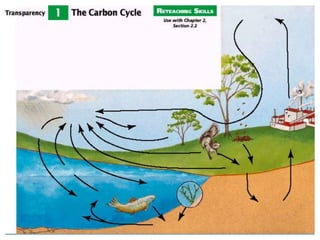
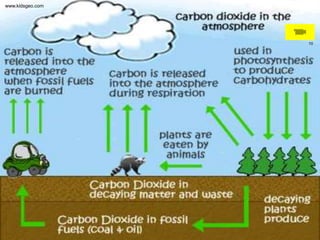
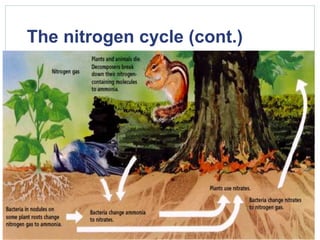
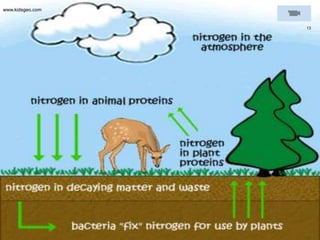
This document summarizes the cycling of important materials like water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus through ecosystems. It explains that while energy is lost at each trophic level, the sun replenishes it, and matter is recycled as nutrients move through organisms. The atoms that make up living things today have been on Earth since life began. It then provides more detailed explanations of the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles.