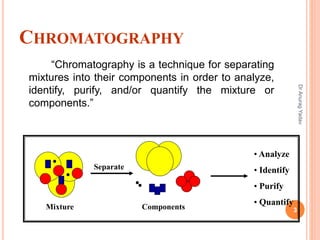
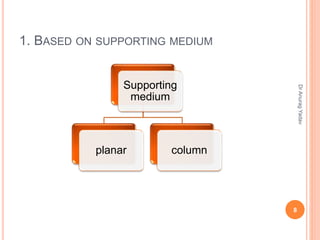
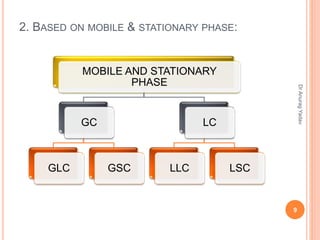
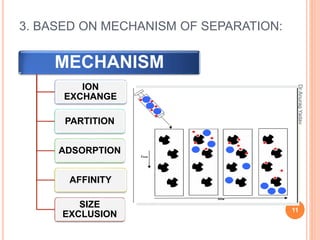
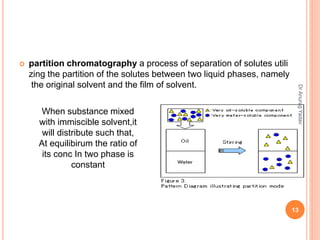
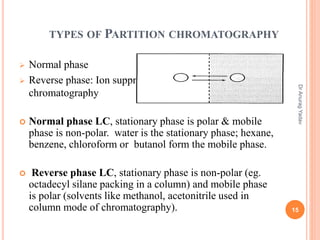
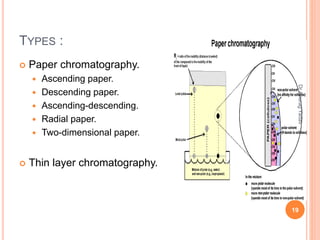
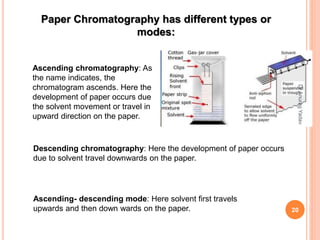
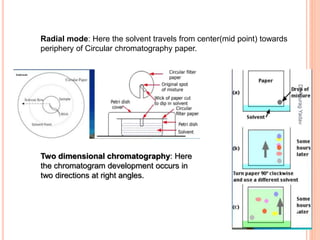
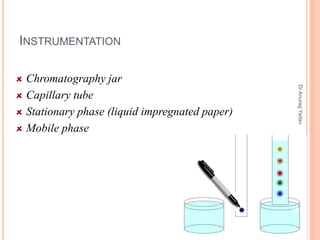
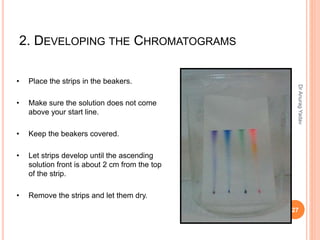
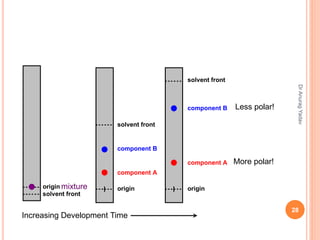
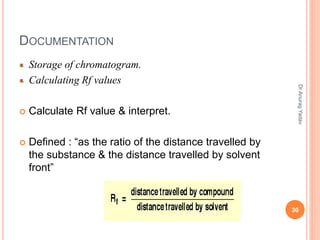
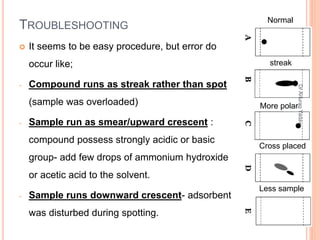
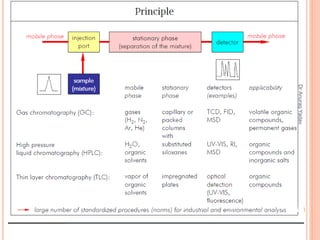
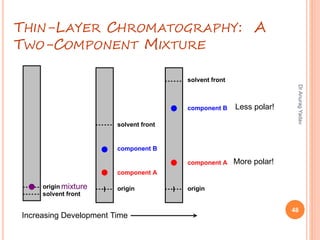
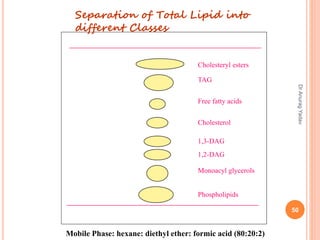
The document provides an in-depth overview of chromatography, including its definitions, terminologies, classifications, types, and applications, primarily in separation and analysis of mixtures. It covers various methods such as paper chromatography and thin-layer chromatography, detailing their procedures, instrumentation, and visual output (chromatogram). Additionally, it discusses the importance of retention time, rf values, and troubleshooting common errors in chromatography techniques.