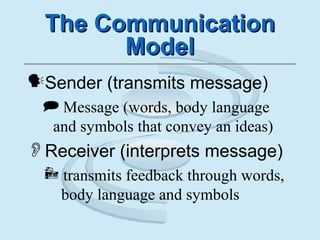
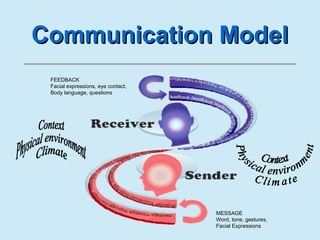
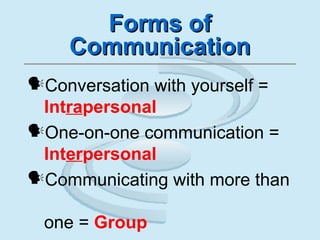
The document provides an overview of communication principles and concepts. It discusses the communication process which includes a sender, message, receiver, and feedback. It also covers non-verbal communication, barriers to communication like stereotyping, and the responsibilities of senders and receivers. Additionally, it examines forms of communication like intrapersonal, interpersonal, group communication and mass media. Aristotle's three types of appeals - logical, emotional, and ethical - are also summarized. The importance of building proper motivation through fairness and setting a good example is emphasized.