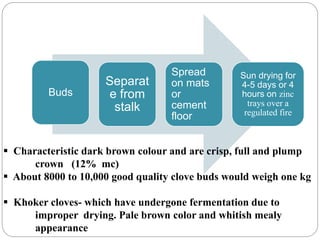
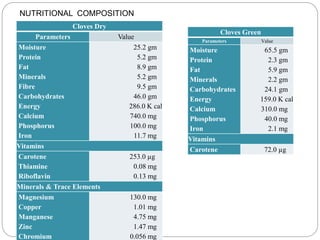
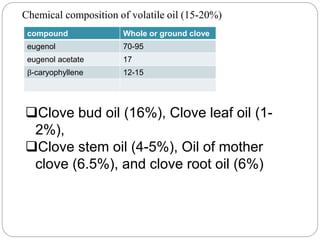
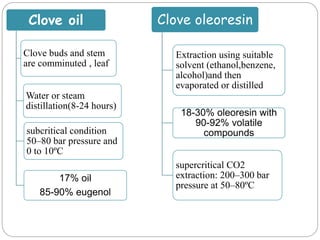
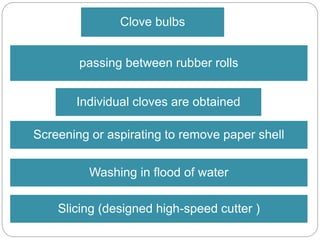
This document provides information on various minor spices categorized as tree spices, seed spices, herbal spices, and other spices. It then focuses on clove and coriander, describing their origin, cultivation practices, chemical composition, uses, and processing. For clove, it details the tree, production areas, harvesting and drying process, essential oil composition, and applications. For coriander, it outlines the plant, nutritional value of seeds and leaves, cultivation practices, harvesting, and uses of both the herb and seeds.