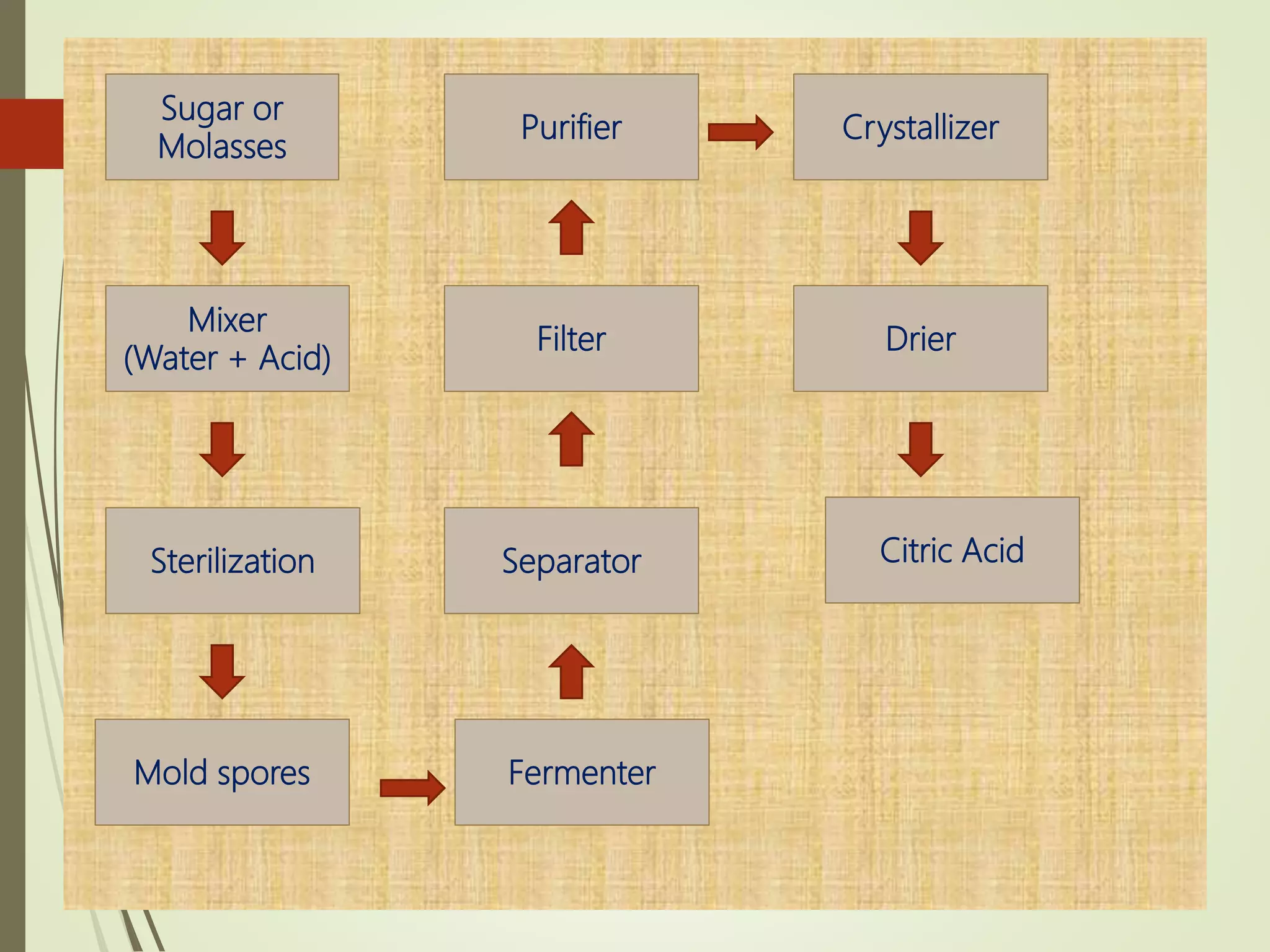
Citric acid, a key metabolic intermediate found in many fruits, is primarily produced through fungal fermentation, particularly using the organism Aspergillus niger due to its high yield and economic efficiency. Various fermentation methods include surface culture, submerged fermentation, and solid-state fermentation, each requiring specific environmental conditions. The recovery of citric acid involves filtration and concentration of the fermented liquid to obtain the final product.