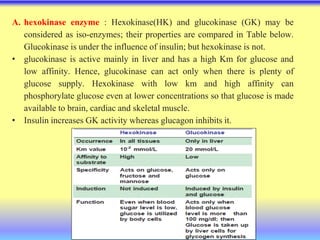
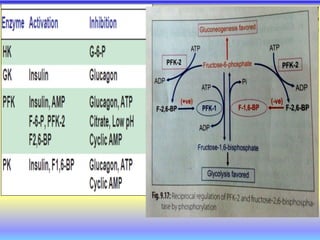
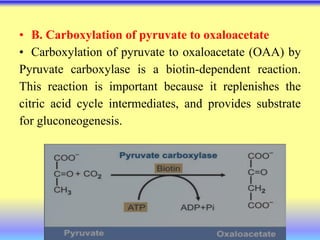
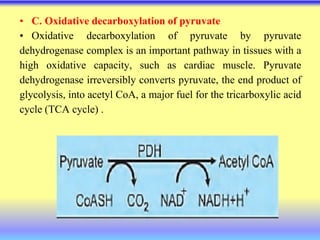
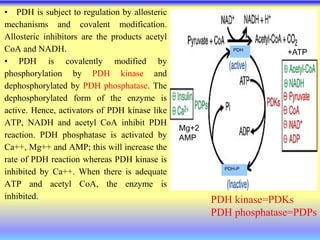
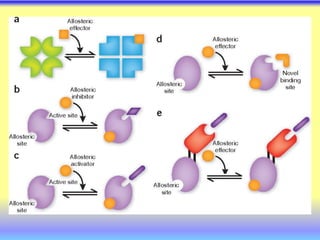
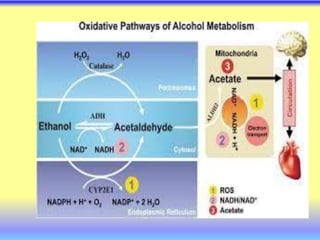
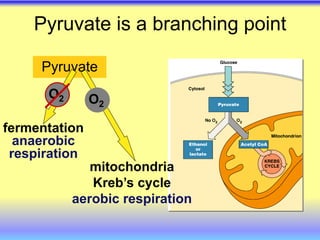
This document summarizes cellular respiration and the three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis involves the breakdown of glucose to pyruvate in the cytoplasm and generates a small amount of ATP. Pyruvate can then enter the mitochondria and be further oxidized through the Krebs cycle or fermented to lactate or ethanol. The overall goal is to extract energy from glucose and use it to produce ATP through the three stages of cellular respiration.