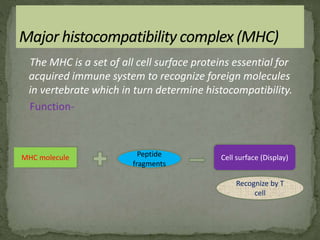
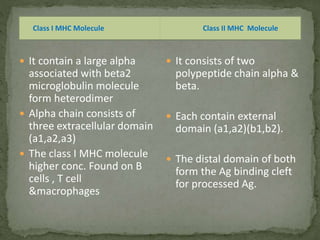
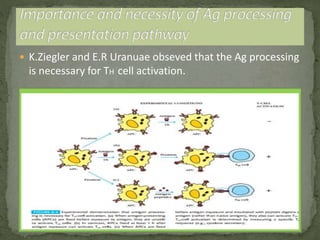
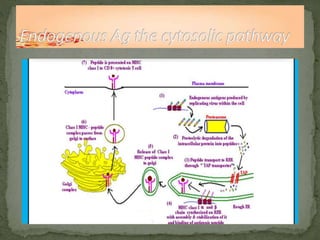
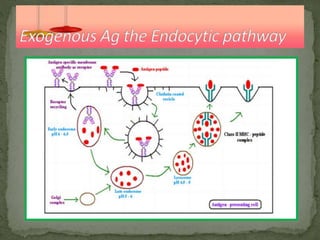
The document discusses antigen processing and presentation pathways. It explains that antigen presenting cells digest proteins from inside or outside the cell and display the resulting peptide fragments on MHC class I or II molecules. MHC class I presents endogenous antigens processed via the cytosolic pathway, while MHC class II presents exogenous antigens processed via the endocytic pathway for recognition by T cells. This process allows the immune system to detect signs of infection or abnormal growth.