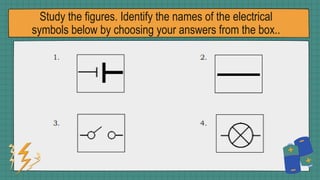
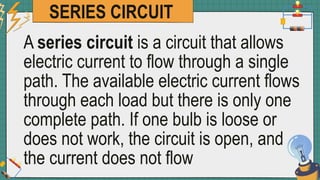
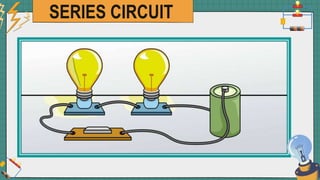
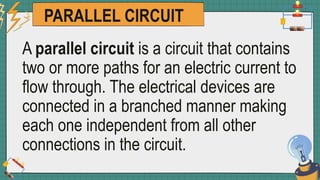
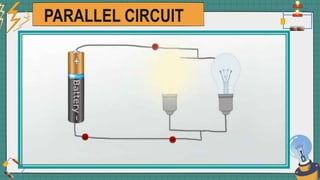
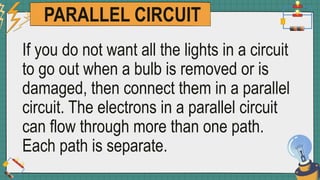
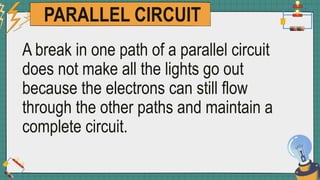
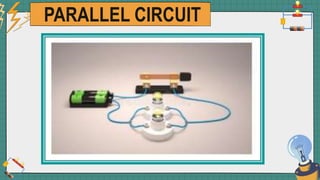
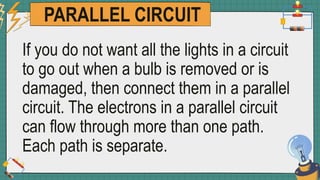
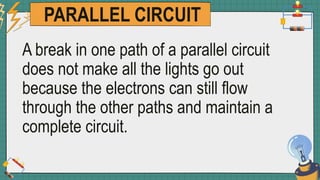
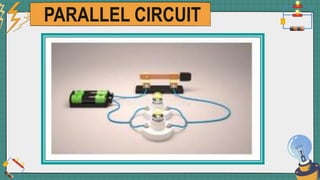
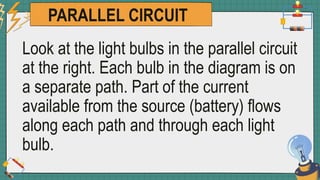
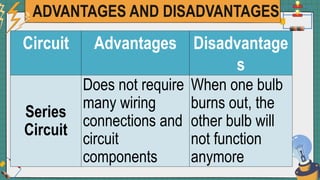
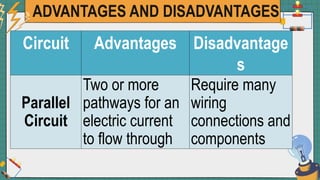
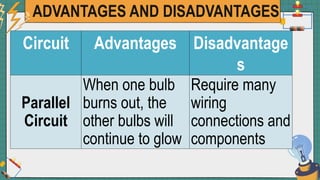
1. The document discusses series and parallel electric circuits. A series circuit allows current to flow through a single path, so if one bulb burns out the entire circuit is broken. In a parallel circuit there are multiple current paths, so individual bulbs can be removed without affecting the others.
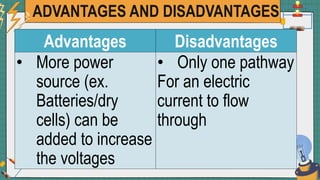
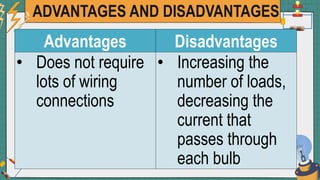
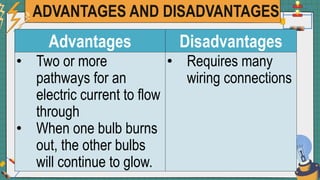
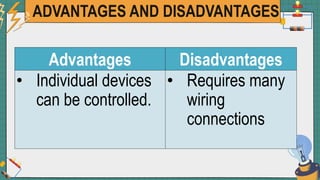
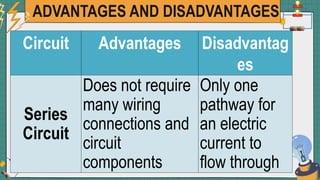
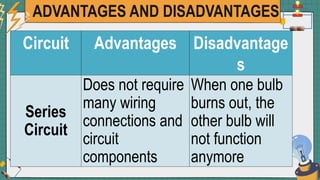
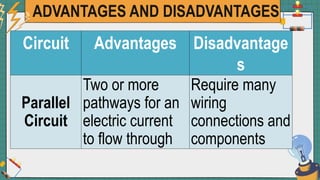
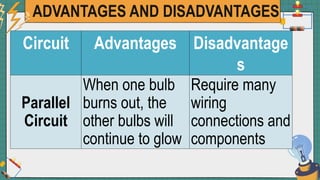
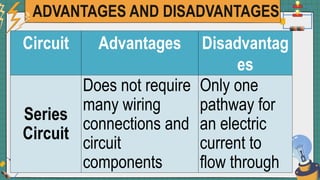
2. It provides examples of series and parallel circuits and compares their advantages and disadvantages. Series circuits require less wiring but the failure of one device disables the whole circuit, while parallel circuits allow individual control but need more complex wiring.
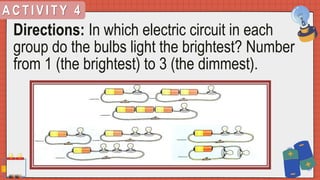
3. The text examines examples of each type of circuit and assesses readers' understanding with questions about circuit parts and their properties in series and parallel configurations.