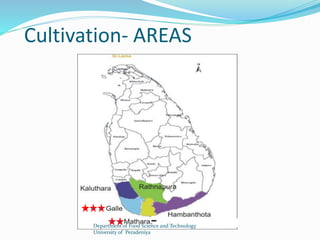
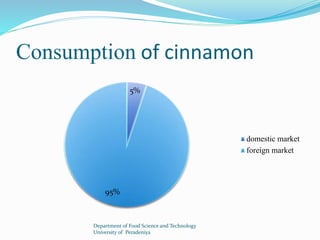
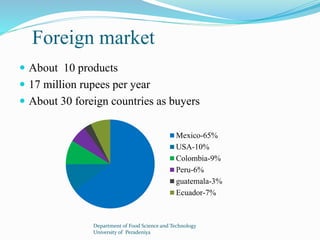
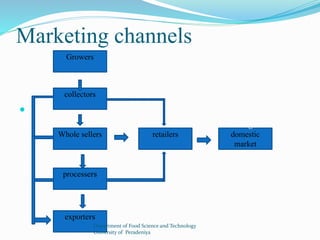
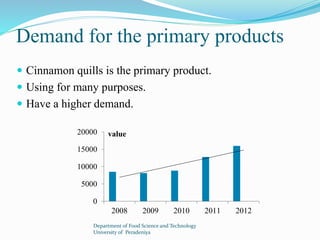
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cinnamon, covering its cultivation methods, processing, and various products, including cinnamon sticks, oils, and oleoresin. It discusses market dynamics, both domestic and foreign, along with regulations governing the cinnamon industry in Sri Lanka. Additionally, it highlights opportunities for investment in cultivation and processing to meet market demands.