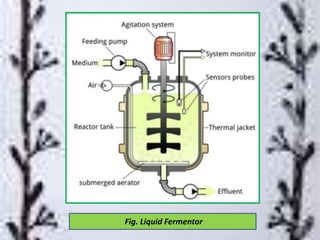
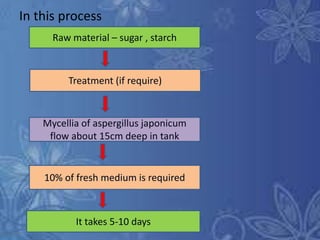
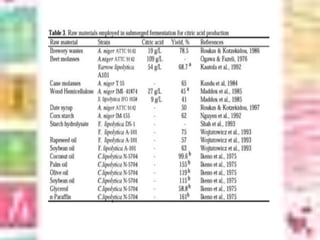
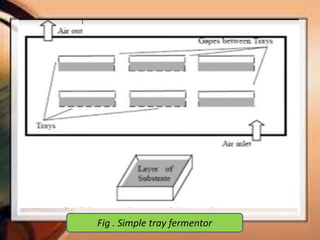
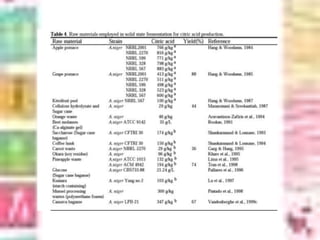
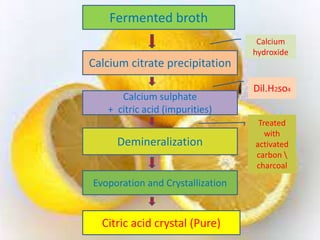
Citric acid is commonly produced through submerged fermentation using Aspergillus niger fungus. There are three main methods - submerged culture fermentation, liquid surface culture fermentation, and KOJI fermentation. Submerged culture fermentation is the most common industrial process, using sugar, starch, or molasses in fermentors along with A. niger over 5-10 days. Citric acid is then recovered through calcium citrate precipitation, demineralization, and crystallization. Finally, citric acid has many uses as a preservative and acidulant in foods, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and other products.