Embed presentation
Downloaded 39 times


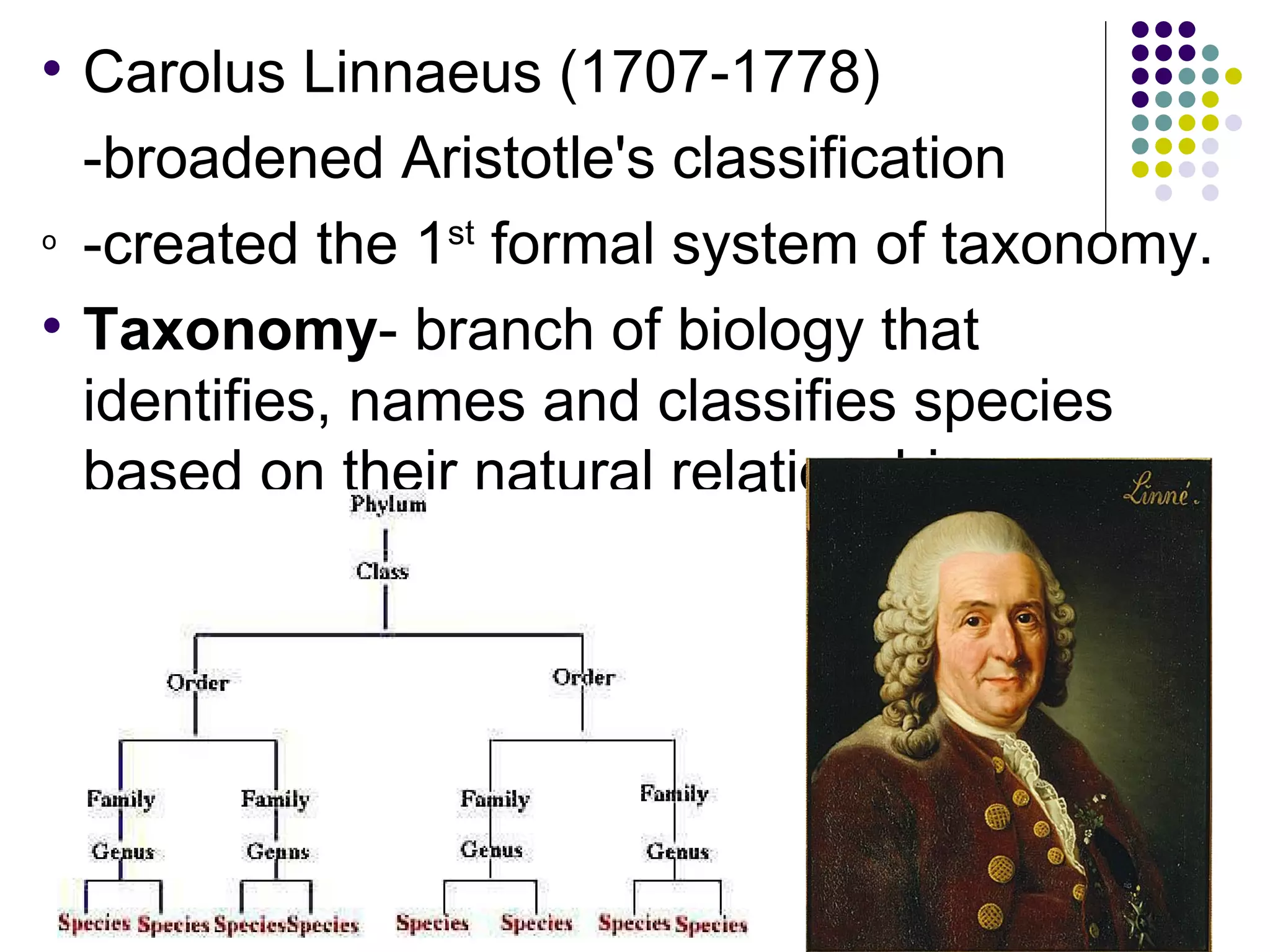

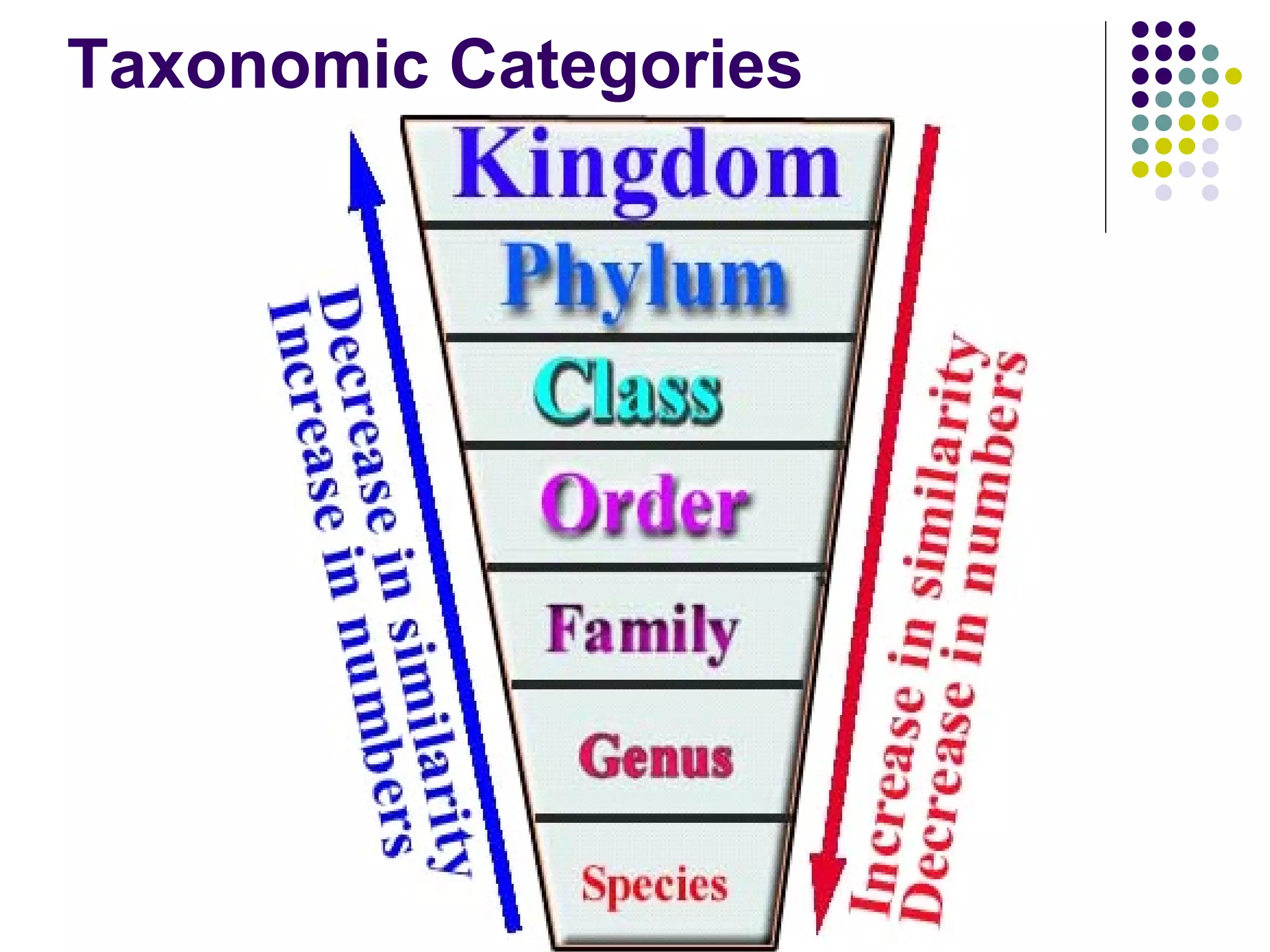


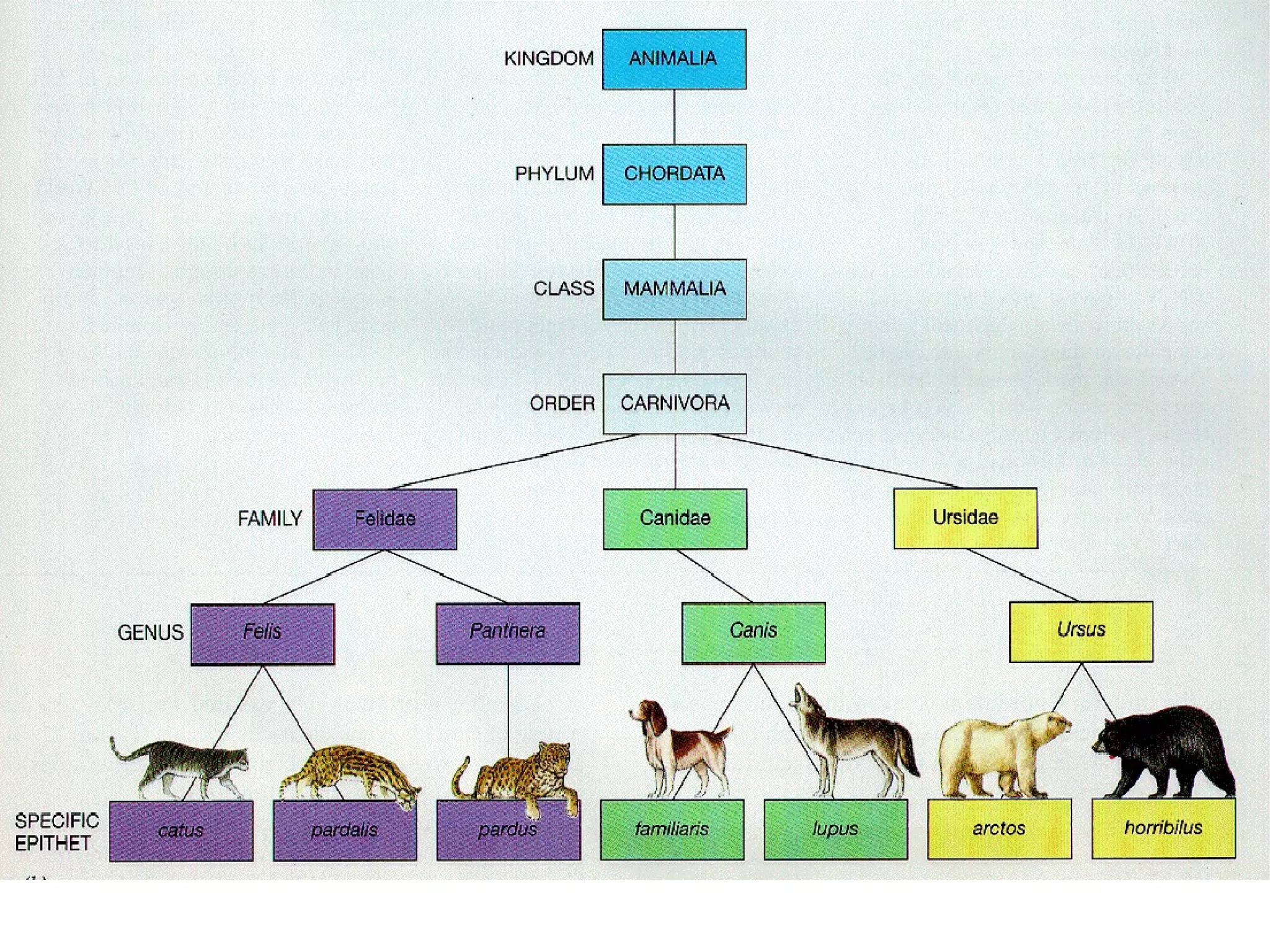

Aristotle first classified organisms as either animals or plants, with plants grouped by size and animals by whether they had blood. Linnaeus broadened Aristotle's system and created the first formal taxonomy, grouping organisms into a binominal nomenclature with a genus and species name. The taxonomic categories from most specific to broad are species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain.
Discusses the evolution of classification starting from Aristotle’s system for animals and plants.
Introduces Carolus Linnaeus' formal system of taxonomy and binomial nomenclature for species identification.
Explains the hierarchical categories of classification such as species, genus, family, and domain.
Provides examples of organisms within various classifications, including red foxes and giant pandas.








