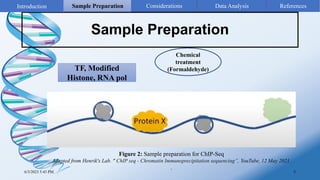
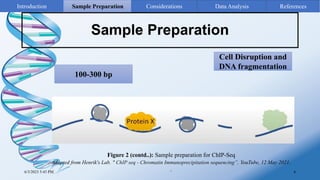
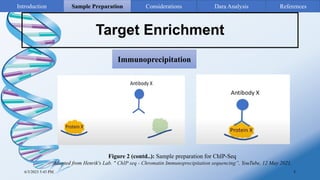
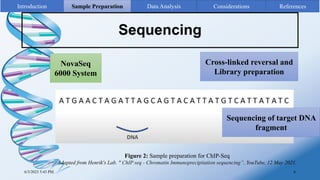
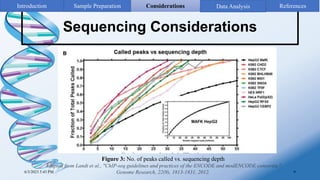
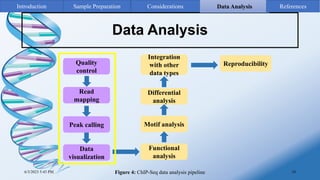
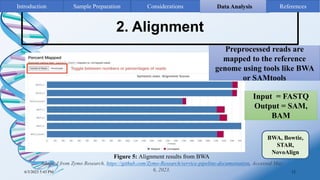
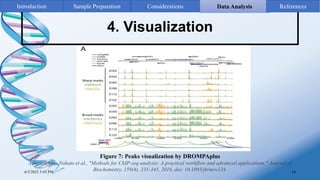
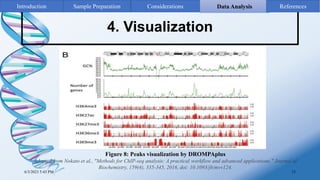
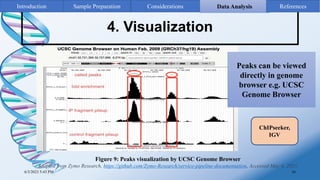
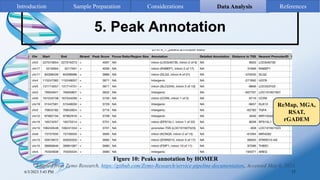
ChIP-sequencing is a method to identify genomic regions bound by specific proteins or modifications. It involves cross-linking proteins to DNA, immunoprecipitating the protein-DNA complexes, sequencing the retrieved DNA fragments to determine the genomic binding sites. The key steps are sample preparation involving cross-linking, fragmentation and enrichment, followed by high-throughput sequencing and computational analysis including mapping, peak calling, annotation and visualization of results.