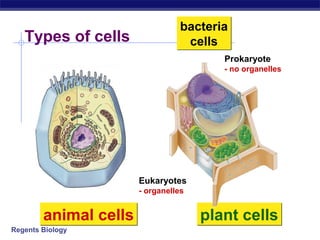
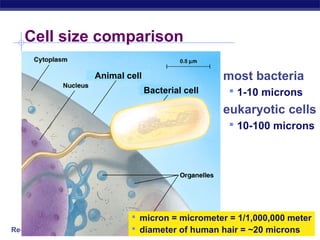
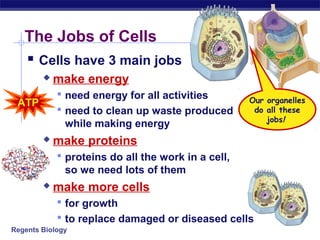
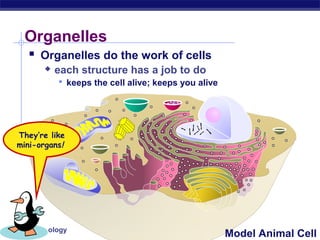
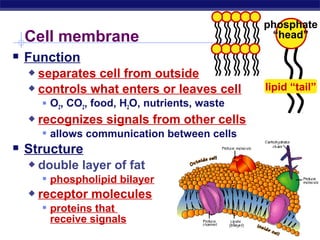
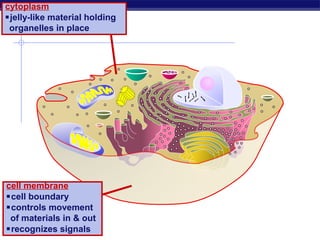
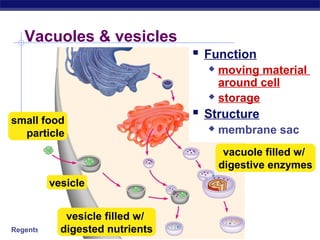
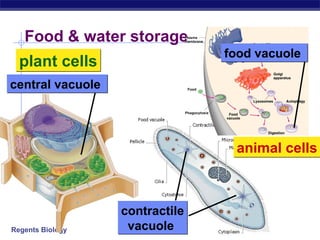
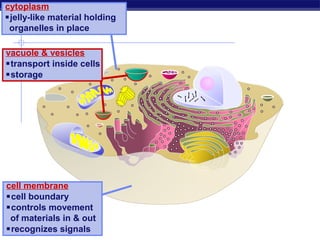
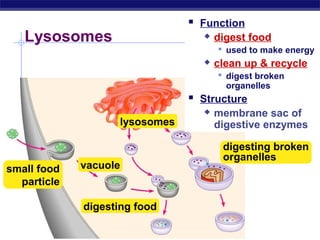
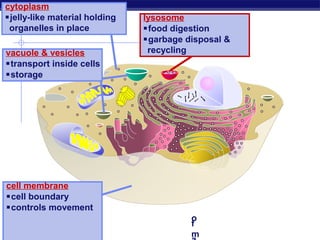
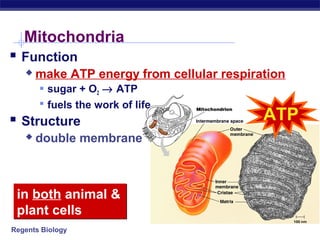
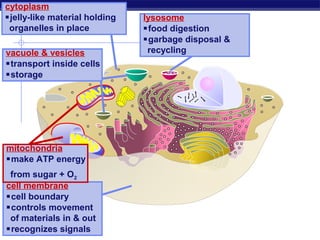
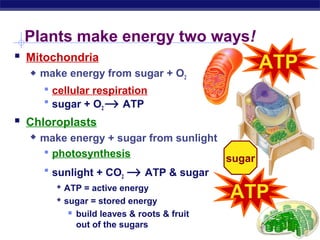
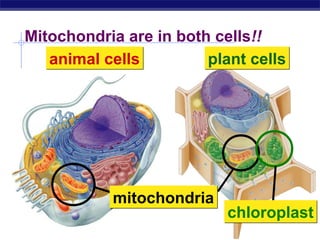
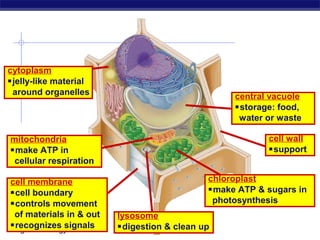
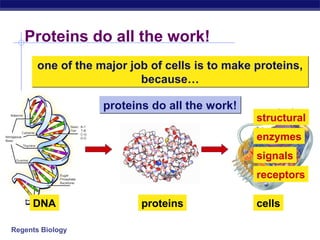
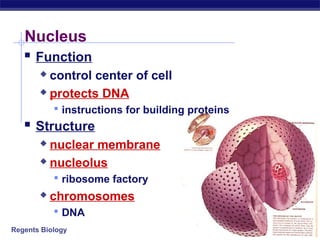
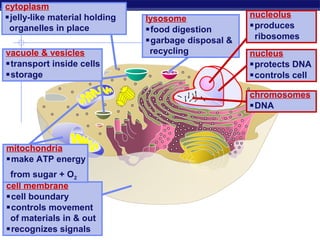
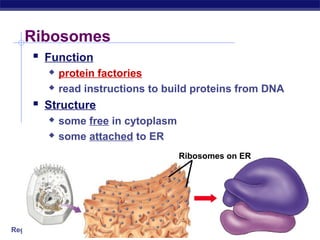
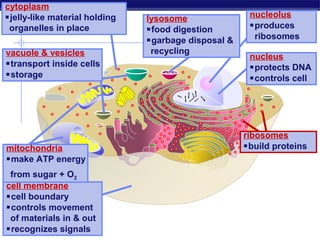
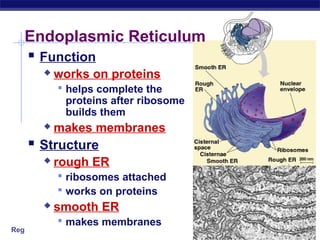
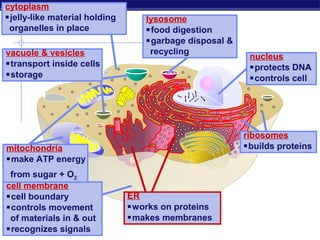
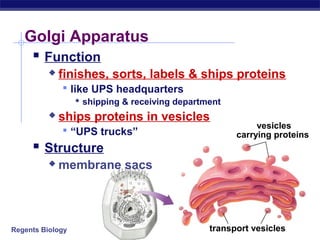
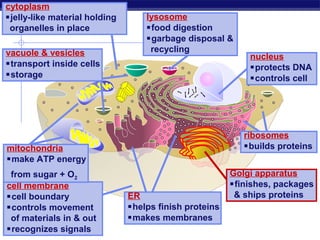
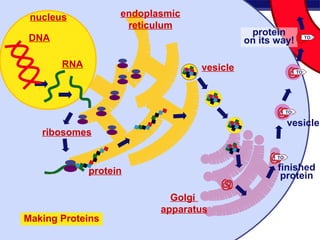
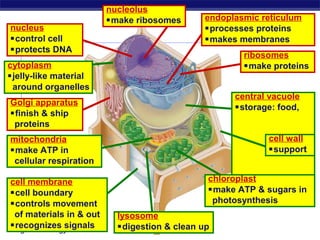
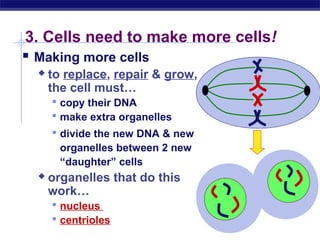
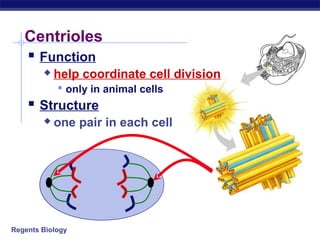
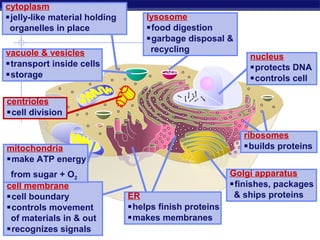
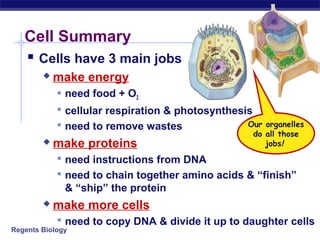
Cells contain specialized organelles that each perform essential functions to keep the cell alive. Mitochondria produce energy through cellular respiration. The nucleus contains DNA and controls the cell, while ribosomes build proteins using instructions from the DNA. Vesicles, vacuoles, and lysosomes transport materials and digest waste. Cells must also generate energy, synthesize proteins, and replicate in order to grow, repair tissues, and reproduce.