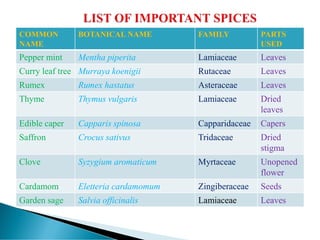
The document provides an extensive overview of various spices, their botanical classifications, uses, and economic importance, particularly focusing on fennel, saffron, clove, and black pepper. It discusses the nutritional and medicinal properties of spices, their role in enhancing food flavor, and different plant parts used in their production. Additionally, it outlines the characteristics and applications of several specific spices, emphasizing their significance in culinary arts and traditional medicine.