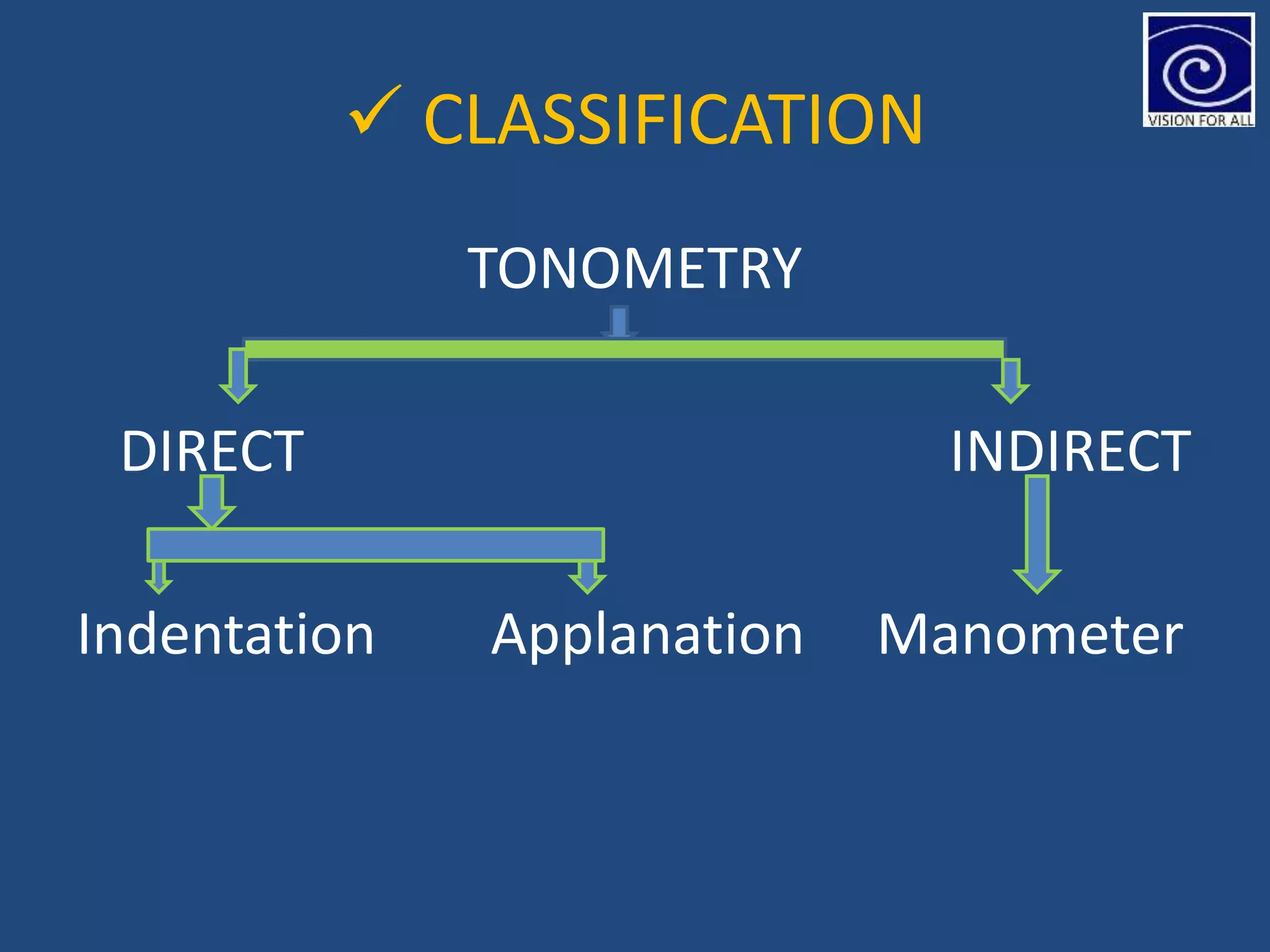
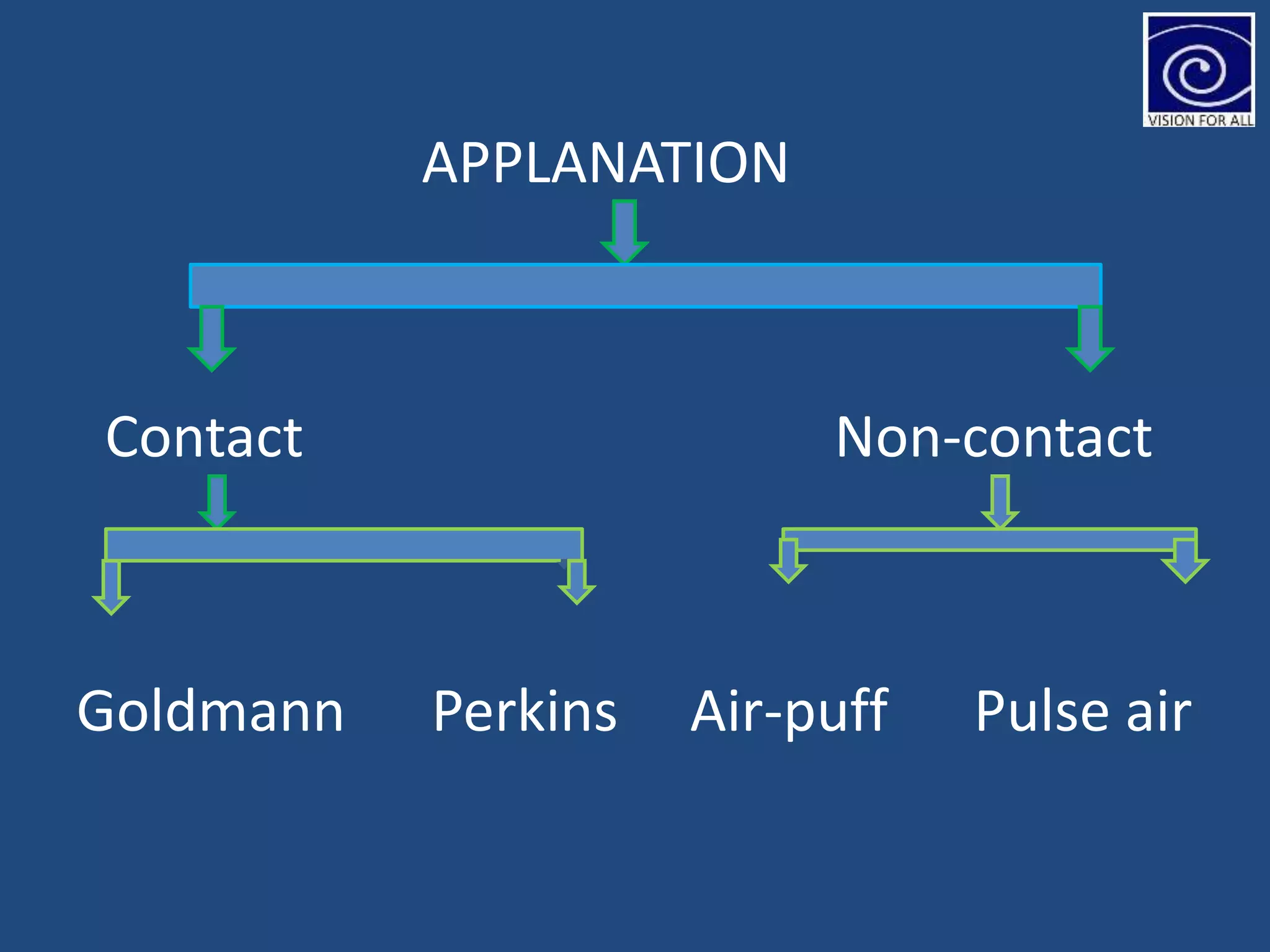
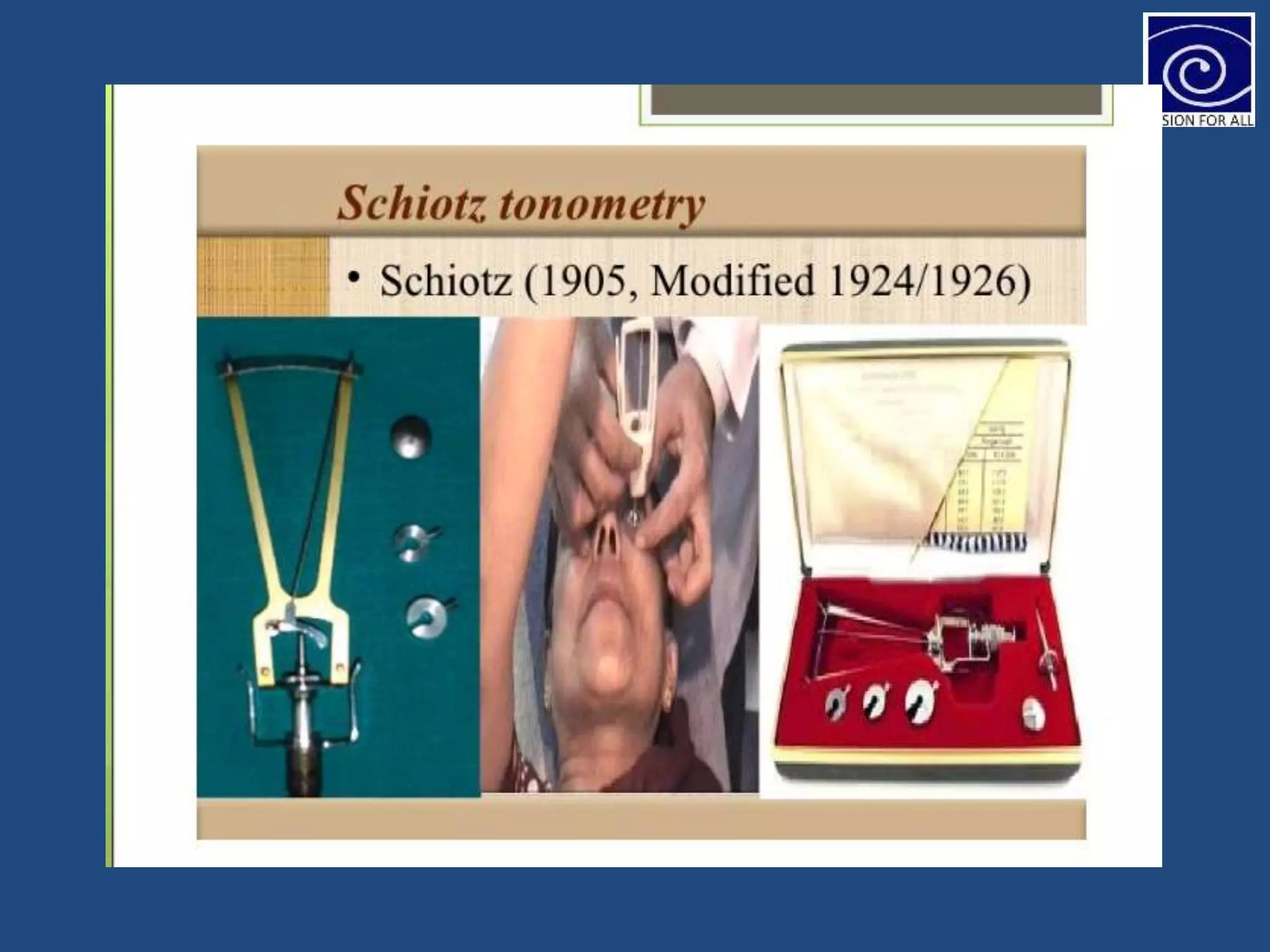
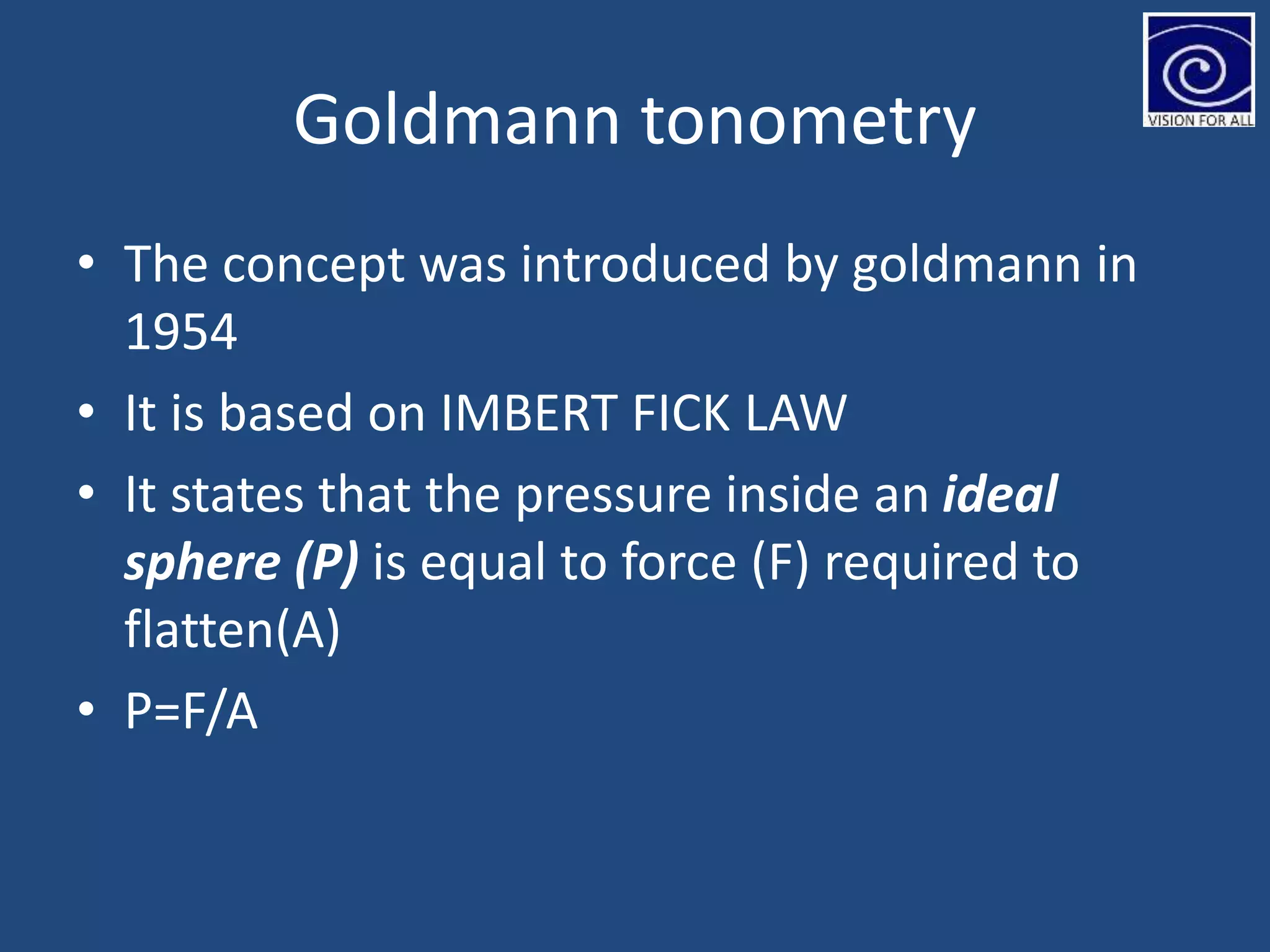
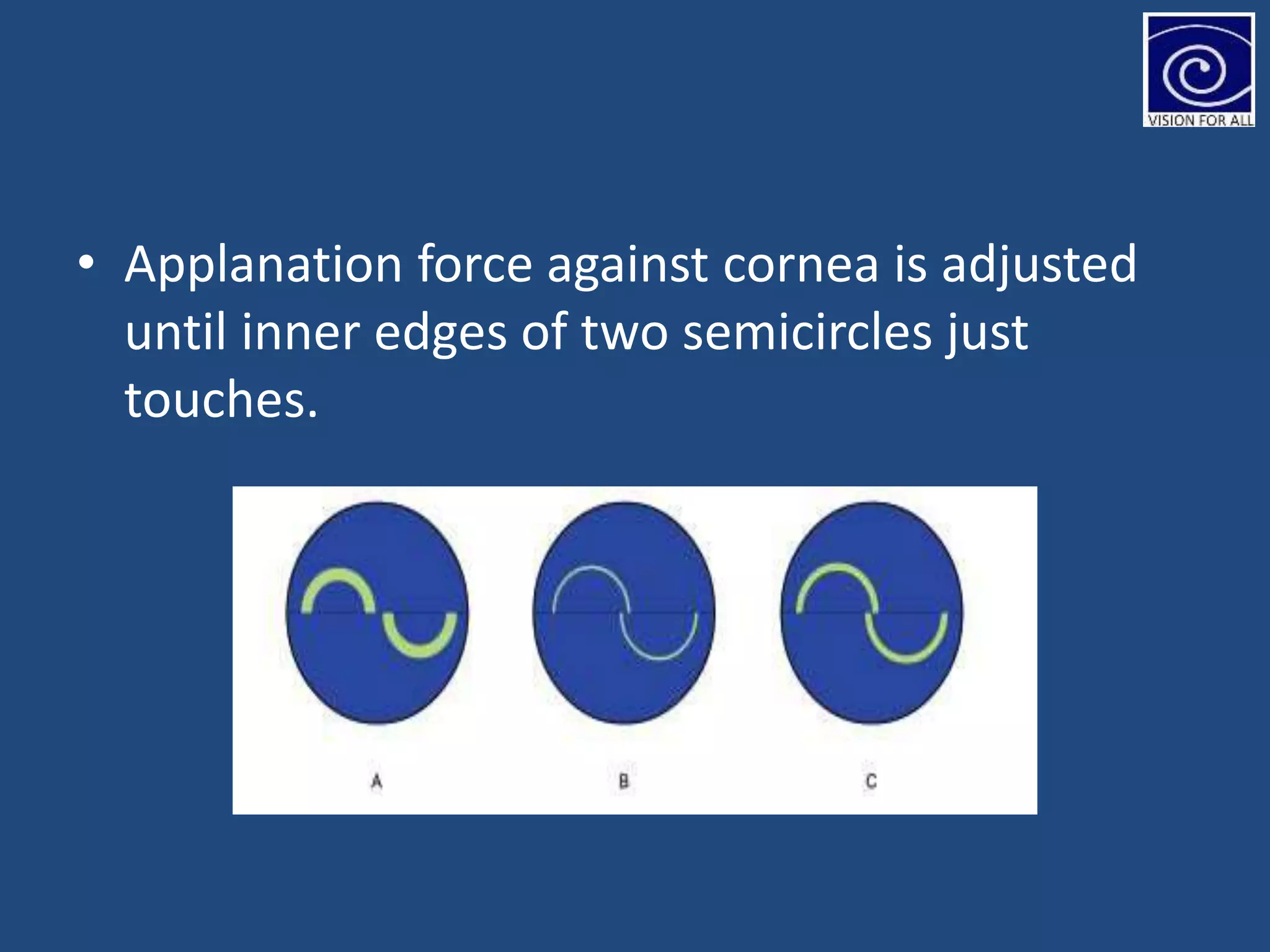
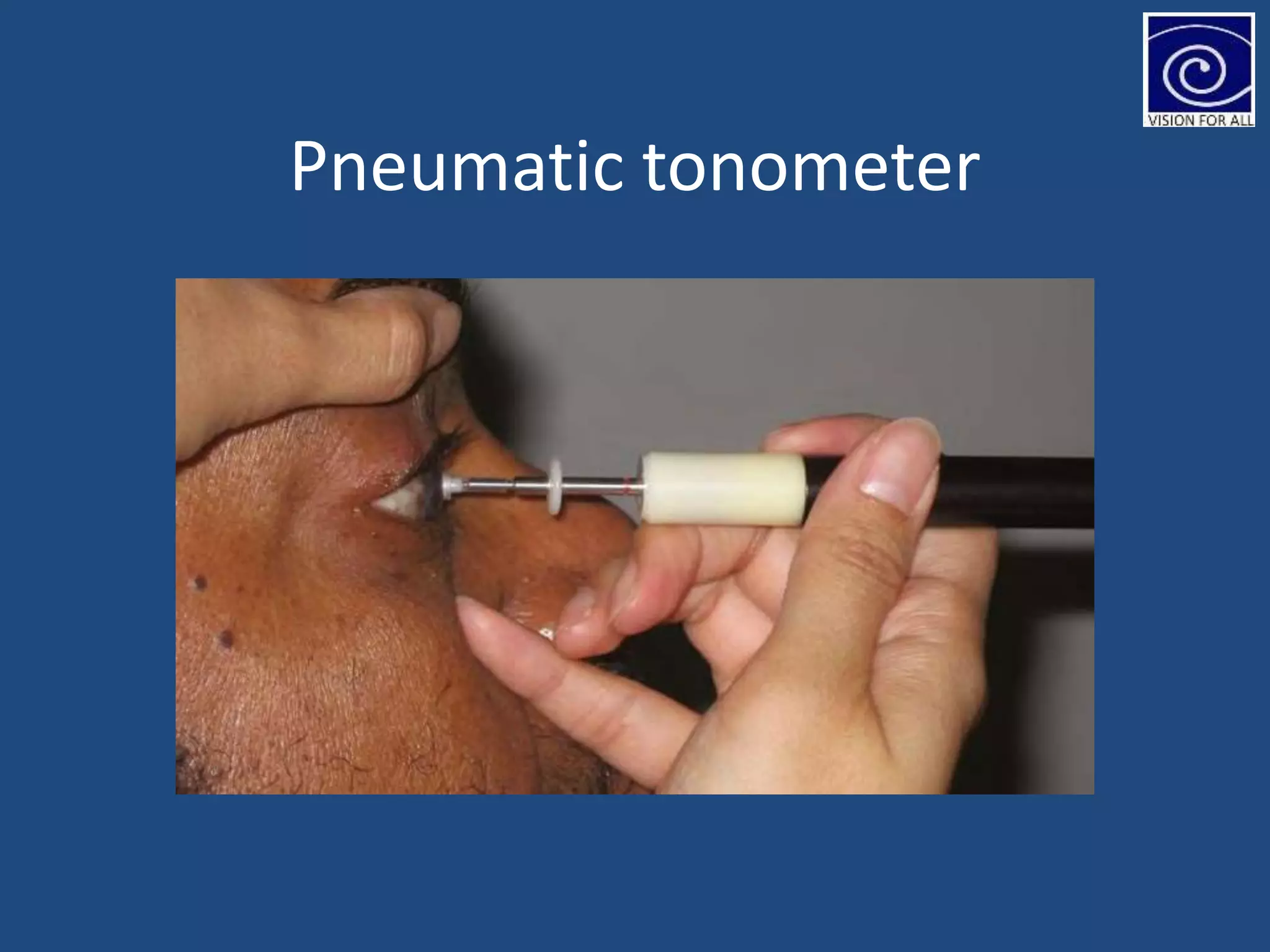
The document discusses tonometry, a procedure for measuring intraocular pressure (IOP), detailing various types including direct and indirect methods such as applanation, indentation, and non-contact tonometers. Key instruments like the Goldman tonometer, Perkins tonometer, and pneumatic tonometer are described, along with their advantages, disadvantages, and procedures involved. The document emphasizes the importance of accurate measurement, potential errors, and the overall significance of tonometry in ophthalmic practice.