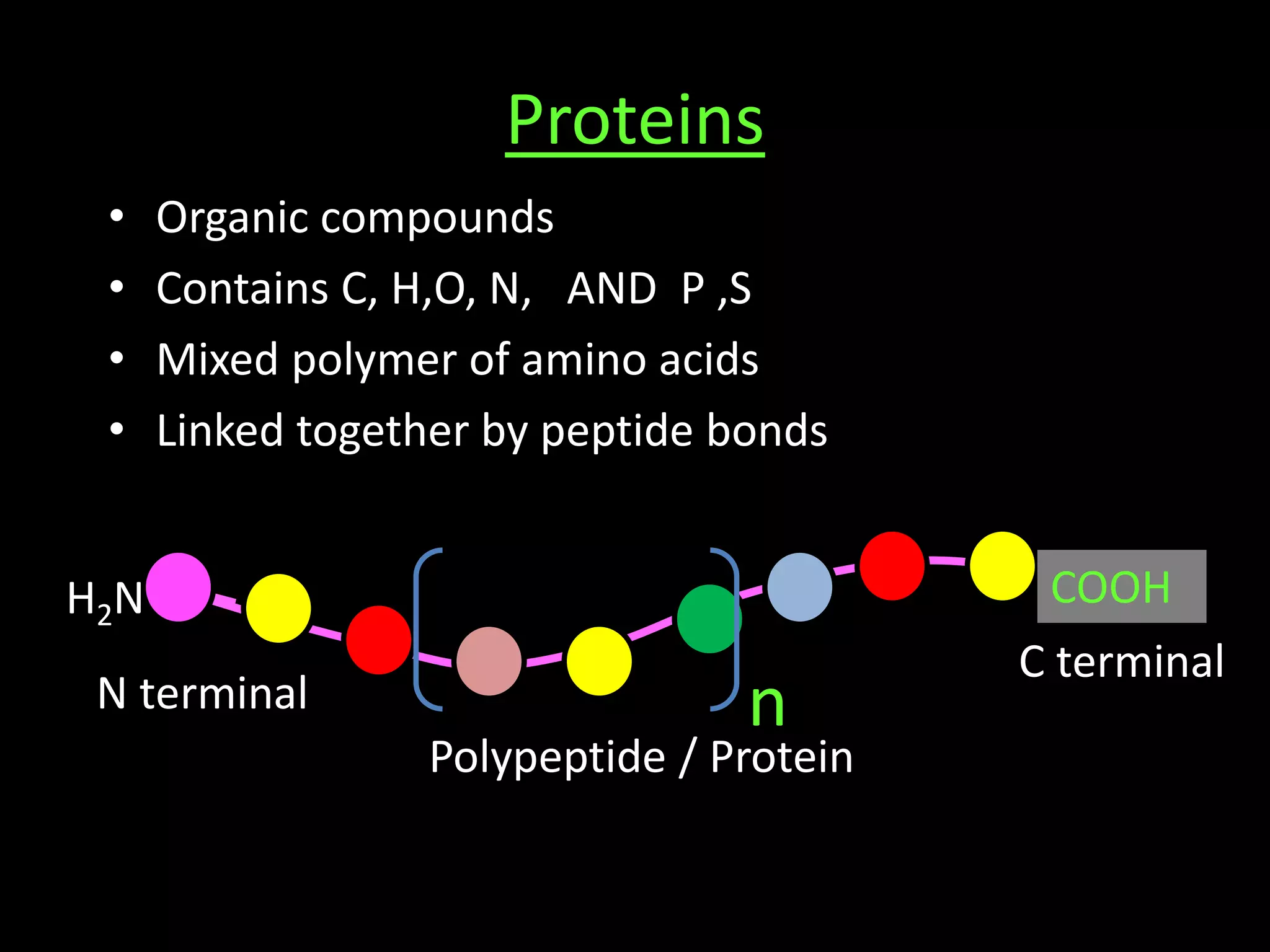
Proteins are organic compounds composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They are classified based on their function in the body. The main classes of proteins include structural, catalytic, contractile, transport, protective, hormonal, immunological, genetic, and nutritive proteins. Structural proteins provide structure to cells and organs, catalytic proteins act as enzymes to speed up metabolic reactions, and transport proteins help move molecules within and between cells.