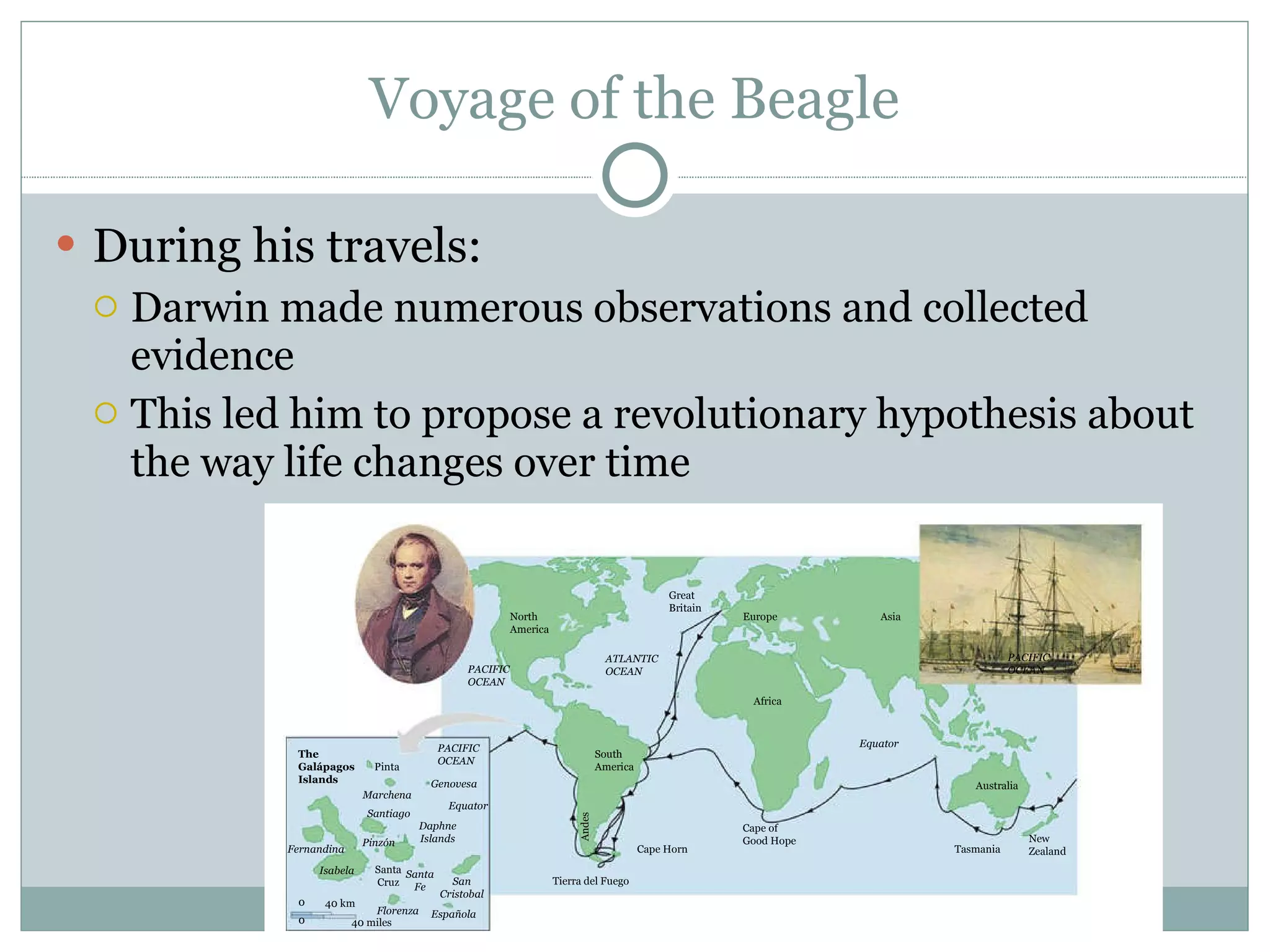
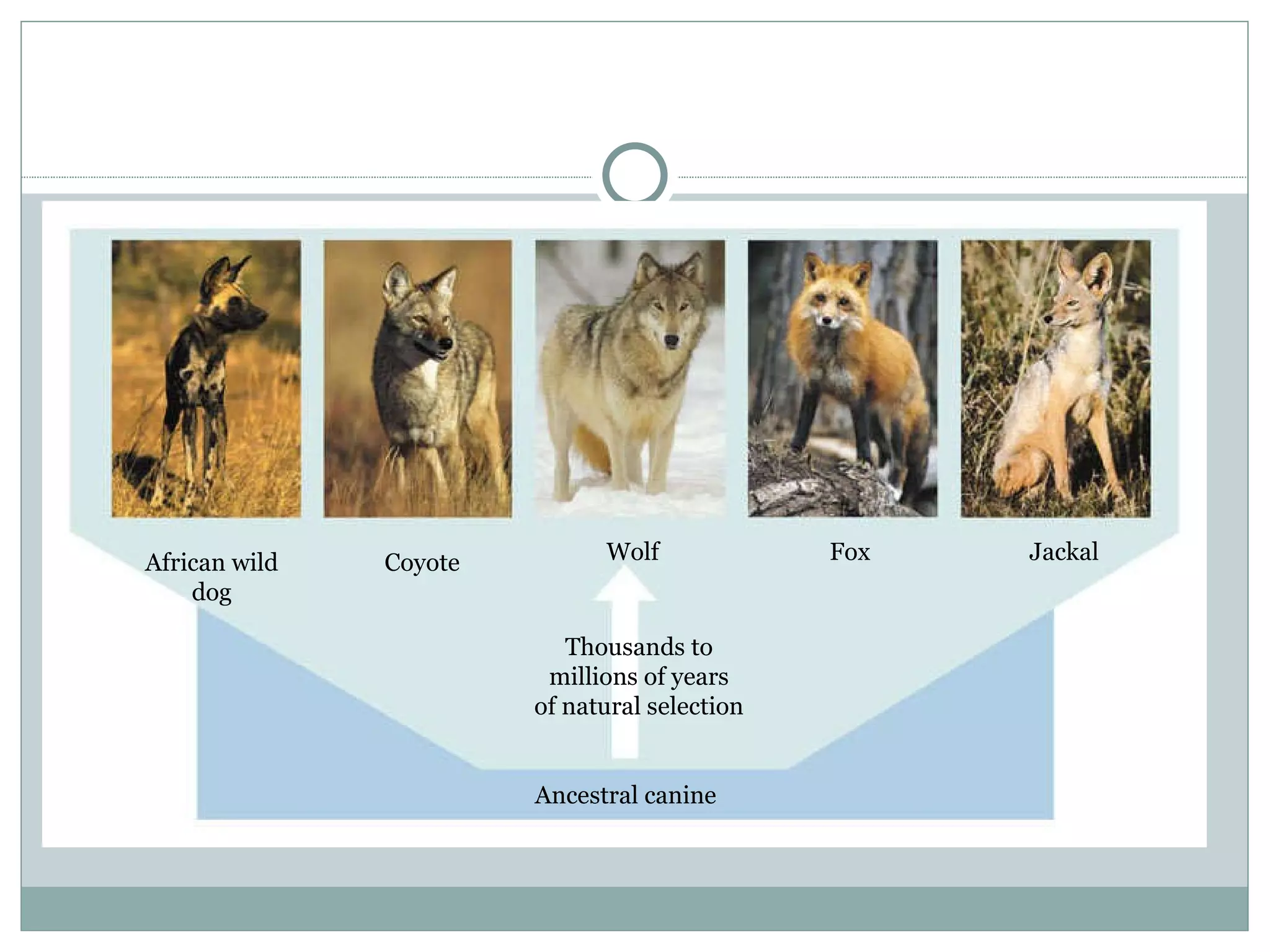
The document summarizes Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. It describes Darwin's voyage on the HMS Beagle where he observed patterns of diversity among species in places like the Galapagos Islands. This led him to propose that life evolves over time through natural selection, where traits beneficial for survival are passed on while others die out. The document also outlines evidence that shaped Darwin's thinking, such as fossils, biogeography, and homologous and vestigial structures between organisms.