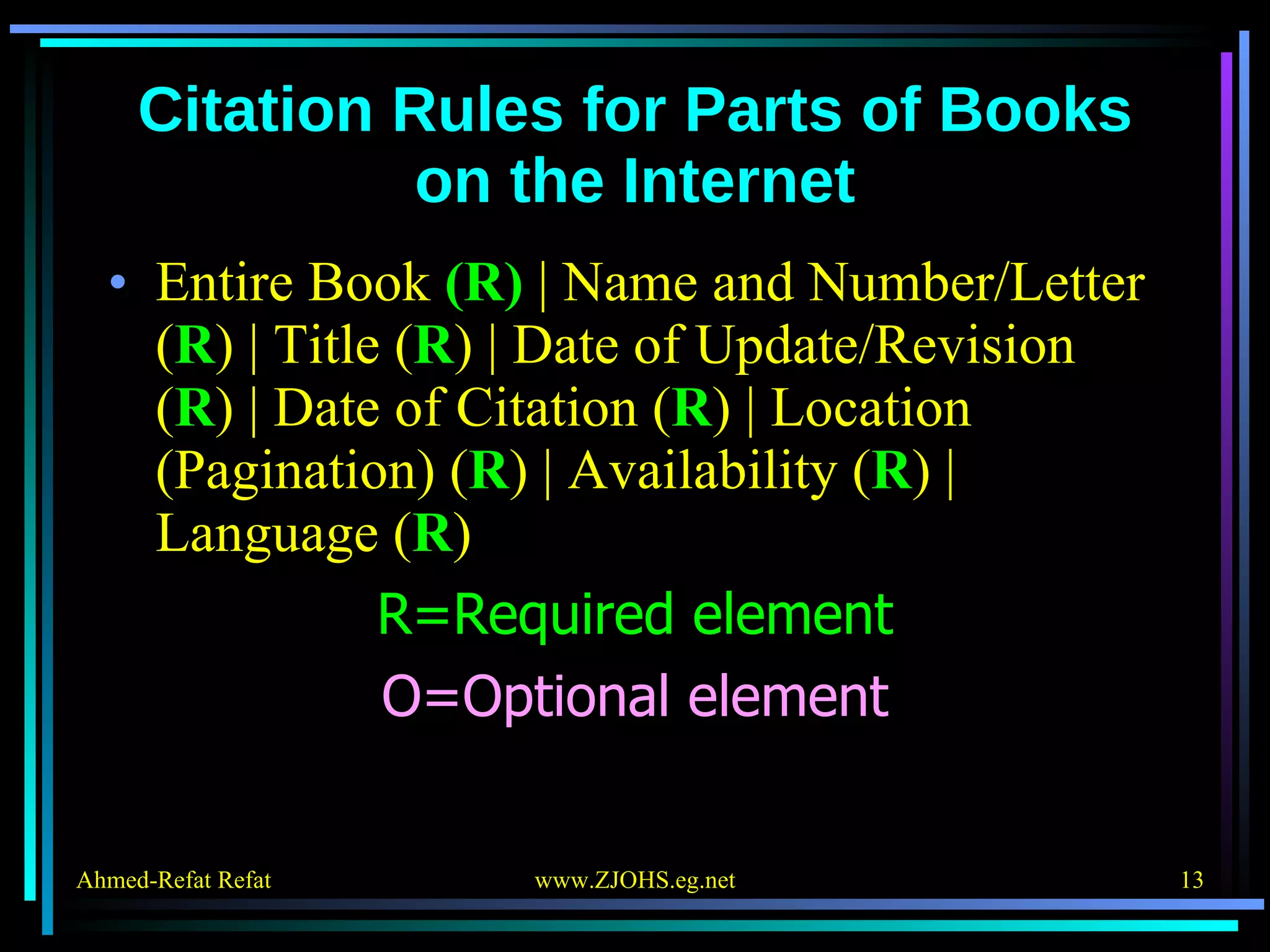
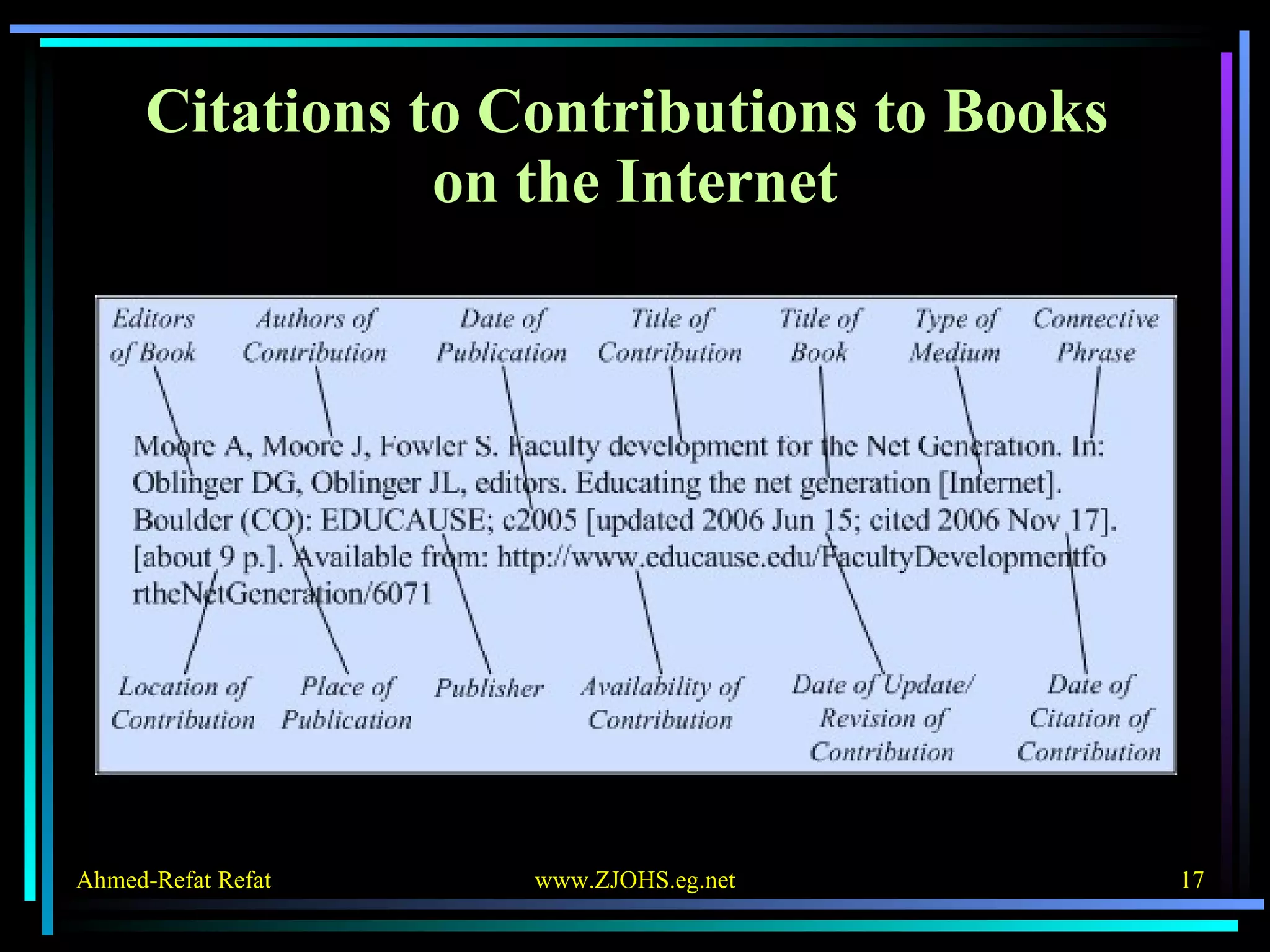
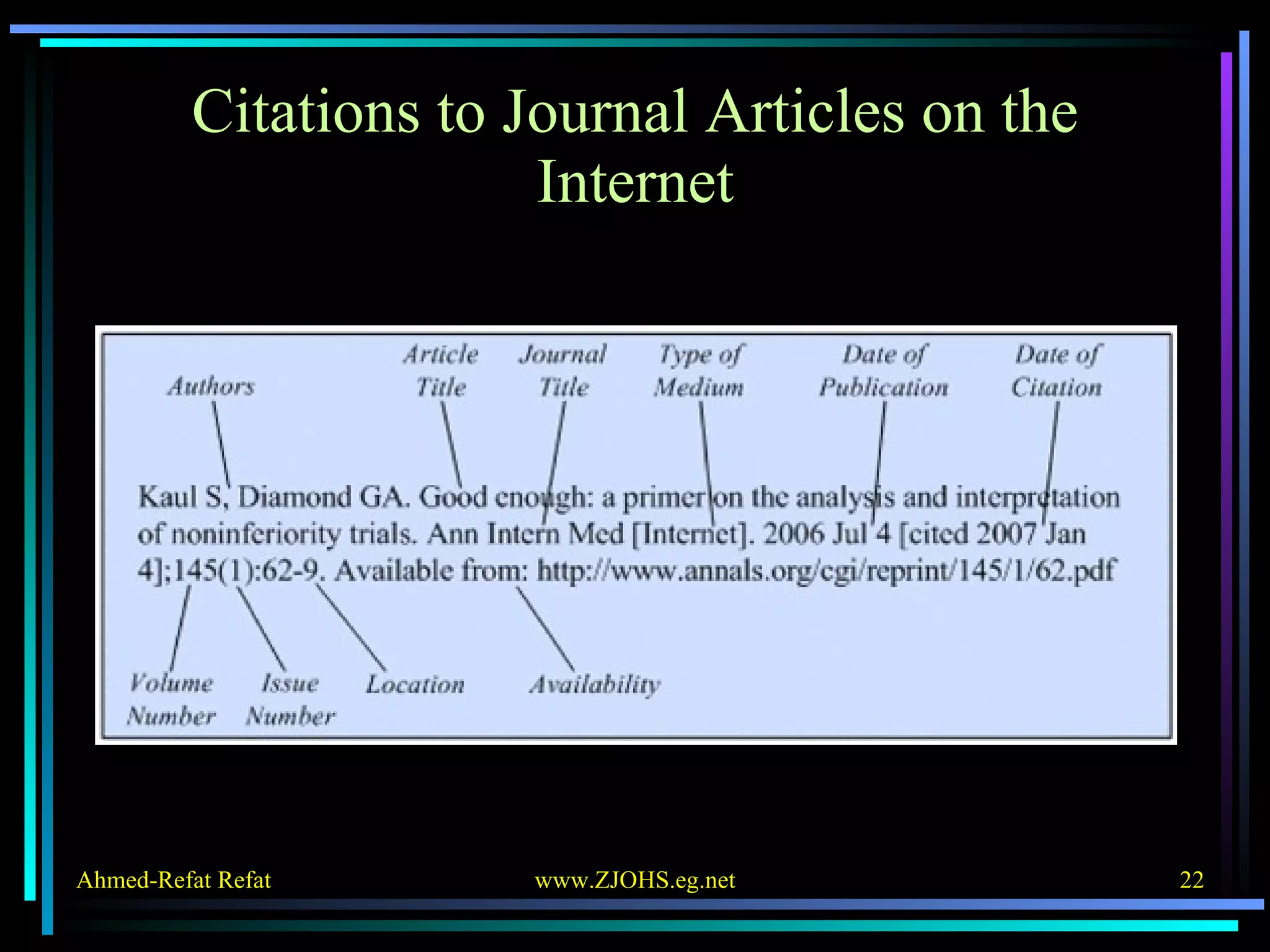
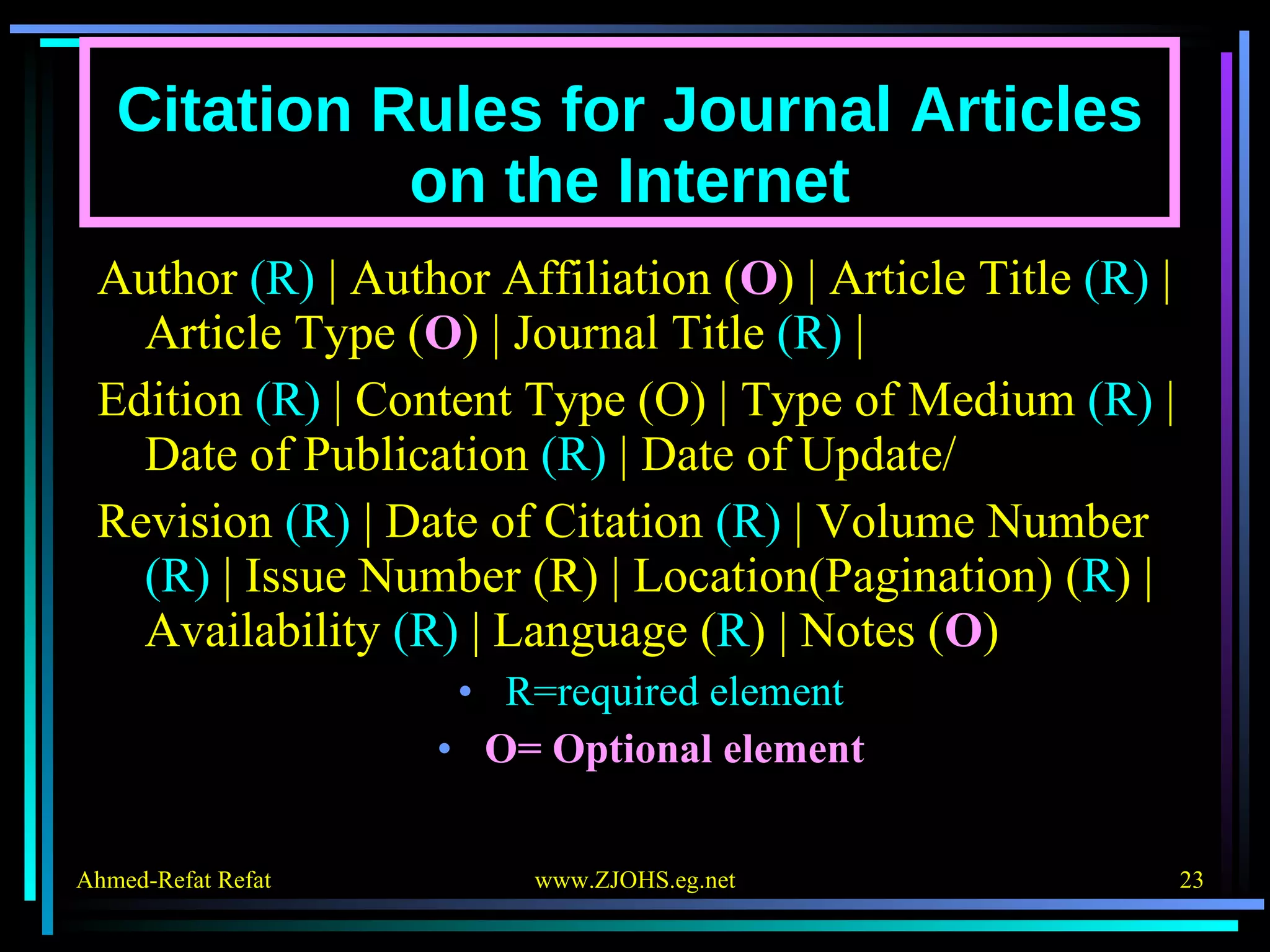
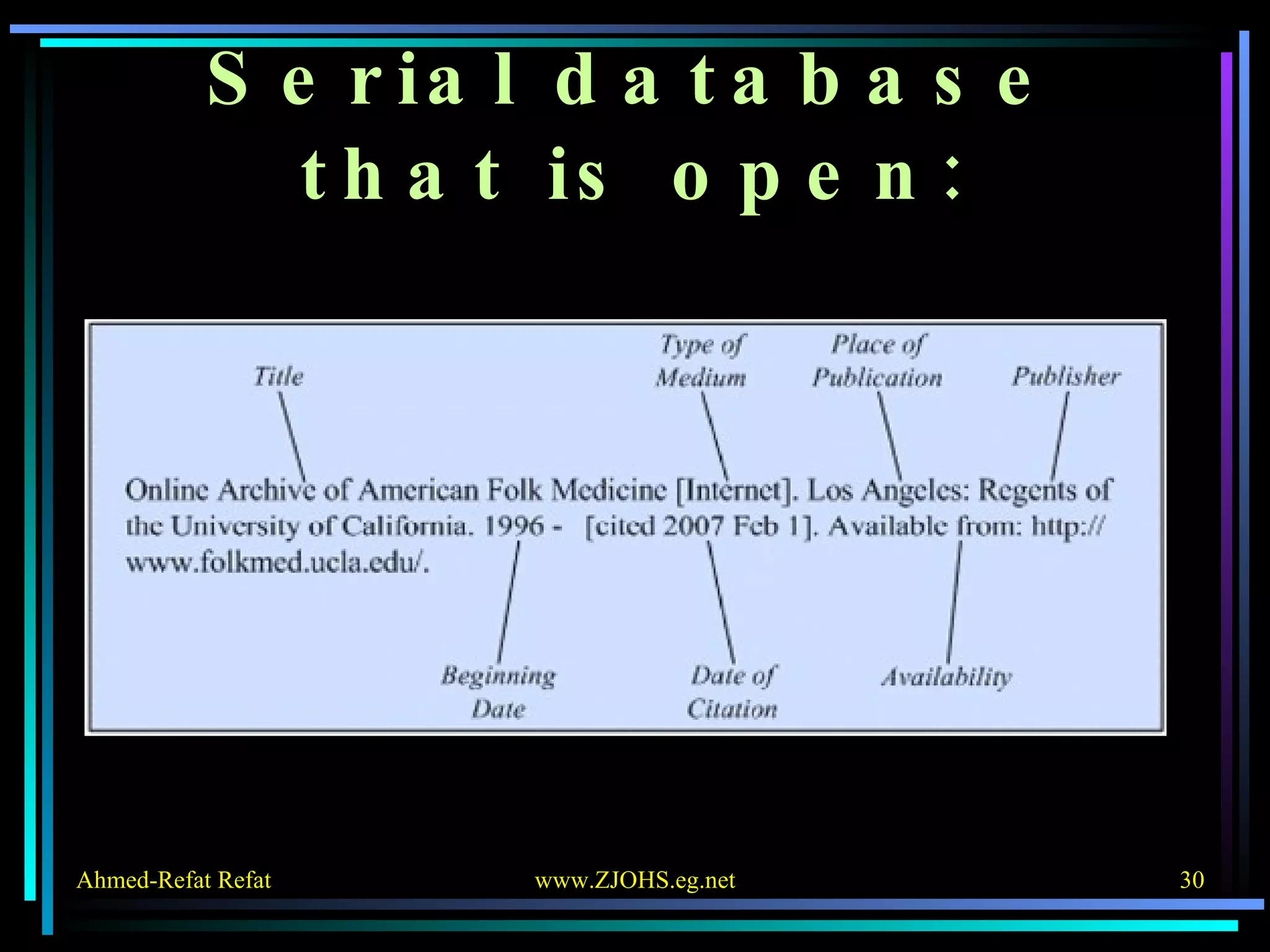
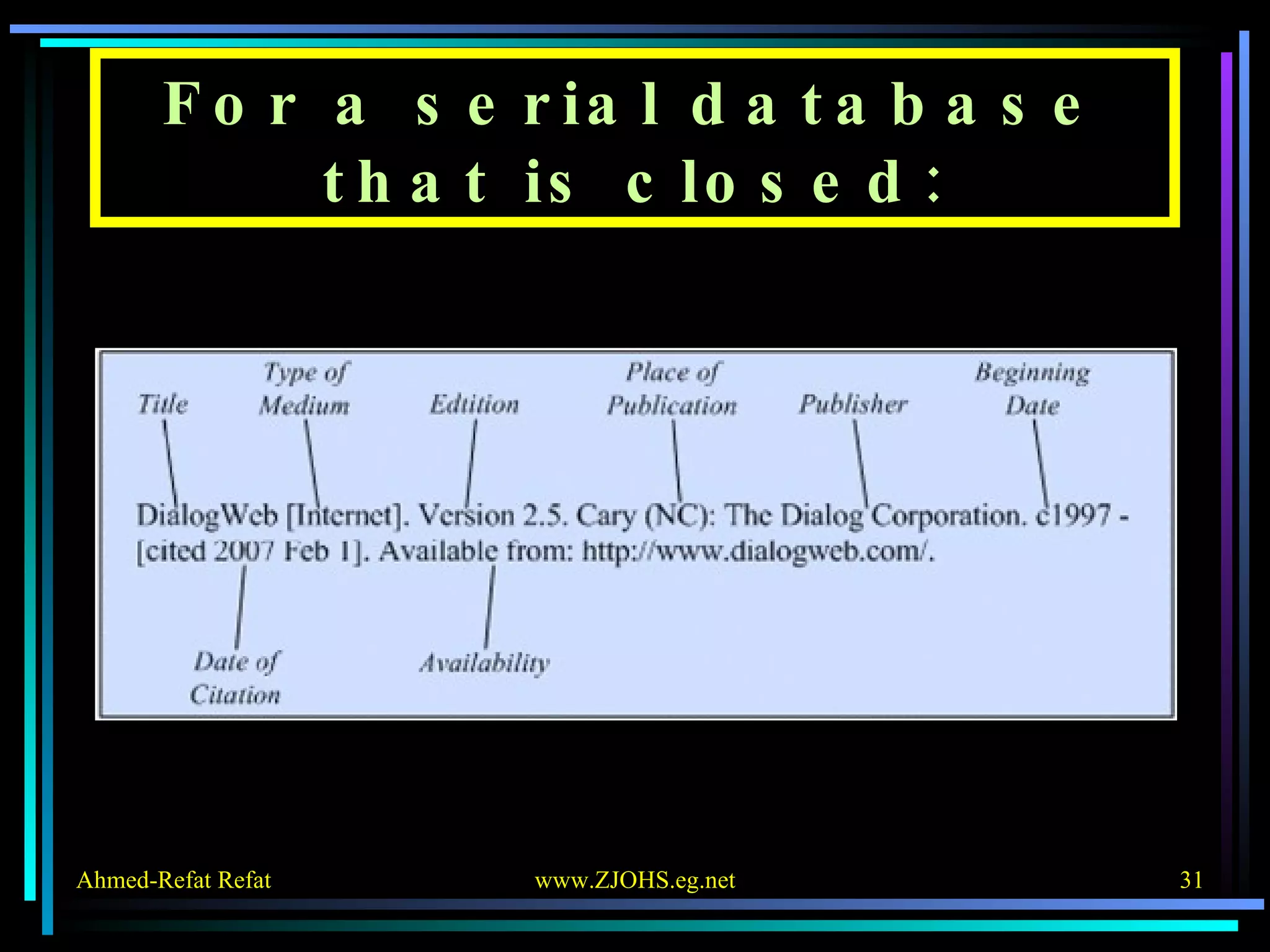
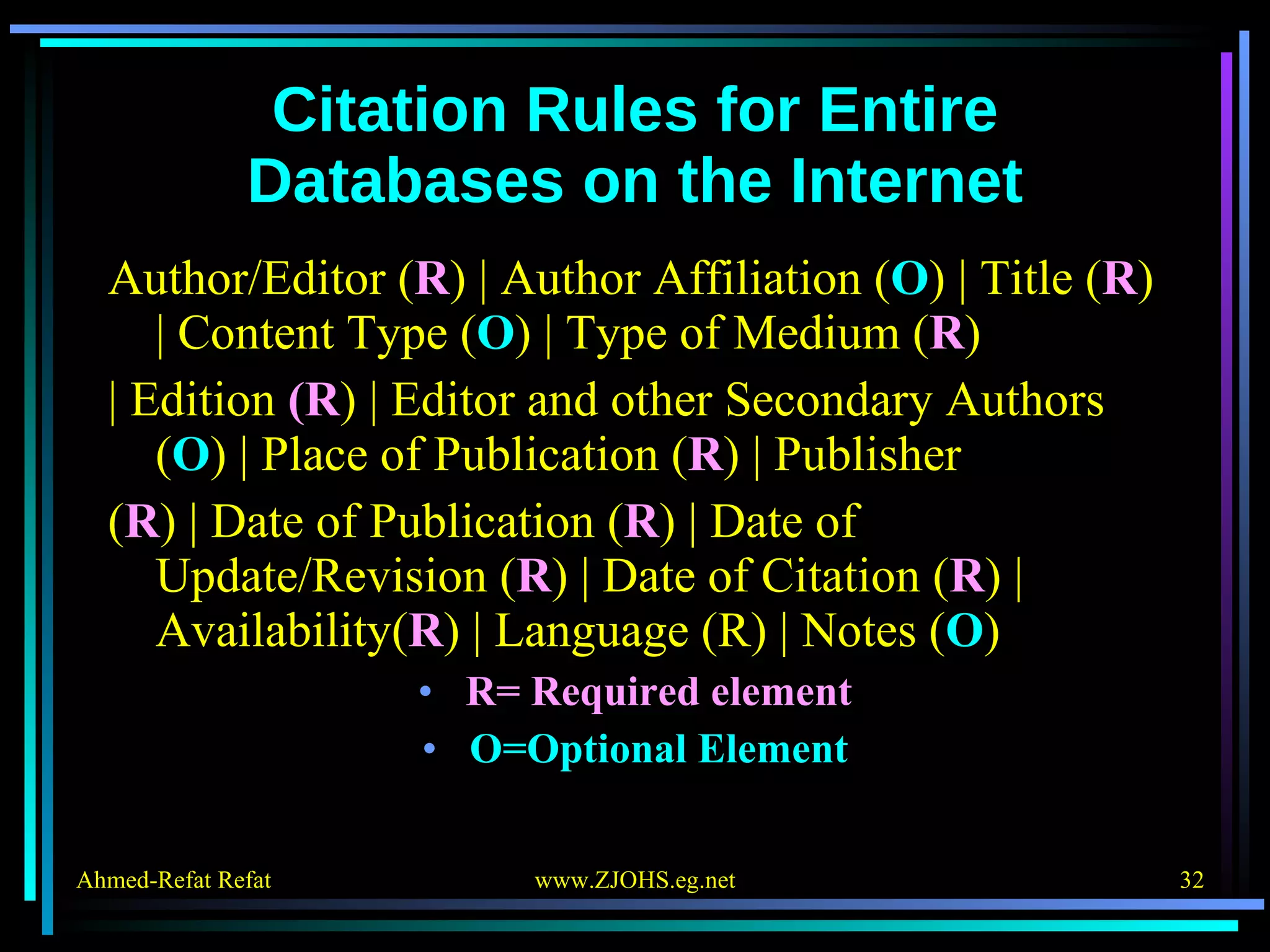
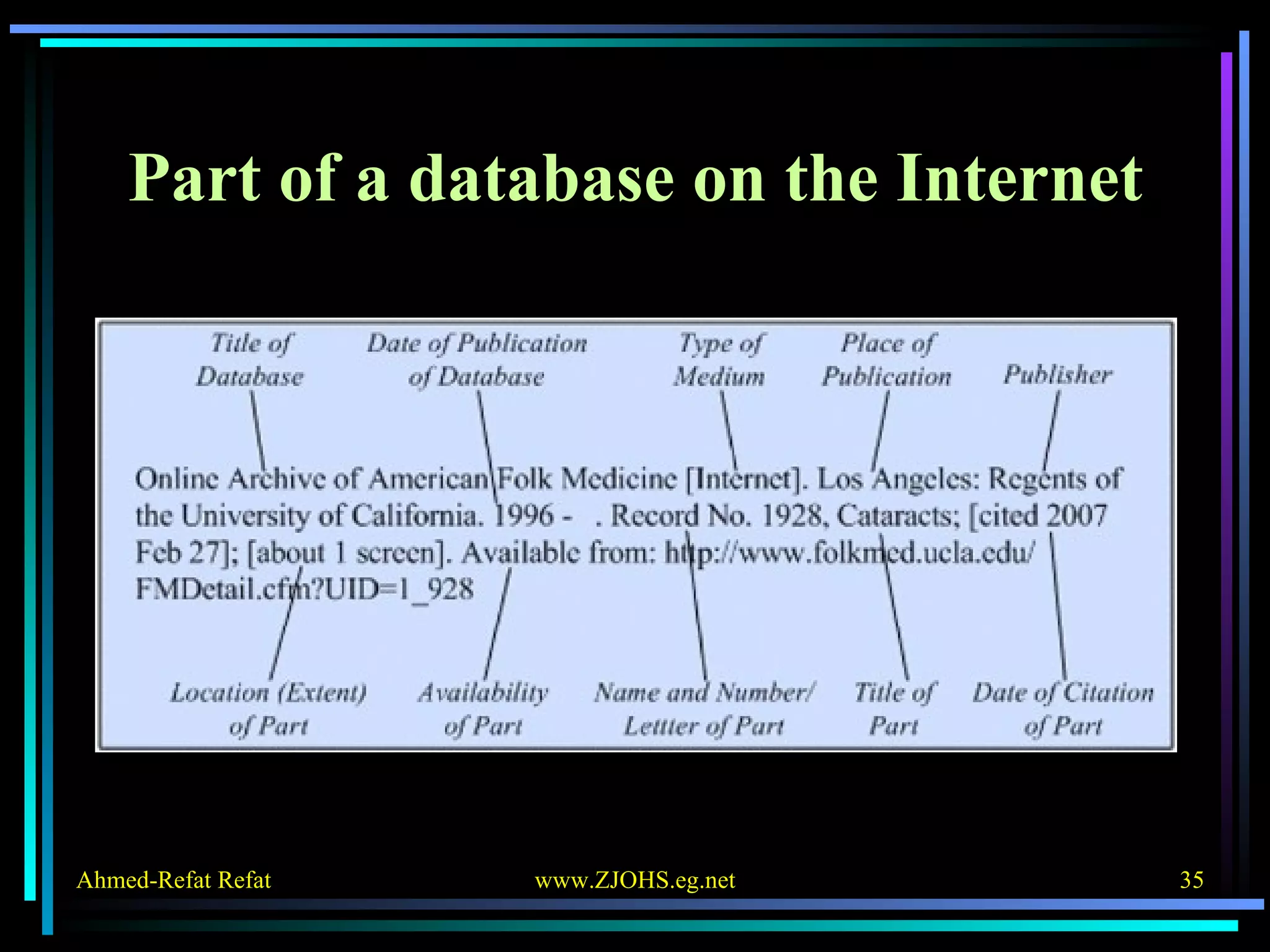
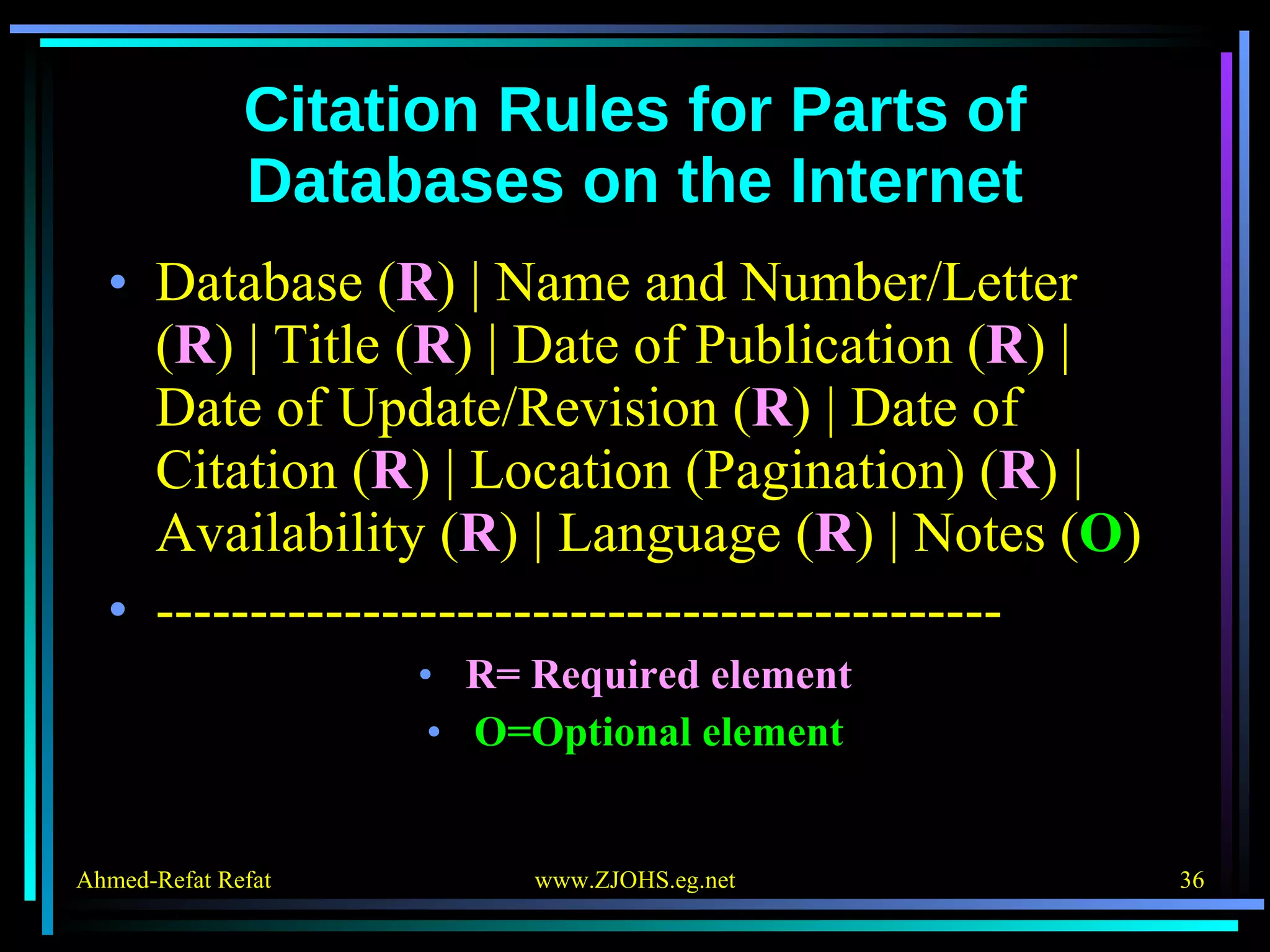
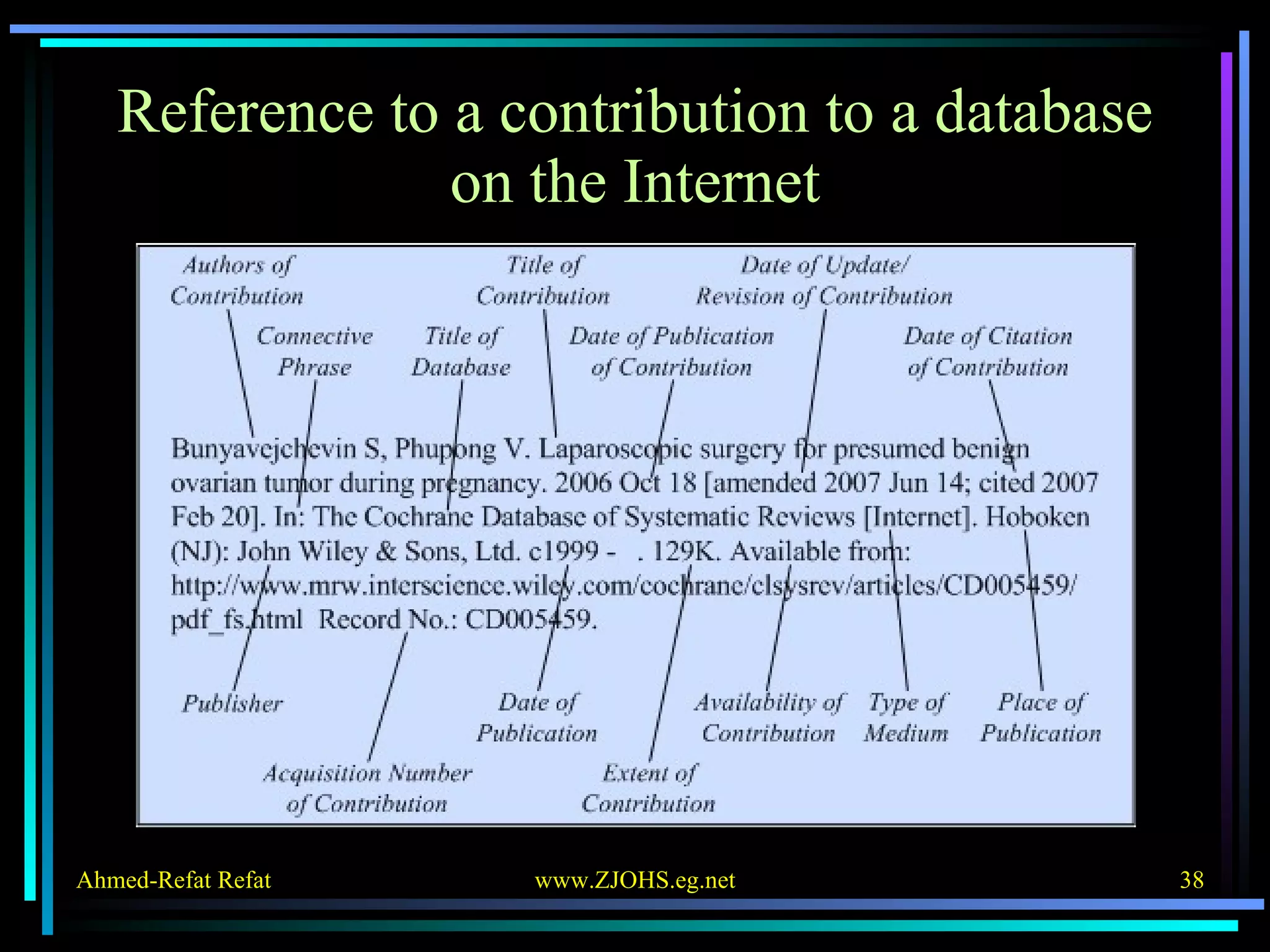
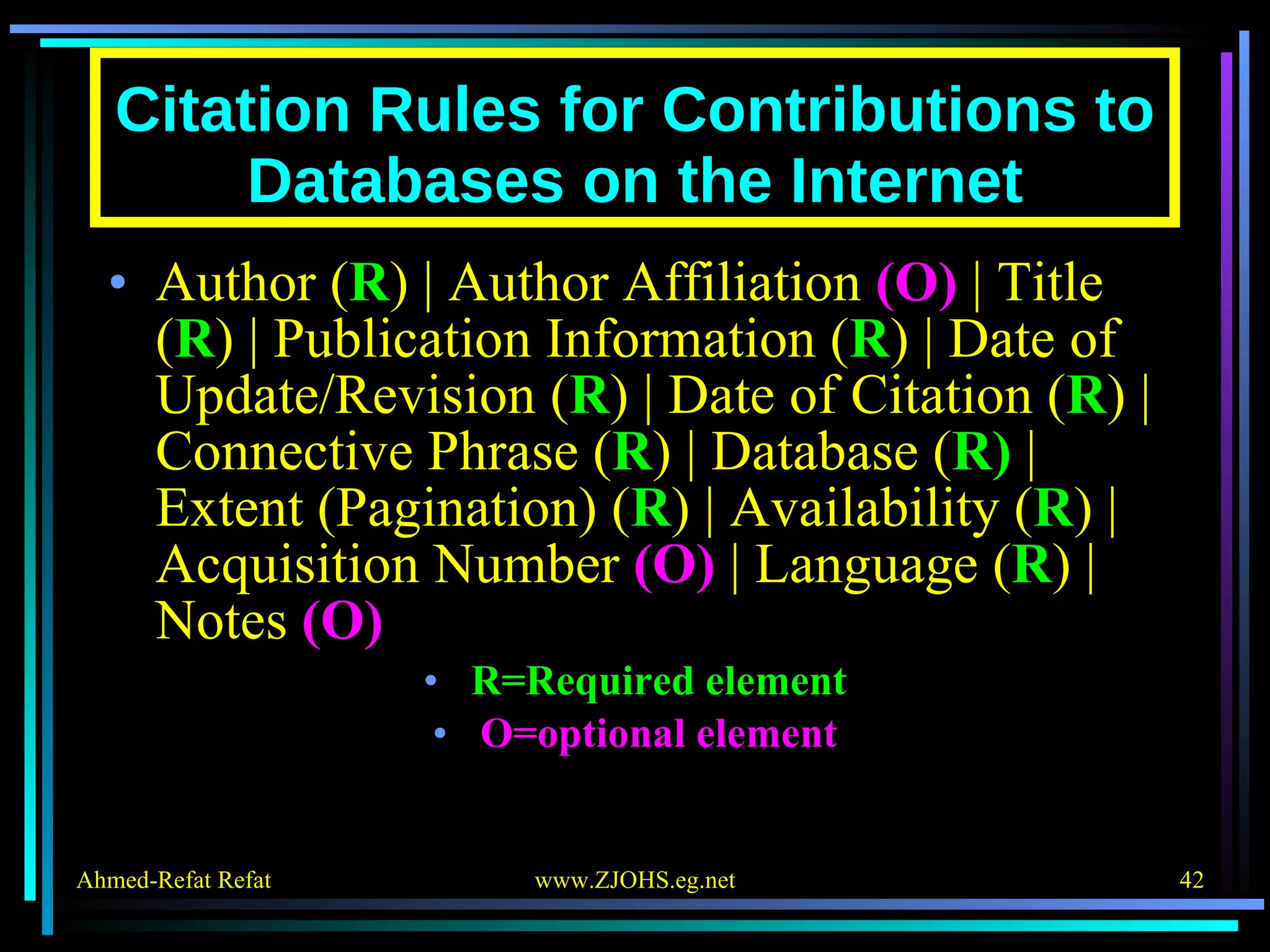
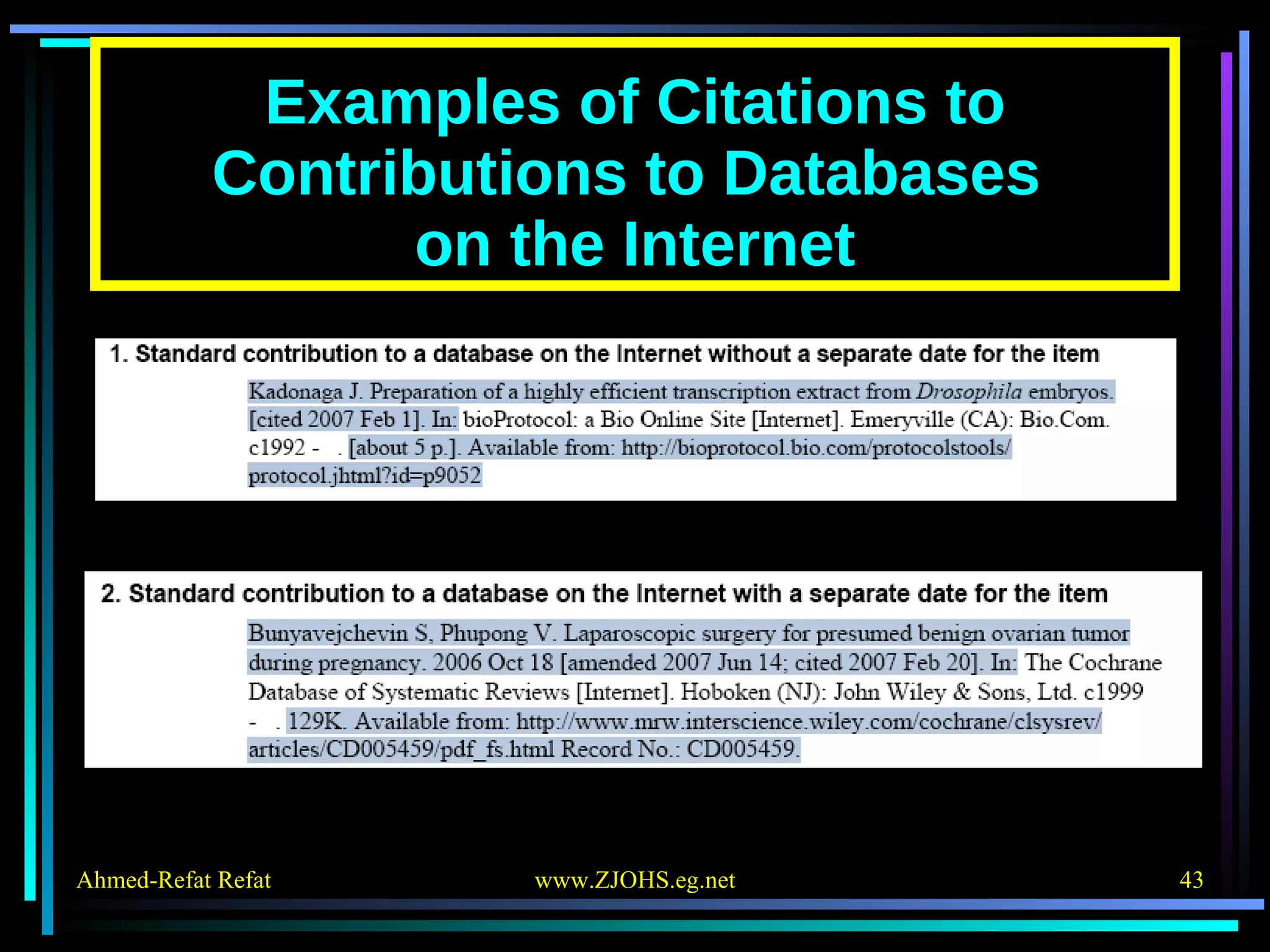
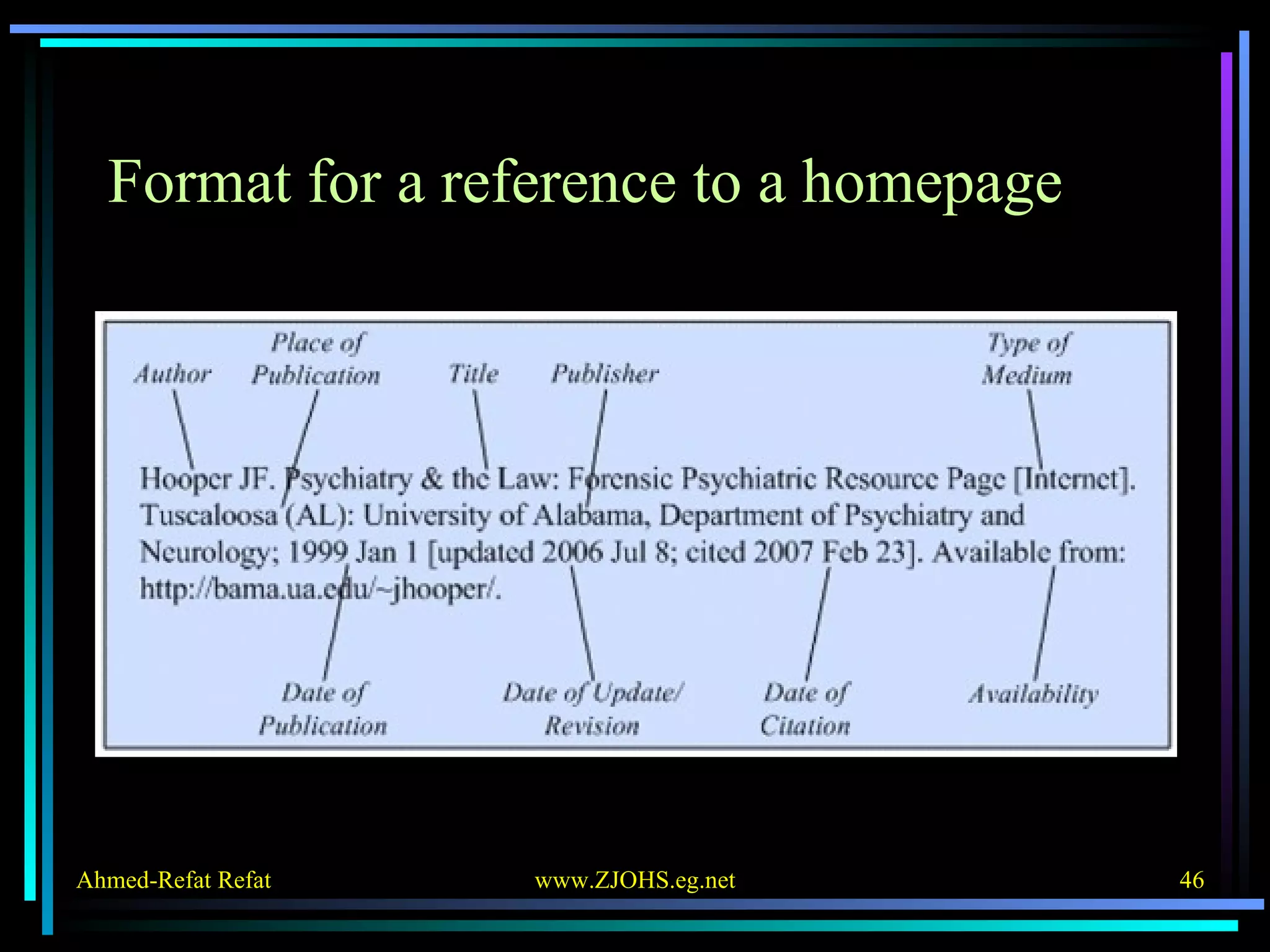
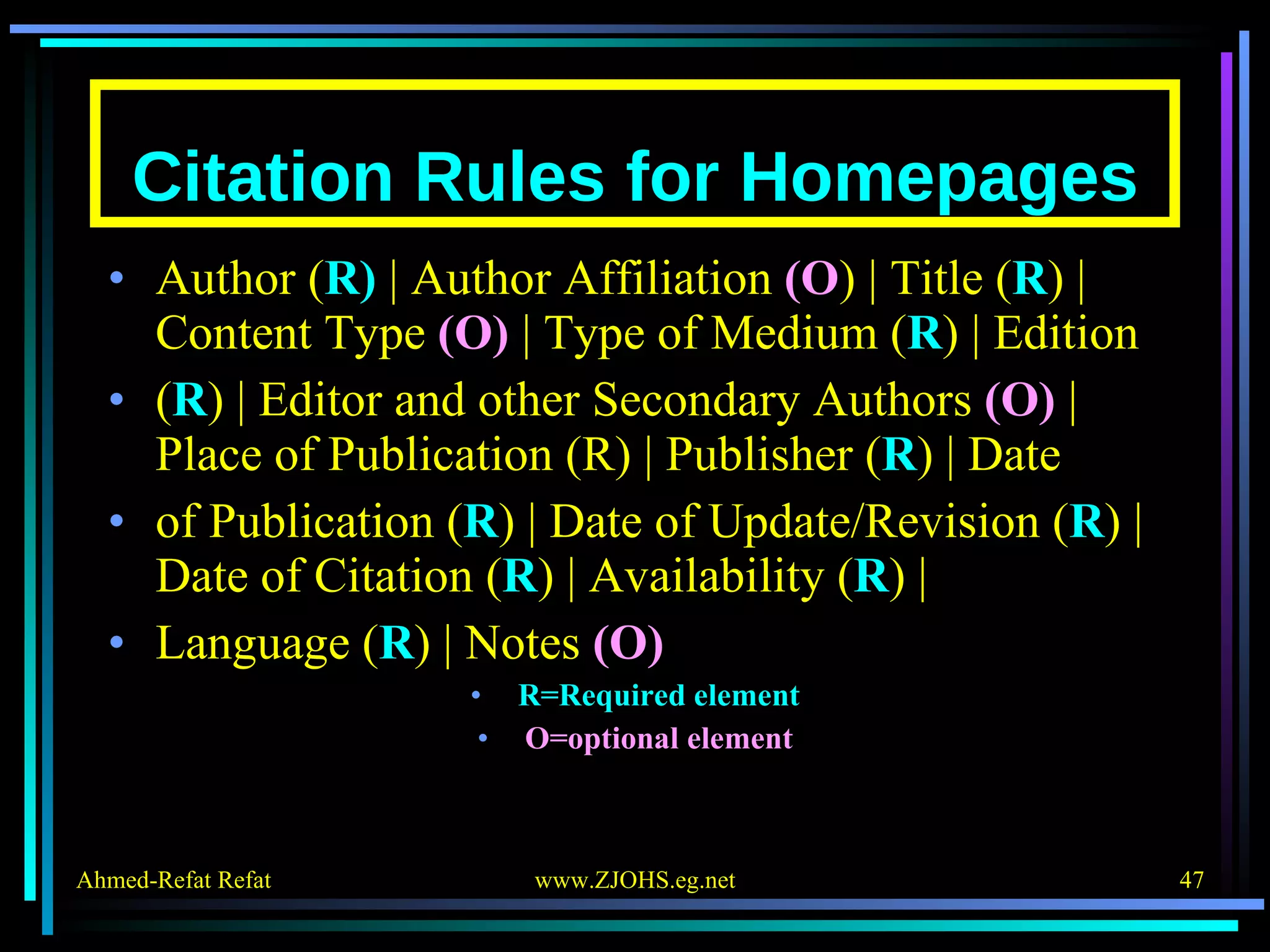
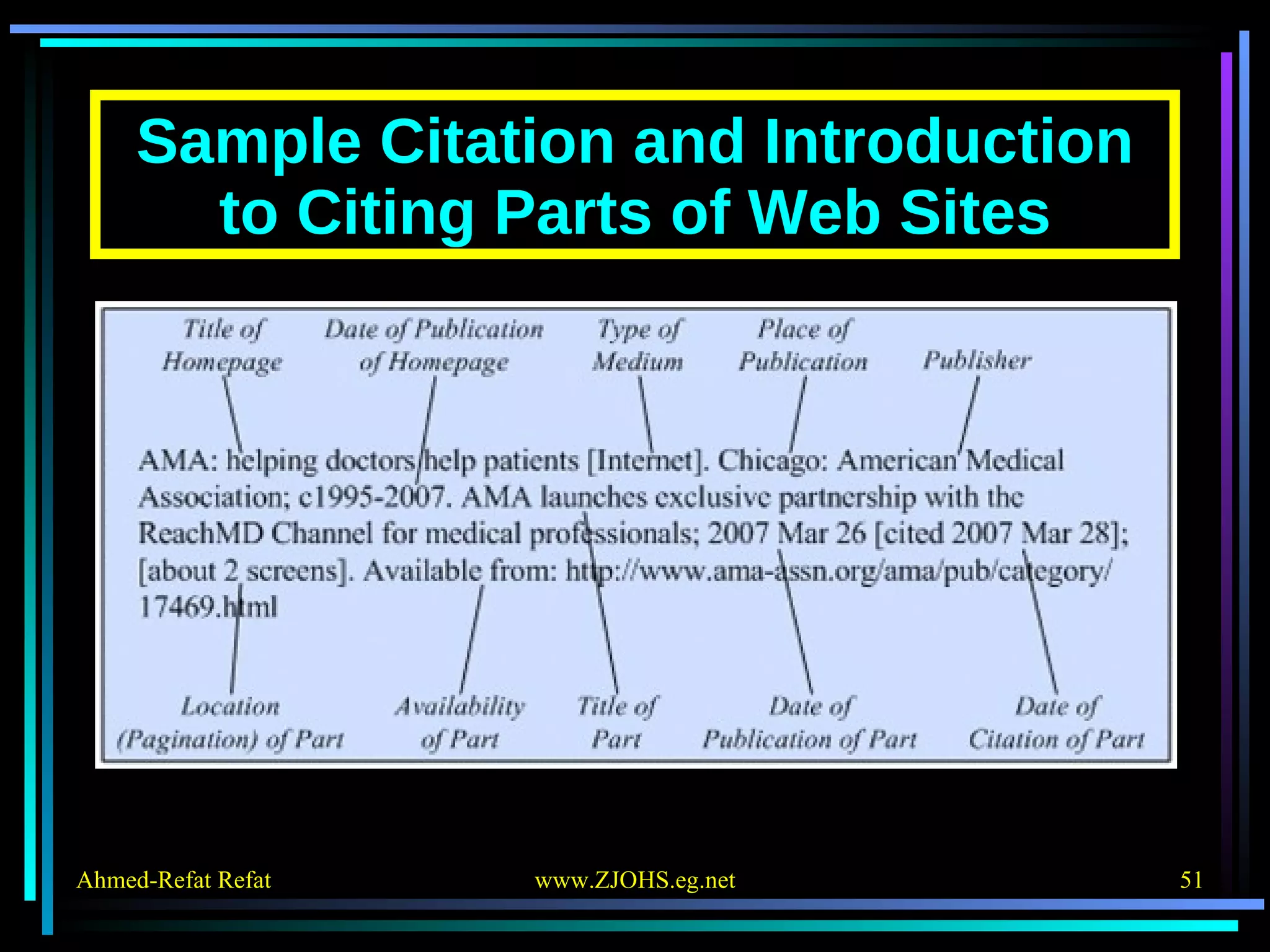
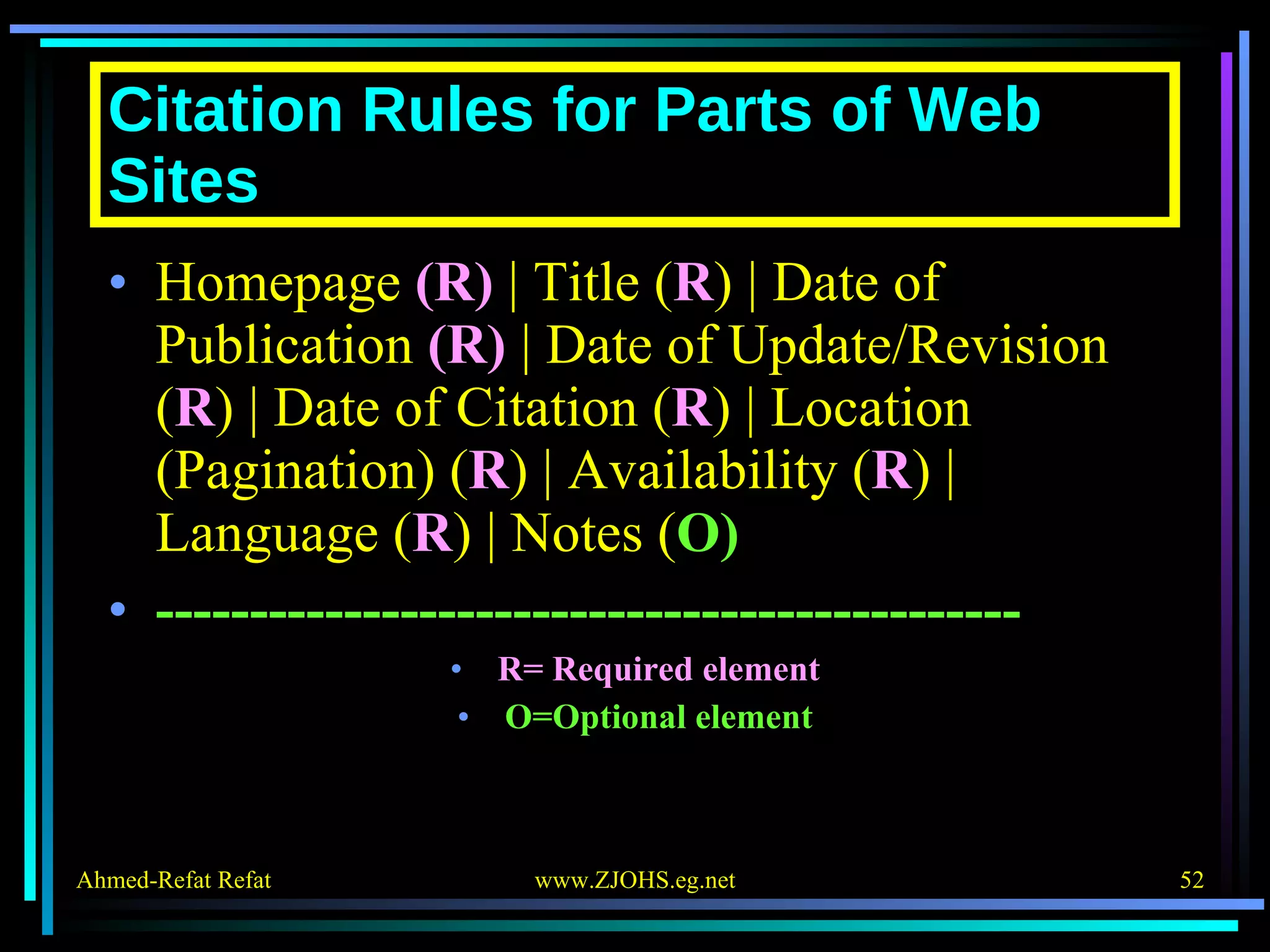
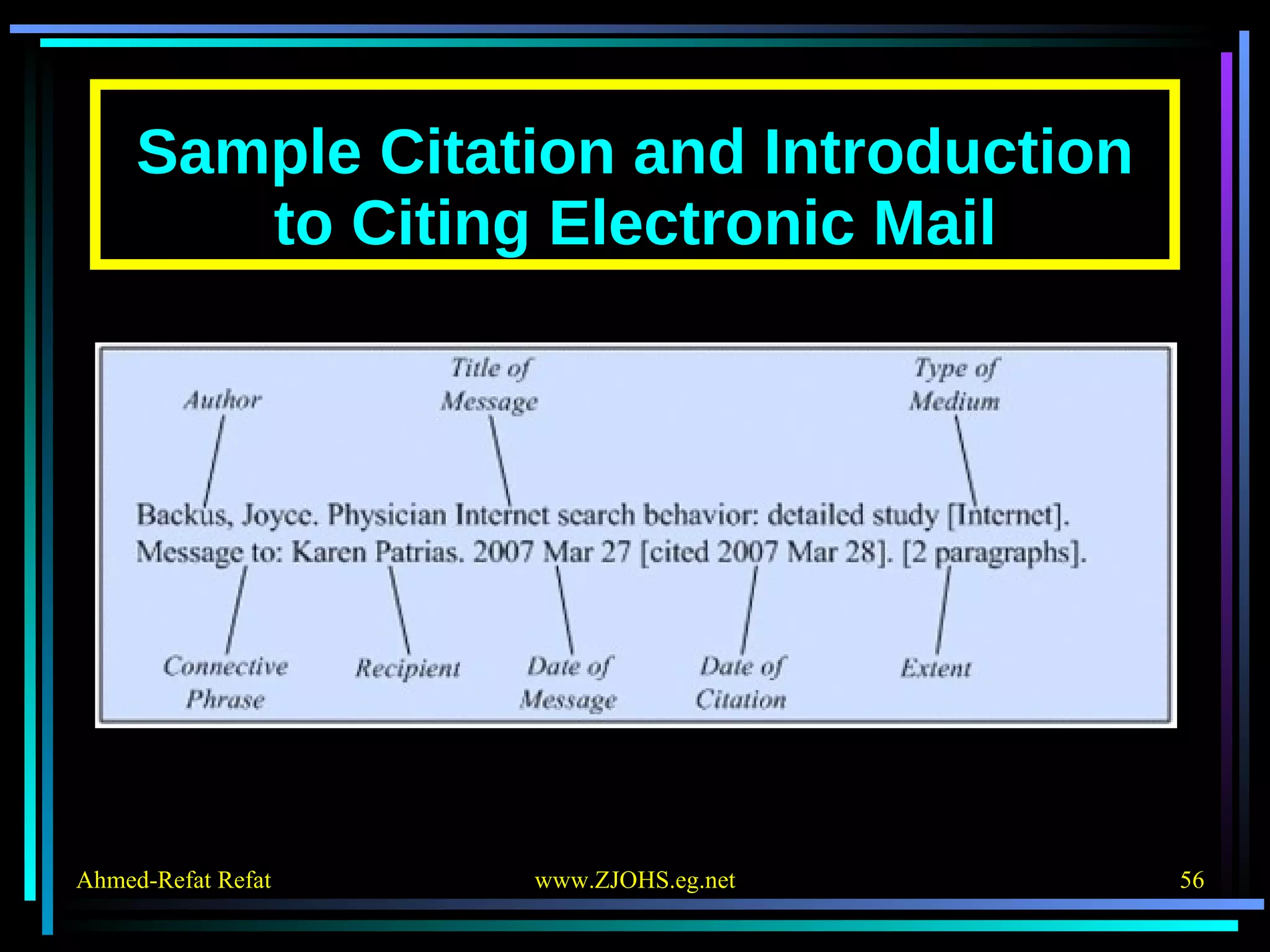
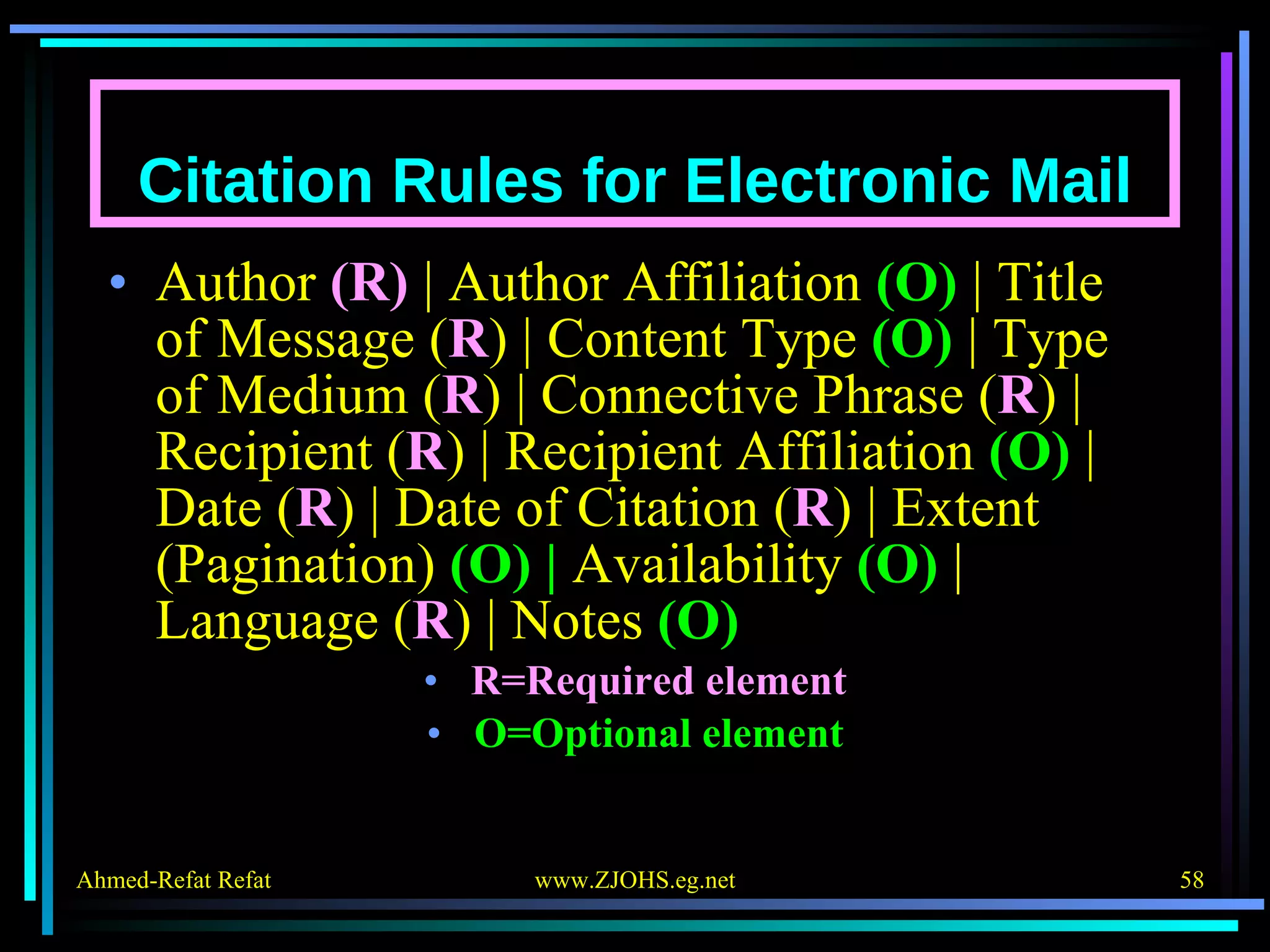
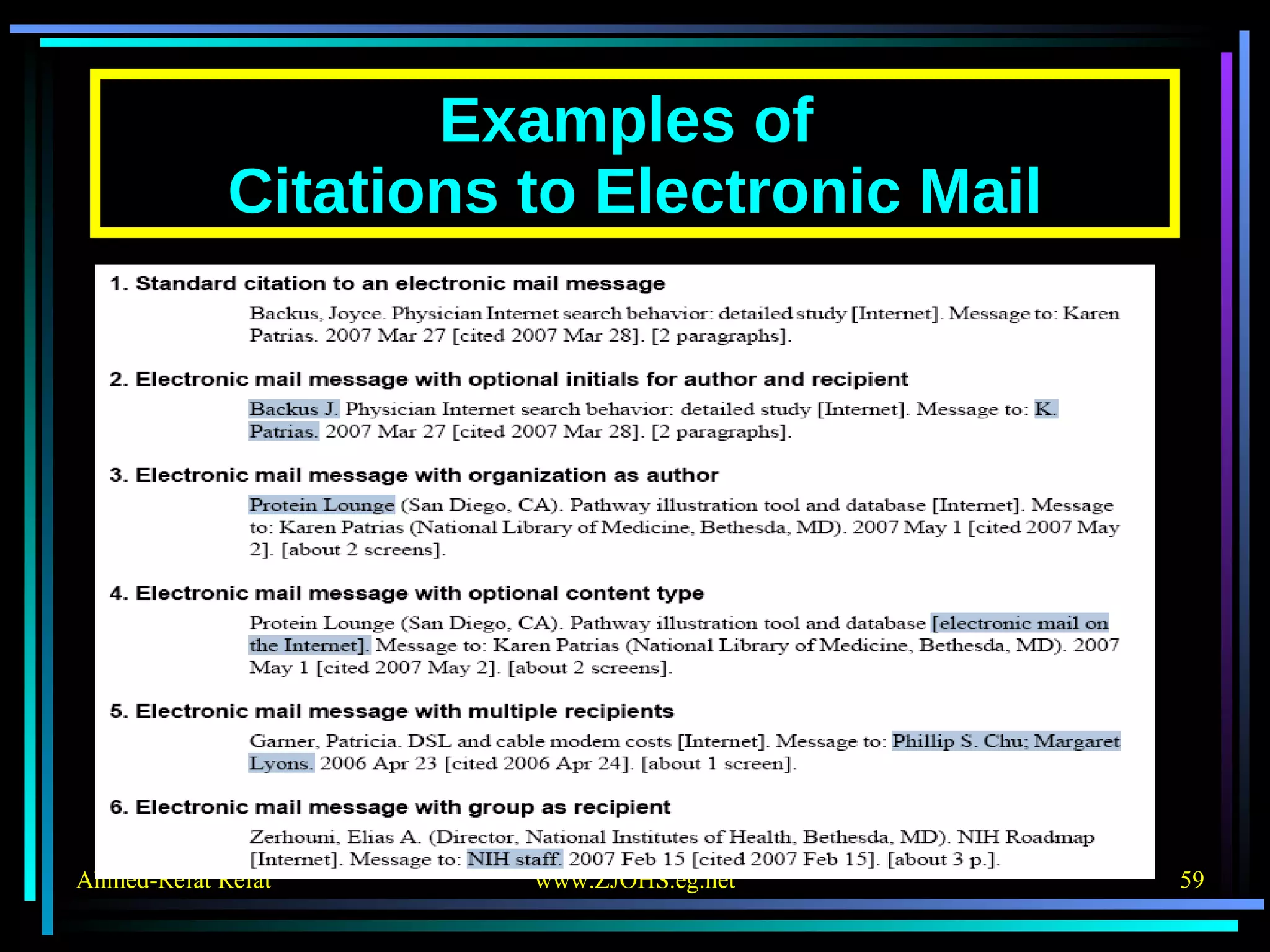
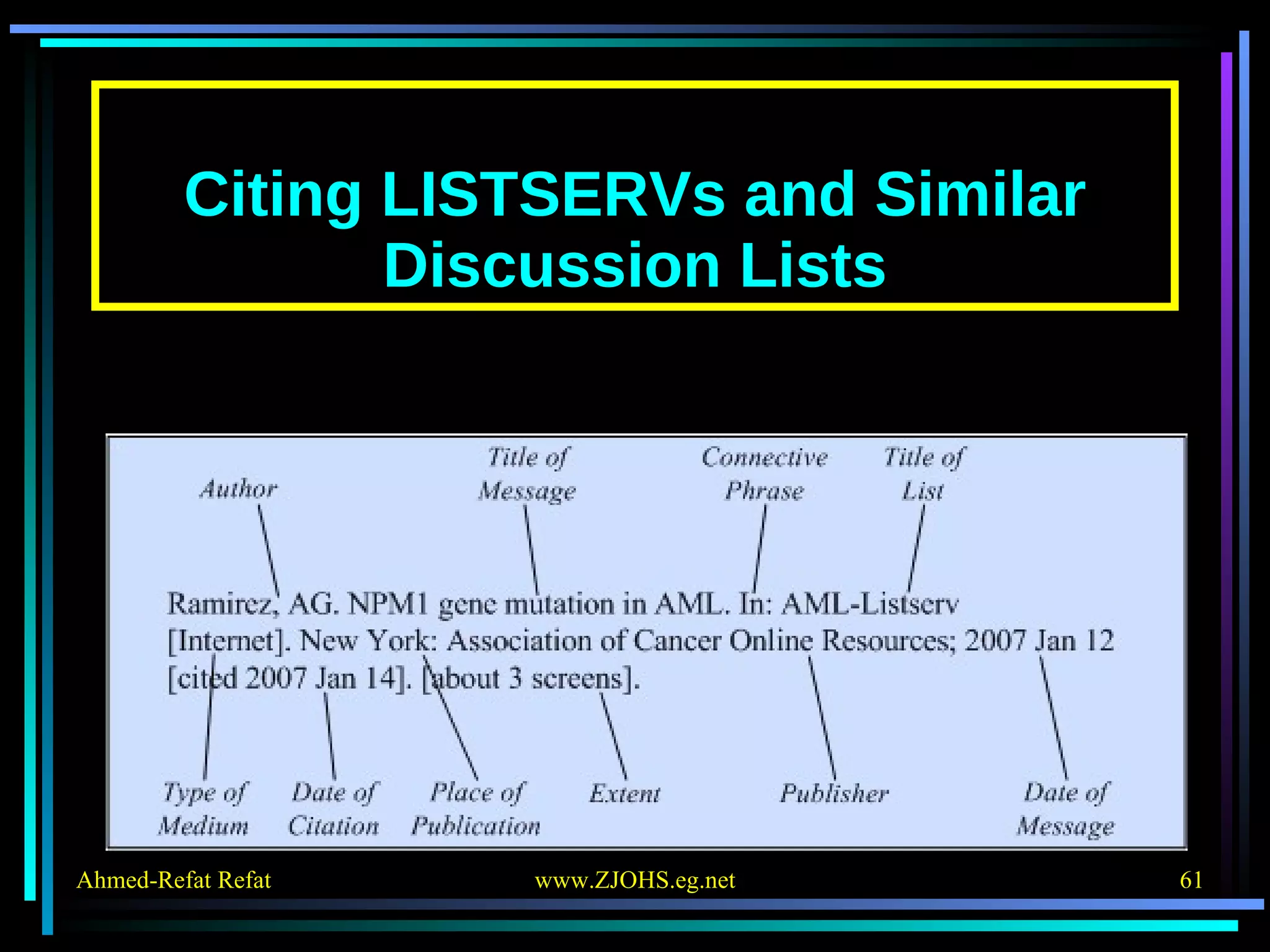
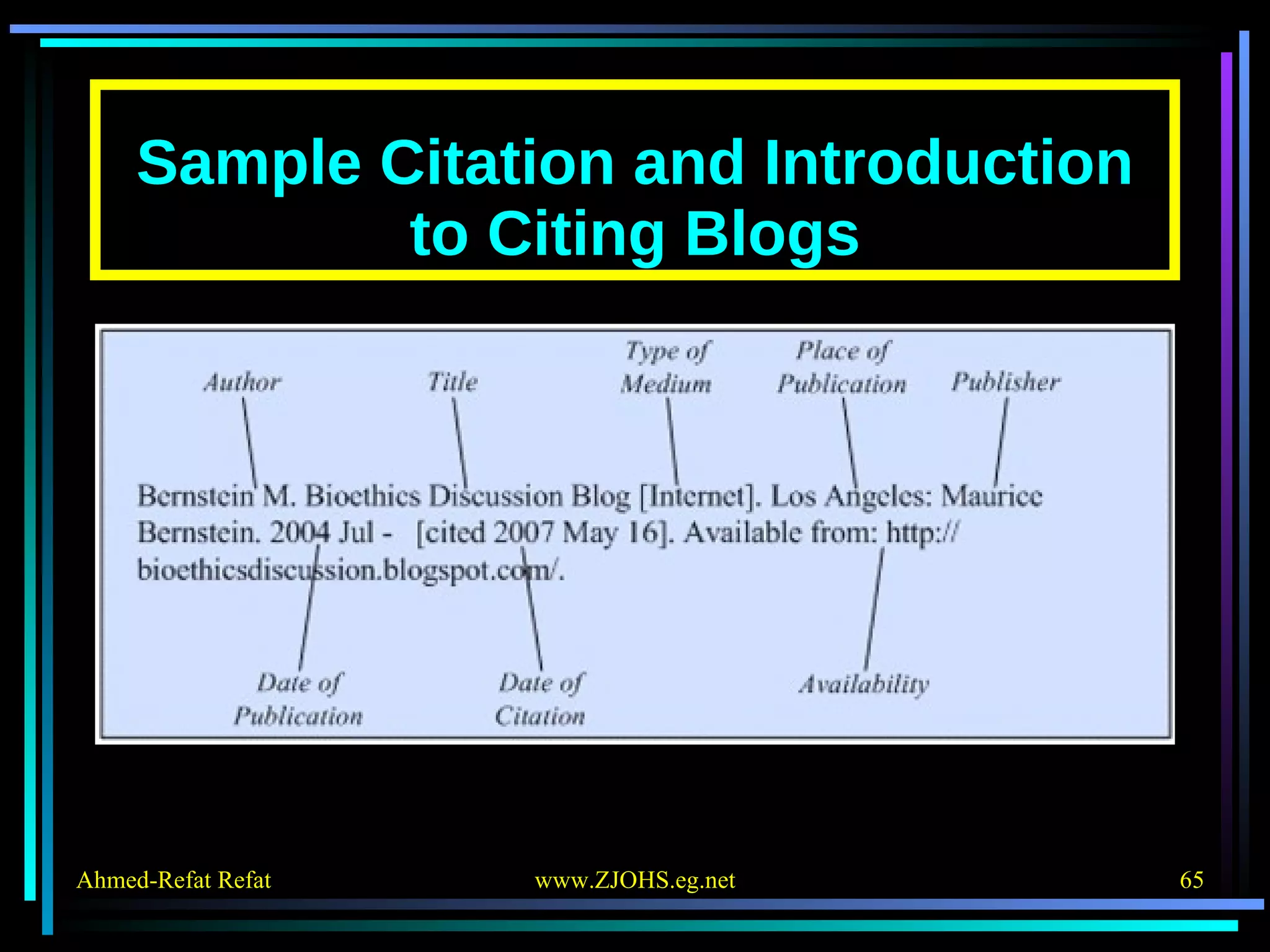
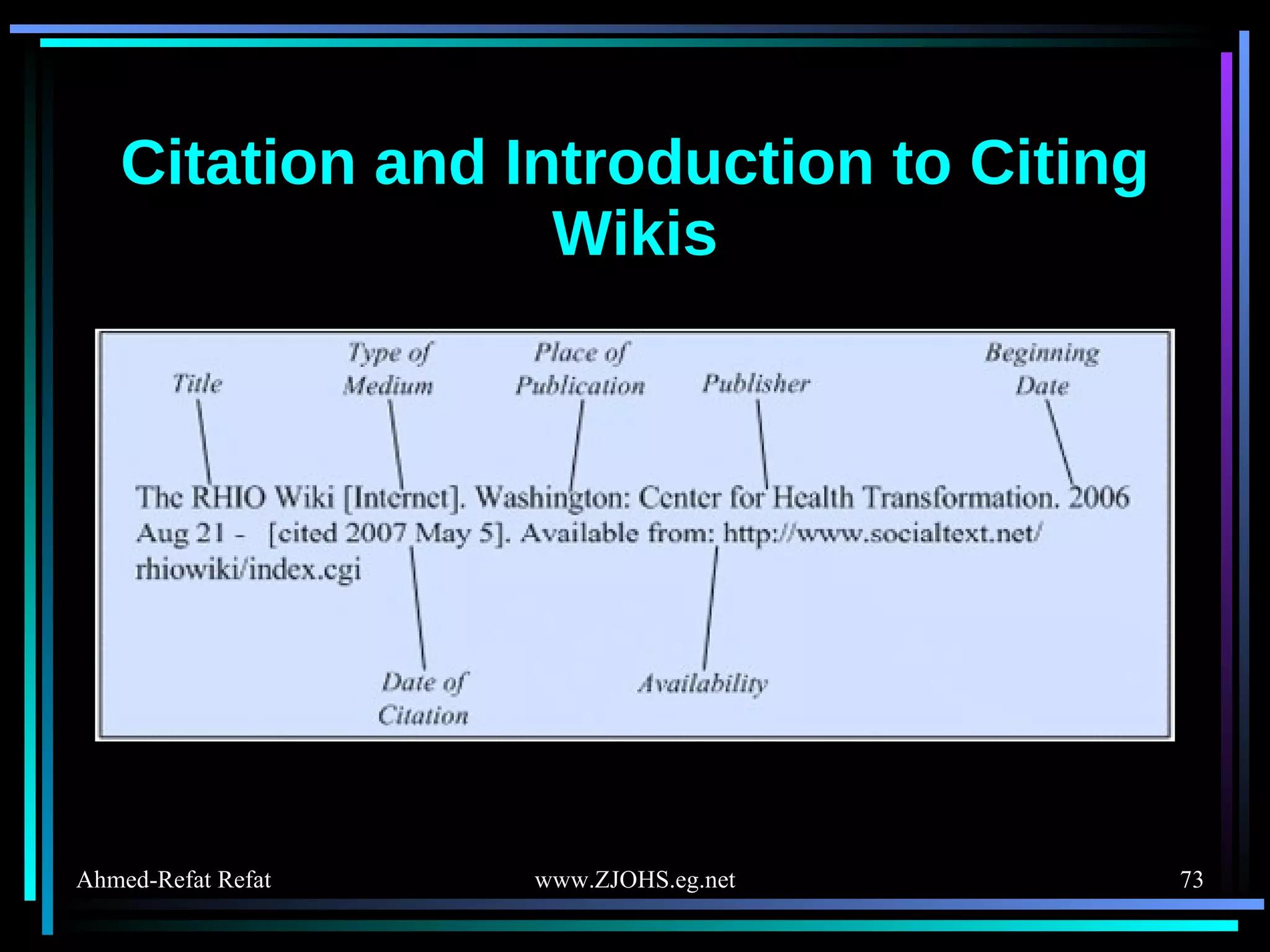
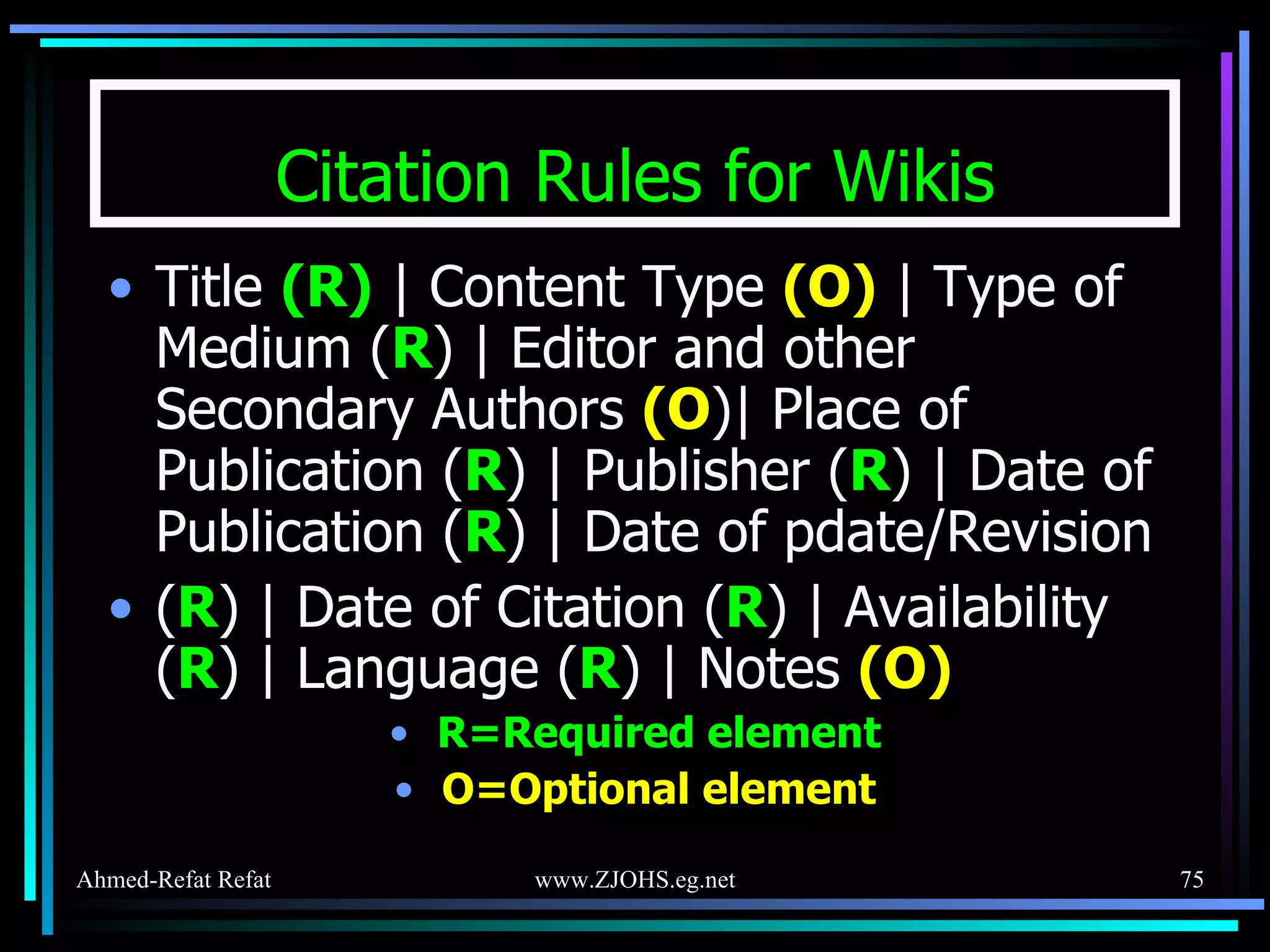
The document provides comprehensive guidelines for citing various online resources, including books, journal articles, databases, homepages, electronic mail, discussion forums, listservs, blogs, and wikis. Each section outlines specific citation rules and required or optional elements for proper attribution. It serves as a valuable reference for authors, editors, and publishers in the context of academic writing and internet sources.