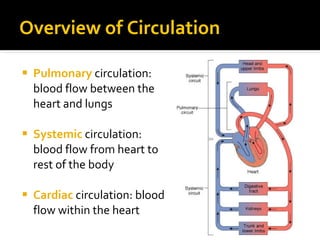
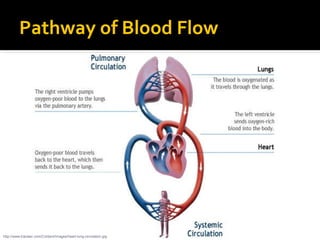
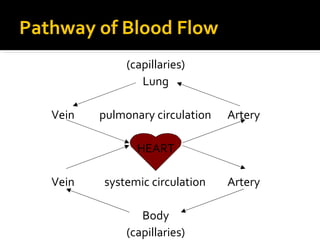
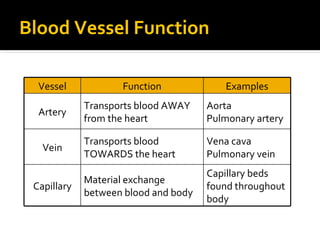
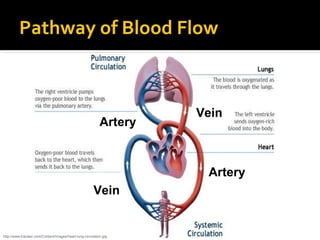
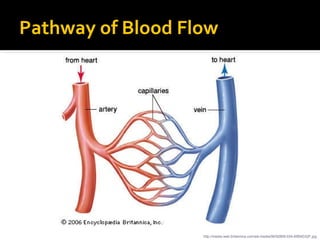
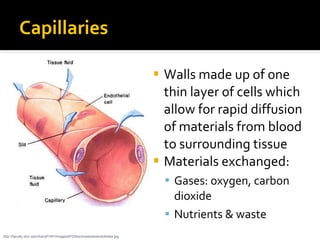
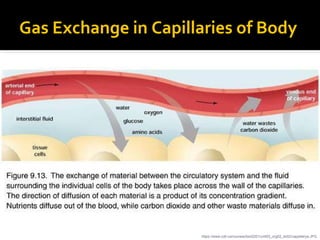
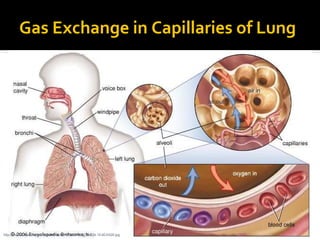
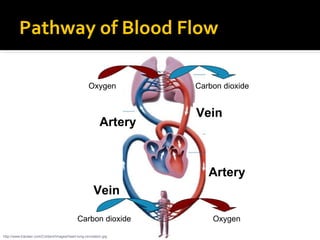
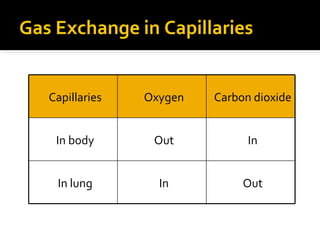
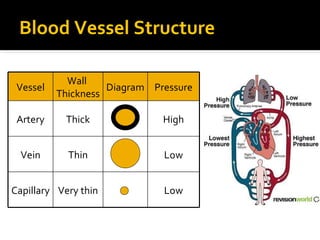
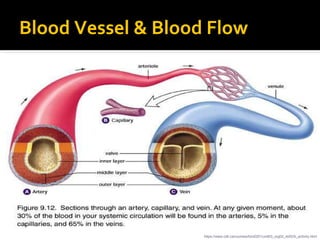
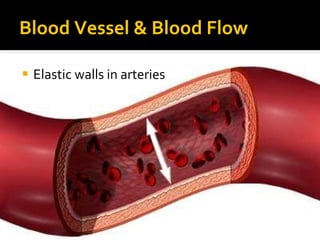
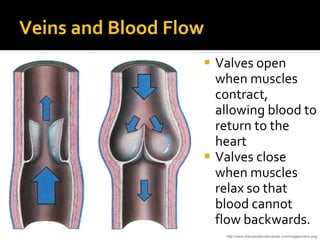
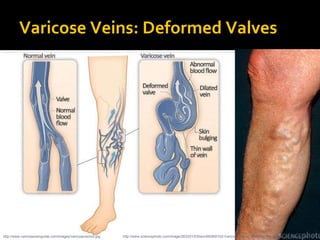
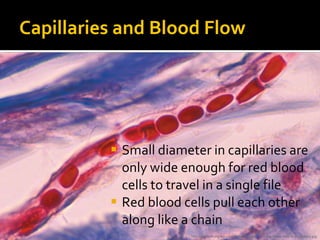
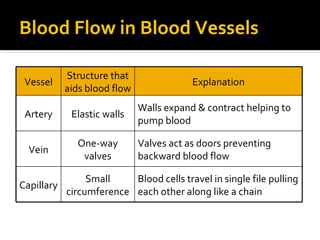
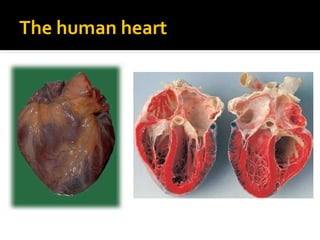
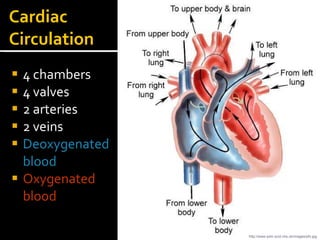
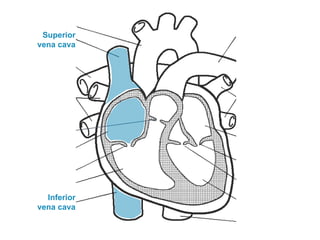
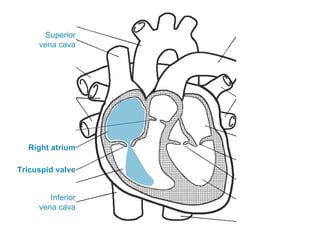
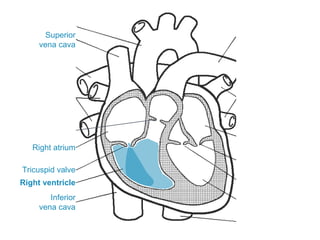
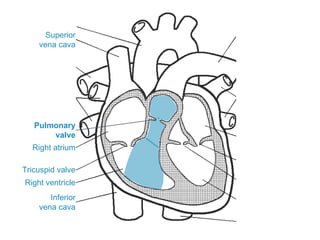
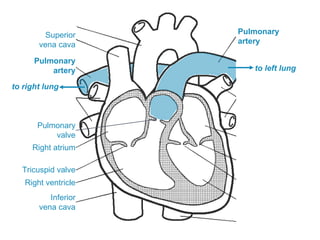
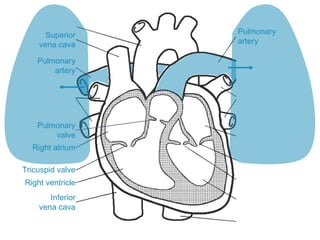
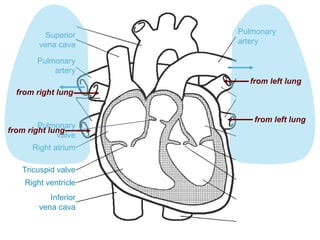
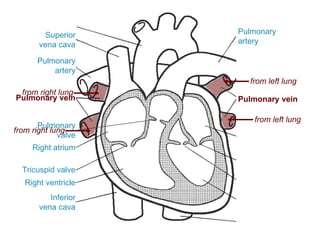
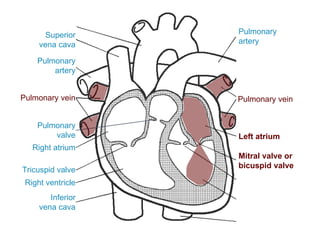
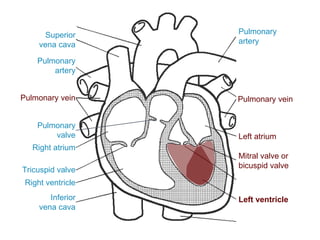
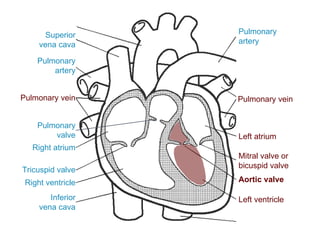
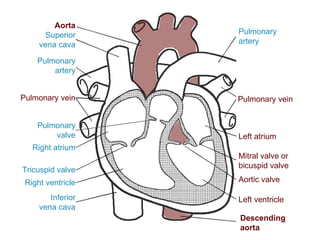
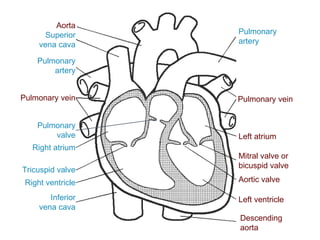
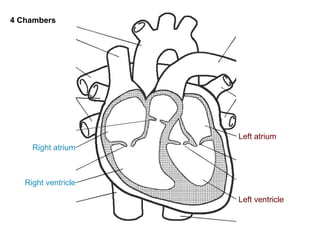
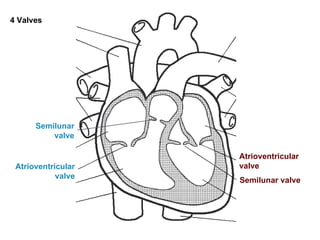
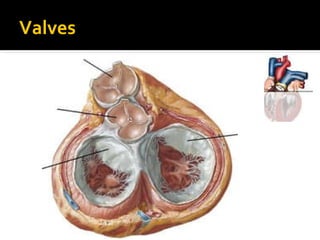
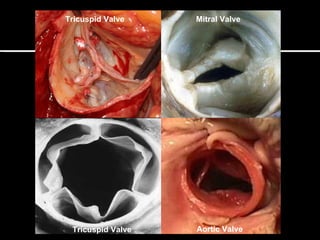
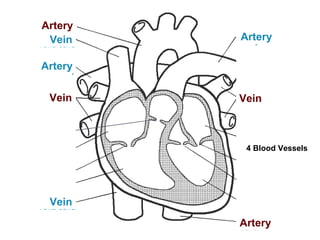
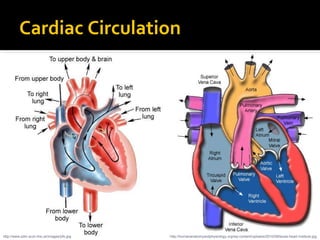
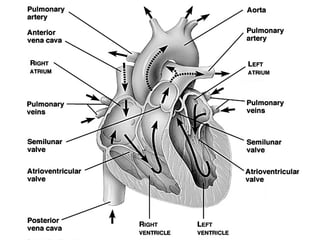
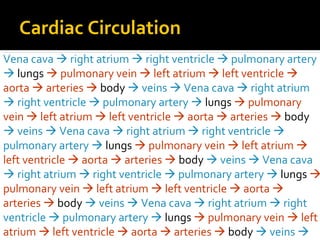
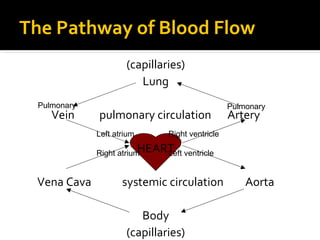
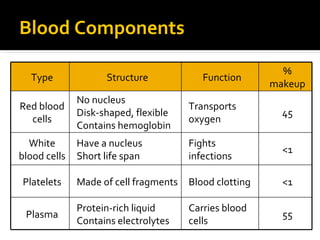
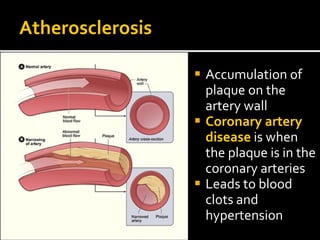
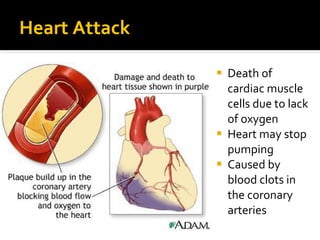
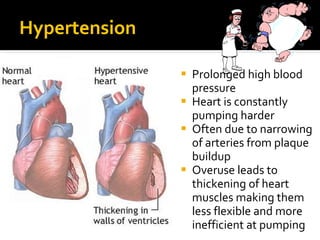
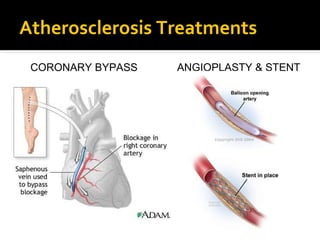
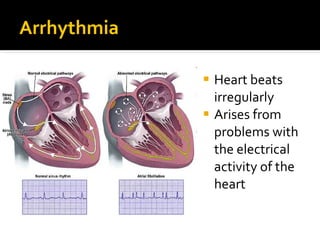
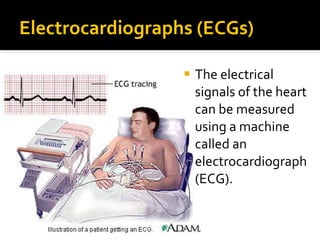
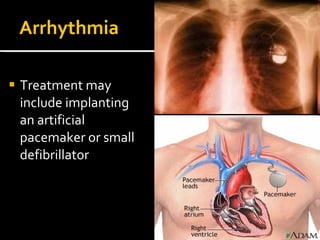
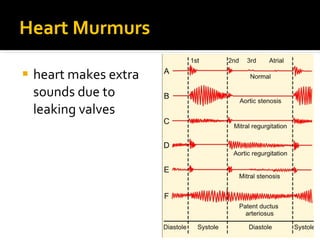
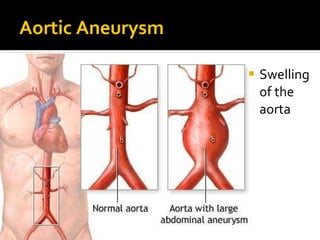
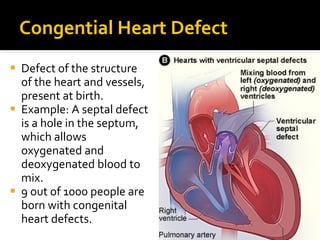
The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body via circulation pathways. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium then flows to the right ventricle, through the pulmonary artery to the lungs, and returns oxygenated to the left atrium and left ventricle. It then exits via the aorta to arteries that feed the body before returning via veins to the vena cava and restarting the cycle. The heart contains four chambers and four valves that ensure one-way blood flow. Diseases can disrupt circulation and include atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and arrhythmias.